On a morning conference call with Wall Street analysts, Comcast continues to misrepresent its vision of broadband usage caps and usage-based billing, claiming customer preferences echoed through Comcast’s performance in the marketplace will tell the company what is “best for consumers,” and guide Comcast how to realize the most value for shareholders.
On a morning conference call with Wall Street analysts, Comcast continues to misrepresent its vision of broadband usage caps and usage-based billing, claiming customer preferences echoed through Comcast’s performance in the marketplace will tell the company what is “best for consumers,” and guide Comcast how to realize the most value for shareholders.
Wall Street is very interested in usage caps and usage-based billing because cable operators can protect video revenue threatened by cord-cutting and boost revenue earned from customers who exceed their allowance.
Vijay Jayant, and analyst at Evercore ISI, quickly zeroed in on the potential loss of anticipated revenue from Comcast’s recent decision to boost its data cap from 300GB to 1TB, something Jiyant characterized as a “hurdle” for future usage-related charges.
“Well we have one terabyte. We moved it up from 300 gigabyte to one terabyte in 14% of our markets where we have usage-based pricing,” responded Neil Smit, Comcast Cable’s president and CEO. “We think we’re going to continue to adjust and look at it as the market evolves and as usage evolves. We have different pricing models, some based on speed, some based on usage, and we’re going to be flexible and kind of let the market tell us which way is best for consumers and how we add the most value. We continue to add speeds. We’ve upped speeds 17 times in 15 years. We’ve built out the fastest Wi-Fi. So we’re going to continue to invest in the network to stay ahead of things.”
Smit’s response was incomplete, however.

Smit
Comcast’s usage and speed-based pricing models are hardly “flexible” and do not co-exist in the same markets. Customers are compelled to obey Comcast’s usage cap, face overlimit fees up to $200 a month, or pay an additional $50 a month to buy back their old unlimited use service. In Comcast markets without usage caps, the cable company only sells speed-based internet tiers with no enforced caps.
Comcast has consciously avoided allowing customers to choose between speed-based or usage-based tiers, because years of experience among other cable operators quickly proved customers intensely dislike usage caps of any kind. In fact, the largest percentage of complaints filed with the FCC about Comcast are about its compulsory usage cap trial and the fees associated with it.
One reason for that hostility may be that Comcast’s broadband prices do not drop as a result of the introduction of usage caps in a service area. The customer effectively receives a lower value broadband product as a result of its arbitrary usage limit, and the potential exposure to overlimit fees or a very expensive “insurance” plan to avoid the cap altogether. Earlier trials offered some customers a small discount if they kept usage under 5GB a month, a difficult prospect for most and in any case not much of a revenue threat for Comcast.
 If Comcast was seriously interested in what its customers think about its usage cap trial, it need only review the FCC’s complaint database. According to a Freedom of Information Law request from The Wall Street Journal, nearly 8,000 complaints received by the FCC in the second half of 2015 were about data caps, and most of those were directed at Comcast.
If Comcast was seriously interested in what its customers think about its usage cap trial, it need only review the FCC’s complaint database. According to a Freedom of Information Law request from The Wall Street Journal, nearly 8,000 complaints received by the FCC in the second half of 2015 were about data caps, and most of those were directed at Comcast.
Comcast’s claim it will let the marketplace decide only delivers a distorted view about usage caps, because many Comcast customers have only one other competitive choice, and there is a significant chance that provider caps customer’s broadband usage as well. AT&T, for example, caps its customers at a level even stingier than Comcast. Those caps have not been enforced with overlimit fees on customer bills (except for AT&T’s DSL customers), although AT&T suggests it is getting serious about collecting future overlimit fees. If Comcast gains new customers leaving AT&T to avoid smaller caps, Comcast executives seem to believe they can claim consumers have ’embraced’ Comcast’s usage billing. But we know that is about as credible as an election in North Korea.
Time Warner Cable has been one of the few honest players about usage billing, giving customers the option of keeping unlimited or switching to a capped plan for a discount. More than 99% of customers have chosen to stay with unlimited and only a few thousand have chosen to limit their usage for a small discount. An honest market test from Comcast would extend a similar option to customers. Keep unlimited or voluntarily limit usage for a small discount. Given this kind of test, we expect the overwhelming majority of customers would keep unlimited at all costs. Doing so would hurt shareholder value, however.
The only value Comcast is concerned with is how much more money they can charge customers for broadband service. In America’s broadband duopoly, where speed-based broadband pricing is already outrageously high, usage caps and usage billing are nothing more than a greedy cash grab. When money is at stake, reputation comes in a distant second at Comcast, as the company continues to prove its poor reputation with American consumers is well-deserved.


