 A plea from unhappy Frontier Communications’ broadband customers in West Virginia to have their complaints about Frontier DSL heard by a judge will get a hearing before Lincoln County Circuit Judge Jay Hoke on Aug. 19.
A plea from unhappy Frontier Communications’ broadband customers in West Virginia to have their complaints about Frontier DSL heard by a judge will get a hearing before Lincoln County Circuit Judge Jay Hoke on Aug. 19.
The class action lawsuit claims Frontier deceptively advertises fast Internet service that in reality is often unreliable and delivers only 5-10 percent of the speeds advertised. Many West Virginians have no other broadband options.
In response, lawyers for Frontier Communications have fought to get the case dismissed. They want customers to take their complaints through Frontier’s binding arbitration dispute resolution process.
In 2011, Frontier changed its terms and conditions, adding a lengthy arbitration provision that forbids customers from bringing class action cases and generally limits the damages customers can receive. Frontier argues customers automatically agreed to the arbitration process by continuing to use Frontier’s broadband service after the changes were announced.
The attorneys bringing the case think Frontier’s insistence that customers are automatically bound by the company’s contractual terms and conditions is ironic.
“No contract. No signatures. No worries,” claims one Frontier ad. “There’s no contract. Yep, that’s right, no contract,” advertises another. Since 2013, Frontier has gone out of its way advertising broadband without the gotchas and hidden fees their competitors charge. “Frontier is now in the unenviable position of trying to enforce hidden terms in the very contracts they repeatedly represented did not exist,” argues the plaintiffs in a court document.

Some Frontier customers never realized they may have given up their right to bring a civil case against Frontier. The company first notified customers about this change in their terms and conditions in 2011 through a small message on Frontier invoices. Customers effectively agreed to those changes through their continued use of Frontier’s service, Frontier claimed. But the plaintiffs signed documents attesting they had never seen or heard of Frontier’s enforced arbitration policy. The lawyers bringing the case are not surprised. A copy of the changed terms and conditions obtained by Stop the Cap! shows the binding arbitration clause buried on page five of a leaflet rendered in very small print in very large paragraphs unlikely to be read or understood by many customers.
The current arbitration policy is reproduced below. Have you read it?:
As explained more fully below and in the terms and conditions document, Frontier’s terms and conditions set forth important details about your relationship with Frontier including the requirement to resolve any dispute with Frontier by binding arbitration, on an individual basis, rather than through a lawsuit, jury trial or class action. If you do not agree to Frontier’s terms and conditions, you may not use the Frontier service and must terminate service immediately.
DISPUTE RESOLUTION WITH FRONTIER BY BINDING ARBITRATION
PLEASE READ THIS CAREFULLY. IT AFFECTS YOUR RIGHTS.
Frontier encourages you to contact our Customer Service department if you have concerns or complaints about your service or Frontier. Generally, customer complaints can be satisfactorily resolved in this way. In the unlikely event that you are not able to resolve your concerns through our Customer Service department, we each agree to resolve all disputes through binding arbitration or a small claims court rather than lawsuits in courts of general jurisdiction, jury trials, or class actions. Arbitration is more informal than a lawsuit. Arbitration uses a neutral arbitrator instead of a judge or jury, allows for more limited discovery than in court, and is subject to very limited review by courts. Arbitrators can award the same damages and individual relief affecting individual parties that a court can award, including an award of attorneys’ fees if the law allows. For any non-frivolous claim that does not exceed $75,000, Frontier will pay all costs of the arbitration. Moreover, in arbitration you are entitled to recover attorneys’ fees from Frontier for your own dispute to the same extent as you would be in court.
In addition, under certain circumstances (as explained below), Frontier will pay you more than the amount of the arbitrator’s award if the arbitrator awards you an amount that is greater than what Frontier has offered you to settle the dispute.
Arbitration Agreement:
(a) You and Frontier agree to arbitrate all disputes and claims between us. This agreement to arbitrate is intended to be broadly interpreted. It includes, but is not limited to, all claims arising out of or relating to any aspect of our relationship, whether based in contract, tort, statute, fraud, misrepresentation or any other legal theory, that arose either before or during this or any prior Agreement, or that may arise after termination of this Agreement. It also includes claims that are currently the subject of purported class action litigation in which you are not a member of a certified class. References to “Frontier,” “you,” and “us” include our respective subsidiaries, affiliates, agents, employees, predecessors in interest, successors, and assigns, as well as all authorized or unauthorized users or beneficiaries of Frontier Broadband under this or prior Agreements between us.
