The French press did not take kindly to comments from MoffettNathanson analyst Craig Moffett, who suggested Altice’s ability to swallow up Charter Communications in a deal worth at least $185 billion dollars was “not credible.”
The French press did not take kindly to comments from MoffettNathanson analyst Craig Moffett, who suggested Altice’s ability to swallow up Charter Communications in a deal worth at least $185 billion dollars was “not credible.”
Panelists appearing on French language business news channel BFM TV chuckled at Mr. Moffett’s ability to predict Altice chairman Patrick Drahi’s next move.
“Mr. Moffett does not know Mr. Drahi like we’ve come to know Mr. Drahi,” noted one analyst. “We’ve learned not to underestimate his ability to put together business deals that some would call bold, others financially reckless, yet he does it again and again. If Mr. Drahi wants [Charter], he shall have it.”
French business reporters have scoffed at Altice for years, well before the company arrived in the United States to acquire Cablevision and Suddenlink and rebrand them as Altice.
“When you don’t take him seriously, that is when he strikes,” reported BFM.
Drahi is a master of using other people’s money to finance massive telecommunications deals. For him, bigger is essential, and that means he’d either have to acquire Comcast or Charter or hope to build a cable empire out of smaller cable companies he’d acquire and combine.

Drahi (center)
Multiple independent media outlets are tracking Drahi’s movements. Le Figaro reports Drahi has spent months laying the groundwork for his next big takeover in the United States and the newspaper knew all along it would be a major deal, because Drahi is banking on the prospects of emptying the pockets of millions of American cable subscribers to fund his operations. Americans pay vastly more for cable television and broadband service than consumers in Europe because of a lack of regulation and competition.
The newspaper adds that Drahi routinely tells investors and reporters he wants to be “number one or two” in all countries where he does business. Right now Altice is the fourth largest cable operator in the United States, an absolutely intolerable situation for Mr. Drahi.
Drahi is well aware of the enormous cost of a Charter acquisition, and Bloomberg News reports he is considering asking the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board and BC Partners to help fund the potential merger. Both groups are already familiar with Mr. Drahi and Altice and were instrumental in his acquisition of Cablevision and Suddenlink. Despite the potential help, Moffett still believes Charter is well outside of Altice’s reach.
“None of the proposed suitors—Verizon, SoftBank, Altice—have the balance sheet to acquire Charter,” Moffett wrote his investor clients in a research note. He notes Greg Maffei, chairman of Liberty Broadband, is unconvinced of the wisdom of allowing a buyer to use its other highly leveraged companies as compensation in a merger deal.
Moffett believes the deal has to make sense to two people to proceed – John Malone, Charter’s largest shareholder and ironically Drahi’s mentor and Charter CEO Thomas Rutledge, who was America’s highest paid executive in 2016. He stands to get considerably richer if he can fend off a deal until he achieves tens of millions in stock option awards, first when Charter’s average share price tops $455.66 a share and stays there for at least 60 days and then again when the share price exceeds $564 a share and stays there for 60 days. This morning, Charter Communications was selling at just over $399 a share. All of the merger and acquisition talk is helping boost Charter’s stock price, but Rutledge doesn’t want the company sold until after he can walk out with his compensation package fully funded or finds a buyer willing to make him whole.
 As for Malone, he’s always been willing to cash out, but only when the deal makes financial sense to him and avoids taxes.
As for Malone, he’s always been willing to cash out, but only when the deal makes financial sense to him and avoids taxes.
“Let’s put a finer point on it,” Moffett added. “The ONLY reason [Liberty Media chief] John Malone would be willing to swap his equity in Charter for equity in Altice would be if he believed, with real conviction, that Altice could simply manage the asset better than Charter’s current management. It is not a knock on Altice to suggest that there is simply no way that Liberty would believe that. Next.”
But then, Time Warner Cable’s management didn’t take an acquisition offer from Charter Communications seriously either when it was first proposed. Time Warner Cable believed selling to Comcast made better sense to shareholders and executives. Like Altice, Charter was a much smaller cable operator proposing to buy a much larger one. In the end, regulators rejected the deal with Comcast and with Wall Street beating the drum for someone to acquire Time Warner Cable, Charter’s sweetened second offer was readily accepted.
Charter’s biggest downside to a potential acquirer is the $60 billion in debt it took on buying Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks. Debt at SoftBank also makes Moffett skeptical of a deal between Sprint and Charter.
 “They [SoftBank] already sit on $135 billion of debt,” Moffett wrote. “Add Charter’s $63 billion and you’re within a rounding error of $200 billion. Add any cash at all for Charter’s equity and you’re flirting with a quarter trillion (trillion!) dollars of debt. Were SoftBank to buy Charter, they would become not only the most heavily indebted non-financial company the world has ever seen, they would in fact be more indebted than most countries.”
“They [SoftBank] already sit on $135 billion of debt,” Moffett wrote. “Add Charter’s $63 billion and you’re within a rounding error of $200 billion. Add any cash at all for Charter’s equity and you’re flirting with a quarter trillion (trillion!) dollars of debt. Were SoftBank to buy Charter, they would become not only the most heavily indebted non-financial company the world has ever seen, they would in fact be more indebted than most countries.”
To avoid crushing debt scuttling a deal, Citigroup speculated in a report to their investors that Comcast and Altice could partner up to divvy up Charter Communications themselves. The Wall Street bank speculates Comcast would help finance a deal if it meant it would take control of Charter’s customers formerly served by Time Warner Cable. Legacy Charter customers and those formerly served by Bright House would become part of the Altice family.
Such a transaction would likely overcome Malone’s objections over an Altice-only offer leaving him with a large pile of Altice USA stock.
Just as with Time Warner Cable, once a company is seen willing to deal, fervor on Wall Street to make a deal — any deal — can drive companies into transactions they might not otherwise have considered earlier. If Charter is seen as a seller, there will be growing pressure to find a buyer, if only to satiate investors and executives hoping for a windfall and Wall Street banks seeking tens of millions in deal advisory fees.
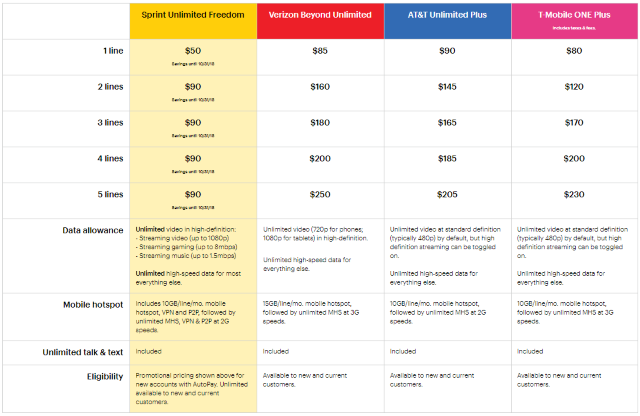
 Sprint has reintroduced a promotion giving customers up to five lines of “unlimited” voice, text, and data service for $90 a month.
Sprint has reintroduced a promotion giving customers up to five lines of “unlimited” voice, text, and data service for $90 a month.

 Subscribe
Subscribe