 Subscribe
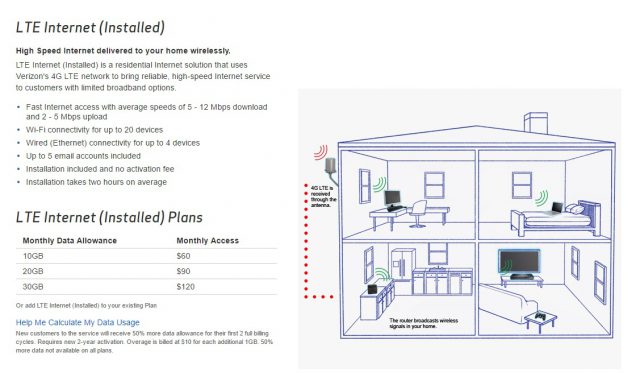
Subscribe Broadband life in Alaska is usually a choice (if you live in Fairbanks, Anchorage, Juneau, or another significantly sized city) between usage-capped cable operator GCI or slow-speed DSL (if you can get it) from Alaska’s two telephone companies – ACS, where unlimited service is still available, or MTA, where a 10Mbps Internet plan starts at $50 and offers up to 50GB of usage a month.
Broadband life in Alaska is usually a choice (if you live in Fairbanks, Anchorage, Juneau, or another significantly sized city) between usage-capped cable operator GCI or slow-speed DSL (if you can get it) from Alaska’s two telephone companies – ACS, where unlimited service is still available, or MTA, where a 10Mbps Internet plan starts at $50 and offers up to 50GB of usage a month.
 CenturyLink will begin a usage-based billing trial in Yakima, Wa., starting July 26 that will combine usage caps with an overlimit fee on customers that exceed their monthly usage allowance. The trial in Washington state may soon be a fact of life for most CenturyLink customers across the country, unless customers rebel.
CenturyLink will begin a usage-based billing trial in Yakima, Wa., starting July 26 that will combine usage caps with an overlimit fee on customers that exceed their monthly usage allowance. The trial in Washington state may soon be a fact of life for most CenturyLink customers across the country, unless customers rebel.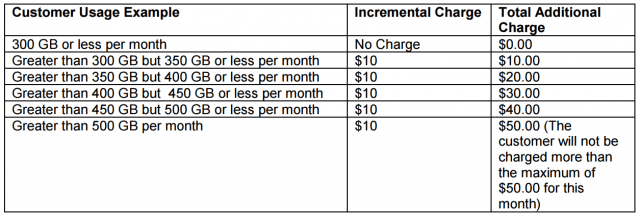


 “Sharing is essential for the future of spectrum utilization. Many of the high-frequency bands we will make available for 5G currently have some satellite users, and some federal users, or at least the possibility of future satellite and federal users,” Wheeler noted. “This means sharing will be required between satellite and terrestrial wireless; an issue that is especially relevant in the 28GHz band. It is also a consideration in the additional bands we will identify for future exploration. We will strike a balance that offers flexibility for satellite users to expand, while providing terrestrial licensees with predictability about the areas in which satellite will locate.”
“Sharing is essential for the future of spectrum utilization. Many of the high-frequency bands we will make available for 5G currently have some satellite users, and some federal users, or at least the possibility of future satellite and federal users,” Wheeler noted. “This means sharing will be required between satellite and terrestrial wireless; an issue that is especially relevant in the 28GHz band. It is also a consideration in the additional bands we will identify for future exploration. We will strike a balance that offers flexibility for satellite users to expand, while providing terrestrial licensees with predictability about the areas in which satellite will locate.”
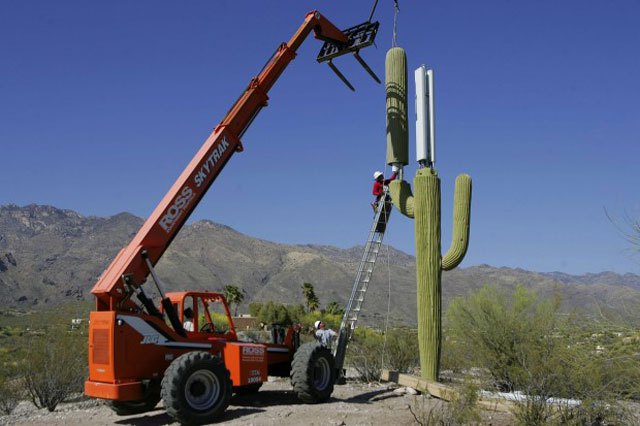





 In other words, it is much easier to justify capital expenses of $300 million on network expansion to Wall Street if you explain it’s primarily for the high-profit wireless side of the business, not to give customers an alternative to Time Warner Cable or Comcast. FiOS powers cell sites as well as much smaller microcells and short-distance antennas designed to manage usage in high traffic neighborhoods.
In other words, it is much easier to justify capital expenses of $300 million on network expansion to Wall Street if you explain it’s primarily for the high-profit wireless side of the business, not to give customers an alternative to Time Warner Cable or Comcast. FiOS powers cell sites as well as much smaller microcells and short-distance antennas designed to manage usage in high traffic neighborhoods.