Notwithstanding the foregoing agreement, Frontier agrees that it will not use arbitration to initiate debt collection against you except in response to claims you have made in arbitration. In addition, by agreeing to resolve disputes through arbitration, you and Frontier agree to each unconditionally waive the right to a trial by jury or to participate in a class action, representative proceeding, or private attorney general action. Instead of arbitration, either party may bring an individual action in a small claims court for disputes or claims that are within the scope of the small claims court’s authority. In addition, you may bring any issues to the attention of federal, state, or local agencies, including, for example, the Federal Communications Commission. Such agencies can, if the law allows, seek relief against us on your behalf.
This agreement evidences a transaction in interstate commerce, and thus the Federal Arbitration Act governs the interpretation and enforcement of this provision, even after the agreement is terminated.
(b) A party who intends to seek arbitration must first send to the other, by certified mail, a written Notice of Dispute (“Notice”). The Notice to Frontier should be addressed to: Frontier Communications, Legal Department – Arbitration, 3 High Ridge Park, Stamford, CT 06905 (“Notice Address”). The Notice must (1) describe the nature and basis of the claim or dispute; and (2) set for the specific relief sought (“Demand”). If Frontier and you do not reach an agreement to resolve the claim within 30 days after the Notice is received, you or Frontier may commence an arbitration proceeding. During the arbitration, the amount of any settlement offer made by Frontier or you shall not be disclosed to the arbitrator until after the arbitrator determines the amount, if any, to which you or Frontier is entitled.
(c) The arbitration will be governed by the Consumer Arbitration Rules (“AAA Rules”) of the American Arbitration Association (“AAA”), as modified by these Terms of Service, and will be administered by the AAA. Procedure, rule and fee information is available from the AAA online at http://www.adr.org, by calling the AAA at 1-800-778-7879, or by calling Frontier at 1-877-462-7320, option 3. The arbitrator is bound by the terms of this Agreement. All issues are for the arbitrator to decide, except that issues relating to the scope and enforceability of the arbitration provision, including the scope, interpretation, and enforceability of section (f) below, are for the court to decide. If your claim is for $25,000 or less, you may choose whether the arbitration will be conducted solely on the basis of documents submitted to the arbitrator, through a telephonic hearing, or by an in person hearing as established by the AAA Rules. If your claim exceeds $25,000, the right to a hearing will be determined by the AAA Rules. Unless Frontier and you agree otherwise, any in person hearings will take place at a location that the AAA selects in the state of your primary residence unless you and Frontier agree otherwise. Regardless of the manner in which the arbitration is conducted, the arbitrator shall issue a reasoned written decision sufficient to explain the essential findings and conclusions on which the award is based.
Frontier agrees to pay your AAA filing, administration, and arbitrator fees (“AAA fees”) for claims for damages of up to $75,000 and for claims for non-monetary relief up to the value of $75,000, as measured from either your or Frontier’s perspective (but excluding attorneys’ fees and expenses). After Frontier receives notice that you have commenced arbitration, it will promptly reimburse you for your payment of the filing fee, unless your claim is for greater than $75,000. (The filing fee currently is $200 but is subject to change by the AAA. If you are unable to pay this fee, Frontier will pay it directly upon receiving a written request.) In addition, Frontier will not pay your share of the AAA fees if the arbitrator finds that either your claim or the relief sought is frivolous or brought for an improper purpose, as measured by the standards of Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 11(b). In such case, the payment of AAA fees will be governed by the AAA Rules, and you agree to reimburse Frontier for all monies previously disbursed by it that are otherwise your obligation to pay under the AAA Rules. If you initiate an arbitration in which you seek relief valued at more than $75,000 (excluding attorneys’ fees and expenses), as measured from either your or Frontier’s perspective, the payment of AAA fees will be governed by the AAA Rules.
(d) If Frontier offers to settle your dispute prior to appointment of the arbitrator and you do not accept the offer, and the arbitrator awards you an amount of money that is more than Frontier’s last written settlement offer, then Frontier will pay you the amount of the award or $5,000 (“the alternative payment”), whichever is greater.
If Frontier does not offer to settle your dispute prior to appointment of the arbitrator, and the arbitrator awards you any relief on the merits, then Frontier agrees to pay you the amount of the award or the alternative payment, whichever is greater. The arbitrator may make rulings and resolve disputes as to the payment and reimbursement of fees, expenses, and the alternative payment at any time during the proceeding and upon request from either party made within fourteen (14) days of the arbitrator’s ruling on the merits.
(e) Although Frontier may have a right to an award of attorneys’ fees and expenses if it prevails, Frontier agrees that it will not seek such an award.
