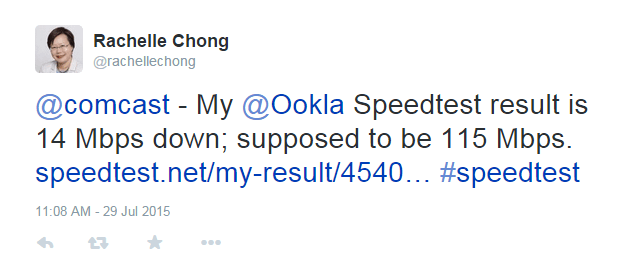
 Comcast is rejecting some requests for its new 2Gbps fiber to the home service, claiming construction costs to provide the service to some homes are too high, even for customers living 0.15 of a mile from Comcast’s nearest fiber optic connection point.
Comcast is rejecting some requests for its new 2Gbps fiber to the home service, claiming construction costs to provide the service to some homes are too high, even for customers living 0.15 of a mile from Comcast’s nearest fiber optic connection point.
Stop the Cap! reader Thomas, who wishes to withhold his last name, was excited at the prospect of signing up for Comcast’s 2Gbps broadband service for his home-based Internet business, despite the steep $1,000 installation fee and $159/mo promotional price he saw in the media.
“For the average person just looking for a faster connection at home, 2Gbps is absolute overkill, but if you run a home-based business that depends on a fast Internet connection, Comcast’s prices are a lot more reasonable than a Metro Ethernet or fiber solution from AT&T,” Thomas said.
Thomas is a Comcast customer in the Chicago area and knew he’d qualify for the service because he watched Comcast crews install/upgrade fiber cables close to his home. Comcast requires customers to live within one-third of a mile of the nearest company-owned fiber connection point to get 2Gbps service. Thomas lives far closer than that and Comcast’s online qualification tool also seemed to show the service would be available to him.
“I assumed it would be easy to order service, but it has not turned out that way at all,” Thomas complained.
Comcast’s regular customer service agents were hit or miss for Thomas. Some are acquainted with Comcast’s Gigabit Pro offering, many others are not. It took three calls for him to find a representative aware of the product, but even then the representative informed him someone would have to call him back to take his order. Two days later, he did receive a call from a Comcast regional office that explained the lengthy ordering and installation procedure. If everything worked as it should, it would take up to three months for Comcast to complete the fiber installation. But Thomas warned there were potential deal-breakers along the way.
Equipment Costs
Comcast will supply some, but not all, of the necessary equipment. A router provided by Comcast adds $19.99/mo to the price, and could be worthwhile to customers wanting to limit their out-of-pocket up front costs. But there are other equipment requirements to consider as well:
- Desktop PC with available PCIe expansion slot
- 1 10G PCIe network interface controller with SFP+ cage ($200-400)
- 1 10G enhanced small form factor pluggable SFP+ transceiver (850nm MMF) ($200-350)
- 1 MMF LC patch cable ($25-30)
To connect multiple devices to the fiber handoff, a compatible and very expensive 10Gbps Layer 3 switch or router is also required, which can run well into the thousands of dollars.
Pricing Gotchas
Installation is $500 and activation costs another $500. There is an early termination fee of $1,100 if you disconnect service before the end of your term contract. On a three-year contract, the amount of the fee is reduced by $100 every three months you keep the service. That $159 promotional price quoted in the press turned out to be another issue. Comcast informed him that offer is only good in the cities of Nashville (a future Google Fiber city also designated for GigaPower U-verse from AT&T) and Chattanooga, Tenn. (which already has gigabit service from EPB). It would cost him $299.95 a month, not $159.
Service Qualification Procedure
 Comcast implies any customer within 1/3rd of a mile of their nearest fiber cable is qualified to get Gigabit Pro service, but Thomas tells us that just isn’t true.
Comcast implies any customer within 1/3rd of a mile of their nearest fiber cable is qualified to get Gigabit Pro service, but Thomas tells us that just isn’t true.
“Comcast treats these installations the same way they would running cable into virgin territories like an unserved neighborhood or office park,” Thomas said. “Once you commit to an order, I am convinced they do a Return On Investment (ROI) and cost analysis to decide if it makes financial sense to actually bring fiber to you.”
It begins with an in-office map survey that reviews Comcast’s existing network and verifies a path from Comcast’s existing fiber network to the customer’s home. This process takes up to 14 days, according to Thomas, and makes certain the customer is within the qualified distance for service.
“But I can say it goes beyond this, because Comcast was also looking at proposed routes to get fiber to me, and the representative was concerned about whether Comcast’s cables in my area were on telephone poles or underground in conduit,” reported Thomas. “There was also an issue with a pedestal and I was informed a site survey was required to check whether existing infrastructure in my neighborhood could support the service.”
Comcast said a visit from a technician would be required — another two-week process, and about then he was told “there was indeed a problem with their existing pedestal and they also ran into a conduit issue,” Thomas said. “At that point, I was informed my order could not go ahead because Comcast would have to spend about $17,000 to correct these issues and cover my installation and that evidently failed their ROI and cost analysis.”
Had Thomas passed all the qualification tests, he would have waited up to 13 weeks (more than three months) from the time he ordered service before he could actually use it. Now, he will wait at least a year for Comcast’s suggested alternative — the arrival of DOCSIS 3.1, which is expected to support gigabit speeds over Comcast’s existing coax cable network.
“I honestly felt mislead by Comcast’s press releases that suggested service was just a matter of where you lived without telling customers they will deny service if it costs Comcast over a certain dollar amount, no matter how close you live to their existing fiber,” Thomas added. “Promoting a service and actually providing it are two very different things and it seems Comcast just isn’t providing it, at least to me.”
Have you explored Comcast Gigabit Pro? If so, share your experiences in the comment section. We’d love to hear from you if you actually have the service installed.


 Subscribe
Subscribe After months of issuing
After months of issuing 

 Residents of one of the world’s most isolated countries will soon have the option of getting fiber-to-the-home service that will offer faster Internet access than most Americans get with traditional DSL from their phone company.
Residents of one of the world’s most isolated countries will soon have the option of getting fiber-to-the-home service that will offer faster Internet access than most Americans get with traditional DSL from their phone company.
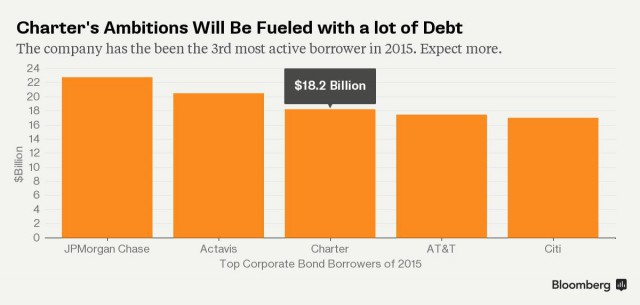
 The Marcus-led opposition campaign against Charter gave Comcast just the time it needed to mount a competing bid — all in Comcast stock, then worth around $159 a share. Comcast also offered Marcus an $80 million golden parachute if the deal succeeded.
The Marcus-led opposition campaign against Charter gave Comcast just the time it needed to mount a competing bid — all in Comcast stock, then worth around $159 a share. Comcast also offered Marcus an $80 million golden parachute if the deal succeeded.
