Stop the Cap! reader Jeff from Palo Alto, Calif., dropped us a line over the weekend asking about a story published last week by the Salisbury Post regarding a bill that would banish community-owned broadband providers in the state of North Carolina. The legislation, custom-written by Big Telecom companies, could eventually spell doom for truly competitive service from community-owned providers like Fibrant, based in Salisbury.
Stop the Cap! reader Jeff from Palo Alto, Calif., dropped us a line over the weekend asking about a story published last week by the Salisbury Post regarding a bill that would banish community-owned broadband providers in the state of North Carolina. The legislation, custom-written by Big Telecom companies, could eventually spell doom for truly competitive service from community-owned providers like Fibrant, based in Salisbury.
“I got the impression that it said Salisbury was agreeing not to oppose the proposed legislation, in exchange for being exempted from it,” Jeff writes. “That seemed like a long-term victory for Time Warner. Am I missing something?”
The reporter who accepted propaganda at face value from the cable industry certainly did.
The article, “Lawmakers Eye Blocks on Fiber Optic Systems,” was replete with demonstrably false statements from both Time Warner Cable and a high-powered cable industry lobbyist less-menacingly-labeled “a lawyer for the N.C. Cable Telecommunications Association.” (Perry Mason he isn’t.)
In fact, communities across the state continue to oppose this special interest favoritism, bought and paid for by the telecommunications industry. But getting people acquainted with the facts is a problem when reporters don’t bother to fact-check some of the rhetoric from the cable industry, which at times leaves some with the ludicrous impression they are “the little guy.”
Rep. Marilyn Avila — The Representative for Time Warner Cable
The Post seems to suggest local officials are negotiating passage to the lifeboats before Rep. Marilyn Avila’s legislative gift to Time Warner Cable becomes the legal iceberg that sinks community broadband in the state.
In reality, city officials are pointing out they harbor no resentment towards any telecommunications company operating in the state. In fact, they welcome them to participate by securing space on their advanced networks at competitive rates in public-private partnerships.
Unfortunately, they are up against Avila’s “bull in a china shop” bill that would cut the legs out from community-owned networks before such partnerships can become reality. In fact, Avila’s abdication of her responsibilities to her constituents for the benefit of Time Warner Cable is even worse because it could ultimately harm the state’s credit rating and image if such networks can be run out of business at the behest of a competitor.
For a “small government conservative” to write a bill laden with regulations, rules, and taxes anathema to the “free market” is a testament to just how willing she is to abandon her principles when Big Cable comes calling.
Avila has suggested that existing community-owned networks are exempt in the current language of the bill. That statement is patently untrue because the micro-management regulations found within it would apply to all community broadband networks, but exempt privately-owned ones. That’s fair, right?
For mayors in communities with these networks, securing a strong exemption is part of a full-court press against this bill. If it were to become law, keeping a pre-existing network in business becomes an important priority.

Rep. Marilyn Avila (R-Time Warner Cable)
Mayor Susan Kluttz told the Post she is hopeful state lawmakers will rewrite the bill to exempt Salisbury and other cities with networks that are up and running.
But the mayor is smart enough to also realize at least some of the people at the table do not have the city’s best interests at heart when it comes to Fibrant.
Sources tell Stop the Cap! there are several members of the General Assembly, Republicans and Democrats, who are more than a little unhappy with Avila’s attempts to ram the bill through. Not only does the water-carrying look bad inside (and outside) of the state, it will also destroy the potential of expanding broadband service to many poorly reached parts of North Carolina.
“This bill guarantees Time Warner will hold the keys to the broadband kingdom in North Carolina for years to come,” a well-placed source told us. “Even public-private partnerships to develop broadband in rural areas of the state are directly threatened by her bill.”
Citizens across North Carolina are calling and writing legislators in opposition, but Avila doesn’t show signs of moving away from her pro-cable bill so far.
“Empty promises are being made to some legislators that suggest if they support this bill, Time Warner will magically wire unserved areas for service,” sources tell us. “The company that had no intention of wiring these areas over the past two decades will continue to ignore them whether this bill passes or not.”
Indeed, Time Warner Cable and other companies use a standard business calculation when determining whether or not to wire outlying communities. If too few customers live within a square mile radius, they don’t receive cable service. Nothing has ever changed that unless it is mandated in a formal local franchise agreement. At AT&T’s behest a few years ago, such local franchise agreements were banished from the state. Rural residents in places like Caswell County pay the price as large sections of the county go without broadband service.
The implications are dire:
Jobs -are- threatened by Avila’s legislation. They belong to the those who manufacture spools of fiber and the equipment that utilizes it, the contractors who install, maintain, and service the network, and the customer support staff that deal with customers on a daily basis.
One of the strengths providers like GreenLight and Fibrant bring to their respective communities is their networks are open to all-comers. Time Warner Cable, AT&T, and other phone companies can obtain access on both to serve their own customers — business and residential. The impetus for building these networks was to benefit everyone.
The only adversarial players here are cable and phone companies that want to own, manage, and control everything themselves. The companies that spent years telling communities they saw no need to enhance service now want to legislate away the chance for others to try.
“We have several Republicans who read Time Warner’s claims about this bill, then looked over the inadequate broadband landscape in their districts back home, and are coming to the conclusion this is one bad bill,” one pro-broadband lobbyist told us. “But this is still going to be a very hard fight unless ordinary consumers make their voices heard loud and clear.”
Fact Checking
 The most disturbing thing about the Post story is the complete lack of fact checking the industry’s arguments, most of which are simply flat out false. A few examples:
The most disturbing thing about the Post story is the complete lack of fact checking the industry’s arguments, most of which are simply flat out false. A few examples:
Melissa Buscher, Time Warner Cable’s vice president of communications for the Carolinas claimed the city of Wilson raised pole attachment fees by 300 percent after launching GreenLight, Wilson’s community-owned network. Buscher suggests that is an example of cross-subsidizing networks. In her mind, mean and nasty Wilson officials jacked up the fees just to put the cable company at a competitive disadvantage.
But the facts tell a different story.
Wilson’s pole attachment fee, unchanged since 1975 while other communities around the nation raised them year after year, was adjusted well before GreenLight opened its doors for business.
“Before 2007, Wilson’s pole fee had stayed the same since 1975,” city spokesman Brian Bowman said. “The attachment fee increase was not related to GreenLight. The old fee schedule was outdated.”
How much money are we talking about here? The old rate was $5 per pole annually. Today it’s $15 per pole per year. That means Time Warner will have to pay $246,000 a year instead of $82,000 in Wilson — petty cash to a multi-billion dollar cable company.
Time Warner itself provided data nearly five years ago in a Tennessee study on pole attachment fees that proves Wilson is hardly being arbitrary and capricious. The cable company was paying up to $13.64 per pole four years ago in North Carolina. The Tennessee Cable Telecommunications Association has been complaining as late as last year over average pole attachment rates of $14.86 per pole in that state, adjacent to North Carolina.
The irony of a cable company that has nearly tripled its basic cable rates over the same period of time complaining about rate increases is lost on them.
Buscher also claims their new competition in Wilson and Salisbury is run by the same city governments that regulate them:
“Cities have unfair advantages,” Buscher told the Post, noting when cities get into the broadband business, they become not only a regulator for incumbent providers, but also a competitor. “If municipalities want to get into a business already offered by the private sector, we welcome the competition, but we want to level the playing field.”
The only thing Time Warner wants to level is the competition from community networks that deliver better broadband service than they offer.
In reality, thanks to industry lobbying in the 1990s, the cable industry is almost completely deregulated. No local, state, or federal government regulates broadband — where it is offered, at what speeds and at what prices.
There is no conflict of interest on the regulatory front.
Time Warner Cable and the North Carolina Cable Telecommunications Association: Waltzing Partners in a Dance of Deception