(f) You and Frontier agree to seek, and further agree that the arbitrator may award, only such relief—whether in the form of damages, an injunction, or other non-monetary relief—as is necessary to resolve any individual injury that either you or Frontier have suffered or may suffer. In particular, if either you or Frontier seek any non-monetary relief, including injunctive or declaratory relief, the arbitrator may award relief on an individual basis only, and may not award relief that affects individuals or entities other than you or Frontier. You and Frontier agree that we each may bring claims against the other only in an individual capacity and not as a plaintiff or class member in any purported class, representative, or private attorney general proceeding. Furthermore, unless both you and Frontier agree otherwise in writing, the arbitrator may not consolidate more than one person’s claims, and may not otherwise preside over any form of a class, representative, or private attorney general proceeding. If a court decides that applicable law precludes enforcement of any of this paragraph (f)’s limitations as to a particular claim for relief, then that claim (and only that claim) must be severed from the arbitration and may be brought in court. Further, an arbitrator’s award and any judgment confirming it shall apply only to that specific case and cannot be used in any other case except to enforce the award itself.
(g) Notwithstanding any provision in these Terms to the contrary, you and Frontier agree that if Frontier makes any change to this arbitration provision during the period of time that you are receiving Frontier services, you may reject that change by providing Frontier with written notice within 30 days of the change to the Notice Address provided above and require Frontier to adhere to the language in this provision. By rejecting any future change, you are agreeing that you will arbitrate any dispute between us in accordance with the language of this provision.
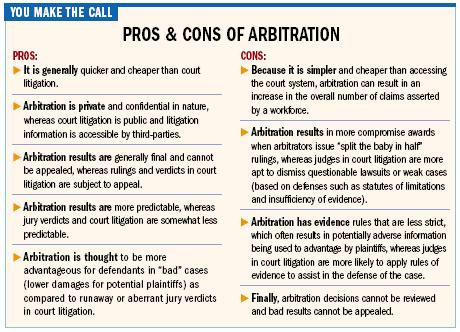 Corporations began to favor private arbitration over the civil courts several years ago, arguing arbitration would save money and lead to faster resolutions of customer complaints. Many customers and trial lawyers disagree, arguing arbitration favors the corporations that pay for arbitration programs, shields bad acts from public disclosure with confidentiality agreements, limits damage awards and prevents class action cases seeking relatively small amounts of damages for a large number of customers who would otherwise never bring a case to court. Early attempts by some companies to offer voluntary arbitration programs as an alternative to civil actions offered more limited benefits and many companies have since moved to mandatory, binding arbitration instead. Disputes subject to mandatory arbitration usually must be resolved through arbitration. The parties give up their right to sue in court, participate in a class action lawsuit, or appeal the arbitration decision.
Corporations began to favor private arbitration over the civil courts several years ago, arguing arbitration would save money and lead to faster resolutions of customer complaints. Many customers and trial lawyers disagree, arguing arbitration favors the corporations that pay for arbitration programs, shields bad acts from public disclosure with confidentiality agreements, limits damage awards and prevents class action cases seeking relatively small amounts of damages for a large number of customers who would otherwise never bring a case to court. Early attempts by some companies to offer voluntary arbitration programs as an alternative to civil actions offered more limited benefits and many companies have since moved to mandatory, binding arbitration instead. Disputes subject to mandatory arbitration usually must be resolved through arbitration. The parties give up their right to sue in court, participate in a class action lawsuit, or appeal the arbitration decision.
The law firms handling the case against Frontier — Bailey Glasser in Charleston and Klein, Sheridan & Glazer in Huntington, are arguing Frontier customers cannot be bound by mandatory arbitration policies without evidence Frontier informed them of the program and can show evidence of their consent. In a lengthy argument to the judge, the attorneys argue Frontier can show neither. They point to Frontier’s website, which “buries” the terms and conditions as a tiny link at the bottom of their main web page. Customers must click that link, then find the link for the arbitration provision, then read and understand it. Notice about the arbitration policy originally came in occasional billing notices. Since the lawsuit was filed, Frontier has given more prominent mention of its terms and conditions, including its arbitration policy, on monthly billing statements.
Frontier’s defense is that the plaintiffs are misrepresenting the meaning of “no contract.” The company argues customers commonly understand that term to mean they will not be asked to sign a term contract for one, two, or three years, facing an early termination penalty if they seek to end the contract early. The fact Frontier advertises “no contract” does not mean there are no terms and conditions, the company’s attorneys argued.
