
Rationing Your Internet Experience: Stick to e-mail and web pages.
This week’s news that the alleged owner of a Wireless ISP serving parts of New England may have fled the country to avoid an investigation by the Securities and Exchange Commission on an unrelated digital currency matter has left about 1,000 Vermont customers of GAW Wireless with no certain future for their Internet Service Provider.
As the “Geniuses At Work” came under pressure from public accusations the company was running a scam on digital currency investors, so went the performance of GAW Wireless. In February, a two-week service outage left many customers without telephone and Internet service. This month, e-mail accounts stopped working for some and nobody appears to be answering the firm’s customer service line. Even Vermont’s Attorney General cannot find the owner.
While Wireless ISPs (WISPs) can be a good option for North America’s unserved rural communities, they are not always the best choice, especially as customers continue to gravitate towards high bandwidth applications like Netflix.
Some rural WISPs have kept up with customer demand and continue to offer good service. Others have educated customers about being a good steward of a limited resource by showing courtesy to other customers by self-limiting heavy traffic applications to off-peak hours.
But other providers have chosen usage-discouraging data caps or usage-based billing to cover up for their inadequate infrastructure investment. In Nova Scotia, Eastlink’s new 15GB monthly usage cap on rural customers is nothing short of Internet rationing, completely ignorant of the fact most customers have moved beyond the Internet applications Eastlink envisioned them using when it built its network in 2006. Nearly a decade later, it is ridiculous to suggest customers should be happy continuing to pay almost $50 a month for a 1.5Mbps connection designed for e-mail, basic web browsing, and occasional dabbling into downloads, music, and video.

Come for the view but don’t stay for the wireless broadband.
Some angry customers suspect Eastlink is simply being greedy. We believe it is more likely Eastlink’s existing wireless network is no longer adequate for the needs of Nova Scotians (or practically anybody else in 2015). The evidence that congestion is the real problem was supplied by customers who have noticed the network’s performance has slowed over the last few years. That is a sign the network is either oversold — too many customers trying to share the same bandwidth limited resource — or has become congested because of the growth of Internet traffic generally. It might even be both.
Implementing draconian usage caps only alienates customers and suggests Eastlink wants to collect as much revenue as it can from a resource that should either be vastly upgraded or retired in favor of superior technology. We have not seen anything from Eastlink that suggests major upgrades are on the way. In fact, the only conclusion we can make from Eastlink’s public comments is they think equal access to an inadequate resource is fairer than actually upgrading it.
Eastlink claims nobody could have envisioned Internet traffic growth from the likes of Netflix. In fact, equipment manufacturers like 3Com and Cisco were issuing scare stories about Internet brownouts and future traffic exafloods since December, 1995 — the year before Eastlink planned its Nova Scotia wireless network. Smart network planners have kept up with demand, which has been made easier by technology improvements accompanying the increased traffic. A good ISP recognizes upgrades are continual and essential to keep up with customer needs. A bad ISP introduces a rationing usage cap and claims it is only trying to be fair to every customer.