'Those community networks are not playing fair. How can we possibly compete?'
The North Carolina Cable Telecommunications Association, which helps deliver a one-two punch for Big Cable’s agenda, delivered the next false claim:
“Fibrant and GreenLight have lower operating costs.”
In reality, Time Warner Cable’s enormous size and scope provides them with benefits and cost saving opportunities across their national footprint that neither community provider can match:
- Volume discounts for programming, equipment, and other infrastructure;
- The power of incumbency, which makes them the default choice for most customers who must be compelled to switch providers;
- Access to grants and agreements like “payments in lieu of taxes” to protect cable jobs. Time Warner hardly pays “rack rates” for taxes across its entire footprint;
- Time Warner’s construction costs were mostly incurred in the 1990s when cable systems were last rebuilt. Suddenlink Cable CEO Jerry Kent said it best: “I think one of the things people don’t realize [relates to] the question of capital intensity and having to keep spending to keep up with capacity,” Kent said. “Those days are basically over, and you are seeing significant free cash flow generated from the cable operators as our capital expenditures continue to come down.” That isn’t true for community networks just opening for business or still in the initial construction phase.
Frontier Communications, a private industry player, discovered all of the benefits in programming costs go to large players like Time Warner, Comcast, Verizon and AT&T when claiming they were forced to raise rates $30 a month because they could not get the same volume discounts big cable and phone companies receive.
Marcus Trathen, the lobbyist running the NCCTA, hopes his fear, uncertainty and doubt campaign will be proven correct with the passage of Avila’s bill. As law, it assures all of the competitive advantages go to the billion dollar incumbents, and any failures will be among the community providers that compete with them:
“Cities are particularly ill-suited to competition in a technology-based industry,” Trathen said in an e-mail to the Post. “Technology changes in an instant.”
Just not for Time Warner customers in Wilson and Salisbury. The genesis of these, and other, community-based networks come from provider intransigence to deliver the kind of broadband service consumers and businesses increasingly seek, at an affordable price.
Fibrant delivers 15/15Mbps service today in its standard broadband package. Time Warner Cable delivers 10/1Mbps service. When Fibrant and Greenlight were first proposed, Time Warner delivered even lower speeds.
The industry cannot have it both ways. On the one hand, they claim community broadband is an economic failure delivering redundant service and mis-managed by government officials who do not understand the business of broadband. On the other hand, these companies and their respective mouthpieces are literally spending tens of millions of dollars lobbying for legislation to keep these “failures” from ever getting off the ground.
As we’ve always said on Stop the Cap!, following the money always leads you to the truth.
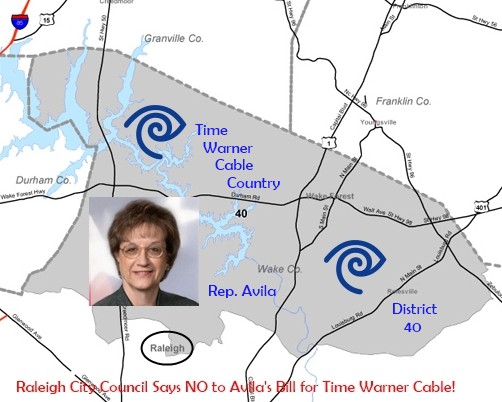 Rep. Marilyn Avila (R-Time Warner Cable) is getting significant blowback from some of her own constituents for introducing a bill that benefits a cable company, and almost nobody else.
Rep. Marilyn Avila (R-Time Warner Cable) is getting significant blowback from some of her own constituents for introducing a bill that benefits a cable company, and almost nobody else.

 Subscribe
Subscribe