A potentially weaker defense is Frontier’s claim that customers can be bound by a contract once they continue to use the service after a change in terms is published. Frontier admitted it could not prove the customers read and understood the change of terms notification or the new terms and conditions. It also never asked customers to directly consent, either in writing or by checking a box on a website, to the new terms and conditions. The plaintiffs also question the legality of Frontier reserving the right to unilaterally change any terms and conditions after a brief notification period and win consent of those changes if subscribers do not cancel service or, in some cases, opt out.
The attorneys call that “take it or leave it” Internet access from Frontier, often the only provider in large parts of rural West Virginia.
Find the terms and conditions link on the bottom of Frontier.com.
 Verizon is ready to push speeds beyond 1Gbps on its fiber to the home network FiOS, after successfully testing the next generation of signaling technology capable of delivering at least 10Gbps to customers.
Verizon is ready to push speeds beyond 1Gbps on its fiber to the home network FiOS, after successfully testing the next generation of signaling technology capable of delivering at least 10Gbps to customers.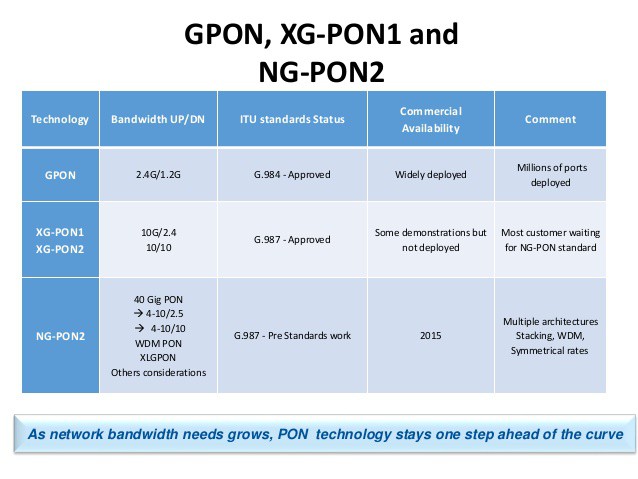


 Subscribe
Subscribe A
A 
 Corporations began to favor private arbitration over the civil courts several years ago, arguing arbitration would save money and lead to faster resolutions of customer complaints. Many customers and trial lawyers disagree, arguing arbitration favors the corporations that pay for arbitration programs, shields bad acts from public disclosure with confidentiality agreements, limits damage awards and prevents class action cases seeking relatively small amounts of damages for a large number of customers who would otherwise never bring a case to court. Early attempts by some companies to offer voluntary arbitration programs as an alternative to civil actions offered more limited benefits and many companies have since moved to mandatory, binding arbitration instead. Disputes subject to mandatory arbitration usually must be resolved through arbitration. The parties give up their right to sue in court, participate in a class action lawsuit, or appeal the arbitration decision.
Corporations began to favor private arbitration over the civil courts several years ago, arguing arbitration would save money and lead to faster resolutions of customer complaints. Many customers and trial lawyers disagree, arguing arbitration favors the corporations that pay for arbitration programs, shields bad acts from public disclosure with confidentiality agreements, limits damage awards and prevents class action cases seeking relatively small amounts of damages for a large number of customers who would otherwise never bring a case to court. Early attempts by some companies to offer voluntary arbitration programs as an alternative to civil actions offered more limited benefits and many companies have since moved to mandatory, binding arbitration instead. Disputes subject to mandatory arbitration usually must be resolved through arbitration. The parties give up their right to sue in court, participate in a class action lawsuit, or appeal the arbitration decision.

 After
After 
 It didn’t take long for consumers to start flooding the Federal Communications Commission with thousands of complaints about poor Internet service, usage caps, and speed throttles.
It didn’t take long for consumers to start flooding the Federal Communications Commission with thousands of complaints about poor Internet service, usage caps, and speed throttles. No more Netflix and Hulu watching for this family: “I have to tell my kids to stop using YouTube and other services and stuff they need for school so we don’t go over the cap,” another consumer wrote, explaining that their Internet-enabled home security camera uses up a significant amount of their monthly data. “By Comcast having this data cap, I don’t have a open Internet … I also think this data cap is very inaccurate, it goes up without anybody being home, and sometimes by a lot.”
No more Netflix and Hulu watching for this family: “I have to tell my kids to stop using YouTube and other services and stuff they need for school so we don’t go over the cap,” another consumer wrote, explaining that their Internet-enabled home security camera uses up a significant amount of their monthly data. “By Comcast having this data cap, I don’t have a open Internet … I also think this data cap is very inaccurate, it goes up without anybody being home, and sometimes by a lot.”