Phillip “Fiber is Good for You” Dampier
Usage caps and usage-based billing have never been about “fairness.” We’ve seen all sorts of usage enforcement schemes imposed on customers since 2008 when Stop the Cap! was founded. In each instance, usage caps were only about the money. Eastlink customers will not see any rate decrease as a result of its rationing plan, giving users less value for their broadband dollar. If an Eastlink customer confines use of their high traffic applications to the overnight hours, when they would cause little or no congestion, they will still eat into their monthly usage allowance.
All the benefits of usage caps accrue to Eastlink, either by reducing traffic on its network and allowing the company to delay necessary upgrades, or by pocketing the inevitable overlimit fees, which may or may not go towards upgrades. In our experience, the case for spending capital on network upgrades has never depended on overlimit fees collected from subscribers squirreled away in a separate bank account.
This is why communities in Vermont, Nova Scotia and beyond should strongly consider investing in fiber optics for broadband delivery and consider wireless only for the least populated areas. A broadband project in rural western Massachusetts can offer a guide to resolving the ongoing problem of unserved or underserved communities ignored by commercial providers. Deprived of upgrades from Verizon and shunned by Comcast and Time Warner Cable, the residents of these towns continue to vote overwhelmingly in favor of fiber optics.
The WiredWest approach is a solid solution. The initiative secures bond authorizations from each participating town in a public vote backed by deposits of $49 per household, held in escrow to be later used to cover the first month of broadband service when the service launches. Each town must have at least a 40% buy-in from residents, providing strong evidence the project has a solid customer base, is financially viable, and can recover construction costs and pay off the bonds estimated at $100-120 million within a reasonable amount of time. The state legislature contributed an additional $40 million dedicated to last mile infrastructure — the cost to wire each home or business. (In contrast, Nova Scotia and the federal government spent $34 million subsidizing the Eastlink wireless network in 2007 that has not aged well. Fiber optics is infinitely upgradable.) By choosing fiber optics, instead of getting rationed, slow speed, or no Internet service, WiredWest towns will be able to subscribe to 25Mbps for $49 a month, 100Mbps service for $79, or 1,000Mbps for $109 a month .
In comparison, Eastlink charges $46.95 a month for “up to” 1.5Mbps with a 15GB cap and GAW Wireless (when working) charges $39.95/mo for “up to 7Mbps.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast will challenge cord cutting and entice cord-nevers with
Comcast will challenge cord cutting and entice cord-nevers with  Comcast will deliver Stream over the same network it uses for content delivery to game consoles that does not count against Comcast’s
Comcast will deliver Stream over the same network it uses for content delivery to game consoles that does not count against Comcast’s 

 Enter GAW, which stands for “Geniuses At Work.” Garza’s business depended on a steady stream of clients investing in his enormous mining operation. GAW Miners claimed it has 200,000 customers and $120 million in revenue in just six months. GAW also reportedly collected 28,000 Bitcoins worth over $10 million in just two months.
Enter GAW, which stands for “Geniuses At Work.” Garza’s business depended on a steady stream of clients investing in his enormous mining operation. GAW Miners claimed it has 200,000 customers and $120 million in revenue in just six months. GAW also reportedly collected 28,000 Bitcoins worth over $10 million in just two months.
 Later this year, the service is also expected to reach further west:
Later this year, the service is also expected to reach further west: A plan to place a 15GB monthly usage cap on Eastlink broadband service in rural Nova Scotia has led to calls to ban data caps, with a NDP Member of the Legislative Assembly of Nova Scotia leading the charge.
A plan to place a 15GB monthly usage cap on Eastlink broadband service in rural Nova Scotia has led to calls to ban data caps, with a NDP Member of the Legislative Assembly of Nova Scotia leading the charge.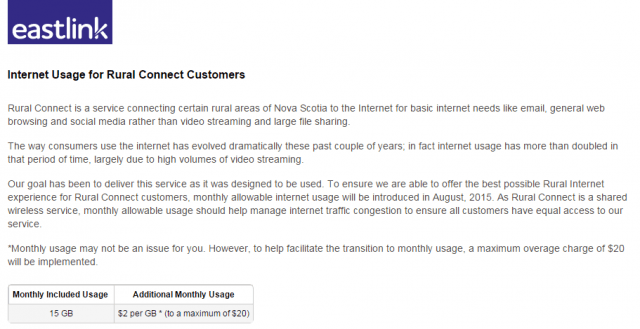

 Fournier suspects Eastlink has not invested enough to keep up with a growing Internet because the service originally advertised itself as a way to listen to online music and watch video. But he also wonders if the data cap is an attempt to force the government to fund additional upgrades to get Eastlink to back down.
Fournier suspects Eastlink has not invested enough to keep up with a growing Internet because the service originally advertised itself as a way to listen to online music and watch video. But he also wonders if the data cap is an attempt to force the government to fund additional upgrades to get Eastlink to back down.