Stop the Cap! reader Bones sends word the FCC needs volunteers to help keep America’s broadband providers honest about their speed claims. But the agency warns heavily usage capped consumers they probably shouldn’t apply, and anyone consuming over 30 GB per month is disqualified.
Stop the Cap! reader Bones sends word the FCC needs volunteers to help keep America’s broadband providers honest about their speed claims. But the agency warns heavily usage capped consumers they probably shouldn’t apply, and anyone consuming over 30 GB per month is disqualified.
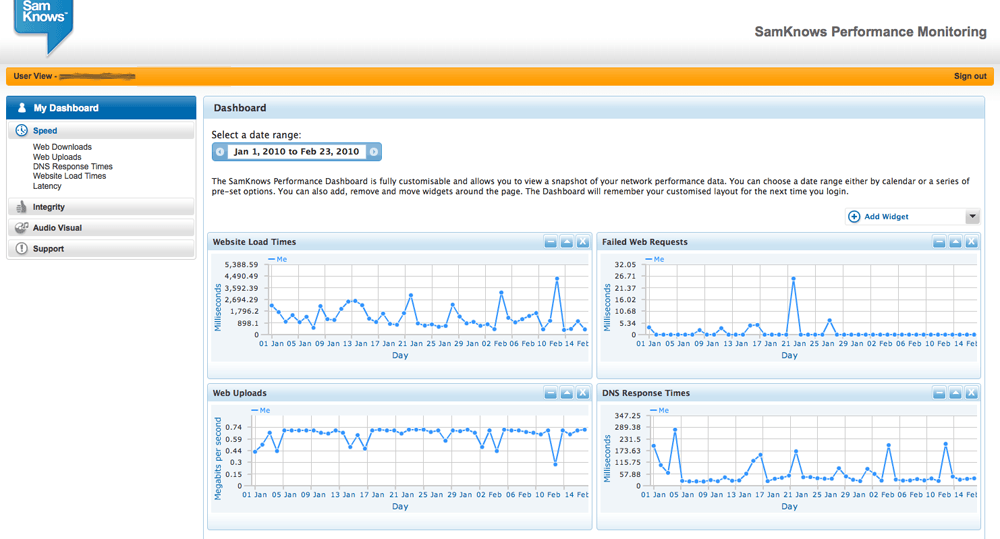
The FCC SamKnows Broadband Community aims to gather and report statistical data on the performance of America’s broadband providers. Thus far, most of the earlier speed results being studied by public officials come from data aggregated from voluntary visits to speed test websites. But the data is subject to considerable variation depending on the speed test site chosen, traffic and capacity issues that only impact the route to the test site, and what else a consumer may doing with their connection during the test. Many also conduct speed tests when a technical problem is apparent, using the speed test site to verify their suspicions.
The FCC will send 10,000 volunteers a free router that will hook up to one’s broadband connection and quietly test it several times daily. Comprehensive measurements to be taken include latency, packet loss, DNS query times and failures, web page loading times, as well as the obligatory suite of speed tests. The testing is done in the background and the results are uploaded to SamKnows for review. The FCC can use the data from all of the volunteers to identify the true performance of national and regional Internet Service Providers. Do their speed claims actually match reality? Do they suffer from congestion problems and at what times of day?
One group of ISPs the agency will have trouble measuring are those that heavily limit their customers’ use. In fact, the Test My ISP website warns off customers with low data caps because the project is expected to send and receive about 4 gigabytes of data in full over the course of each month. While the program designers felt that much data was so insignificant it would not create a problem, some greedy ISPs out there beg to differ. With some providers offering usage allowances at 5 or fewer gigabytes per month, the FCC quickly learned it doesn’t want to be responsible for spiking consumer broadband bills with any overlimit fees.
As a result, they’ve asked those usage capped consumers to think twice about applying for the traditional testing program:
Our units download approximately 2GB per month and upload around 2GB. If you’re on a product with a low usage cap then we’d advise against signing up, or at least informing us beforehand so that we can apply a different testing profile.
The FCC also isn’t interested in sending test units to customers they designate as “heavy downloaders”:
We’d classify anything above 30GB per month as being too heavy for us to gather useful results.
With the increasing use of multimedia content and other high bandwidth applications being released to the Internet masses, we beg to differ with the arbitrary definition that 30 GB constitutes “heavy downloading.” We understand the agency doesn’t want other online usage to create an issue for the accuracy of its speed tests, but they should take better care with their language. One could use a file backup service and easily consume more then 30 GB uploading and never download more than a gigabyte.
Other restrictions:
- You have a fixed line broadband Internet connection to your residence. This is not for WISPs, mobile broadband, or other wireless broadband services.
- You use a standalone device to connect to your broadband service – i.e not a USB ADSL modem.
- You have a stable broadband connection (i.e. it doesn’t disconnect frequently). Note that this is just referring to the connection – not the speed.
- You have a spare power socket near your existing router (or wherever you plan to connect the unit. Keep in mind that a network cable must run between the unit and your router though! We supply a 1m cable).
- You need to be on one of the ISPs that we’re measuring.
- You are not an employee or a family member of an employee of one of the ISPs being monitored.
Also, you must agree to the following:
-
Not to unplug the unit or your ISP’s router unless I’m away for an extended period of time.
-
Not attempt to reverse engineer or alter the unit.
-
To notify Samknows if and when I choose to change ISPs.
-
To return the unit to Samknows should I no longer wish to be involved (Samknows to pay reasonable postage costs).
-
To connect the unit in the way described in the documentation.
-
To keep Samknows updated with valid contact details (i.e. email and postal address).
SamKnows is a British company hired by the FCC to conduct the speed test project. SamKnows is already familiar to British broadband consumers for its comprehensive broadband availability checker showing all of the broadband choices available based on the address where service is to be installed.
The company also reports on broadband news, mostly impacting Europe.
And before the paranoid start suggesting this is Obama’s Internet Spy Box, SamKnows offers this:
However, the unit simply acts as a standard switch or standard router and does not look at any of the packets flowing across your network. It only monitors traffic volumes for the purposes of deciding when to run (or not to run!) the tests and to measure consumption.
Testing information uploaded from the unit to our servers contains no information about you whatsoever. Furthermore, all such communications are encrypted, ensuring that results cannot be tampered with en-route.
Your individual unit’s test results will be available to you alone. Your unit’s results will also be aggregated with others from the same ISP to form a larger average set of results that can be viewed publicly.
We have absolutely no intention of doing anything that may adversely affect your privacy or security.
[flv width=”512″ height=”308″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/ITN News Ofcom report says broadband is not up to speed 7-28-09.flv[/flv]
The implications for the FCC’s national speed test program could mimic Great Britain’s, where providers were held to account for wide variations between speeds promised and those actually delivered. Meaningful broadband reform in the States could include a requirement that providers’ marketing claims be provable, compelling at least some to perform competitive upgrades instead of delivering broken promises. This ITN News report from last summer illustrates what happened when UK provider speed claims were put to the test. (3 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe