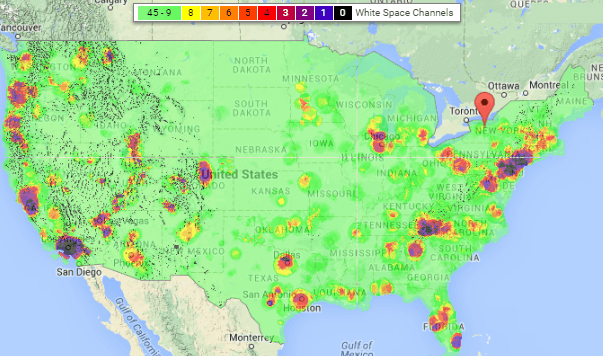
The national map of available white space channels show plenty are available in rural areas, but designing an urban network might prove challenging because open channels often just don’t exist. In a medium-sized city like Rochester, only 11 UHF channels are available, a number likely to dwindle to close to zero if the FCC successfully reallocates much of the UHF band to wireless providers like AT&T and Verizon.
A dozen homes in the middle of the Adirondacks now have access to Internet speeds far faster than what Verizon and Frontier DSL can deliver and without the usage caps or speed throttling common with satellite Internet access.
Thurman, N.Y.’s public-private “white space” wireless network survived months of political wrangling, debate, and even intentional signal interference created by someone intent on disrupting the project. For a community that some maps depict with zero residents, the 1,200 people of Thurman are now more known than ever, winning national attention for one of the first next generation rural wireless networks to use unused space on the UHF dial to provide Internet access.
A dozen homes are the first to receive the service, with nearly 80 more on the way during phase one of the project. A $200,000 New York state broadband grant helped get the project off the ground and defray the cost of equipment installed in each subscriber’s home. But the initial cost isn’t cheap, even with the grant. New customers pay an upfront equipment fee of $292 for a receiver that costs the project up to $600. The monthly service charge is $50. Despite the price, it’s worth it to a lot of subscribers.
“The white space service is truly amazing,” said John Schroeter of Kenyontown, noting he uses the Internet for genealogical research and relied on dial-up access for the last 15 years. “I can go from one web page to another without waiting forever.”
Schroeter told Denton Publications that web pages often failed to load with dial-up, even after hours of waiting. Now he can manage to complete days of research in about an hour, without having to drive 15 miles to the nearest Wi-Fi hotspot.
Despite the fact Verizon and Frontier Communications both run their own fiber cables on the same utility poles in the region, at least 75% of the 400 homes in Thurman have no access to broadband Internet, living out of reach of even basic DSL. Many end up in the parking lot of the town hall to use Wi-Fi. Others depend on prohibitively expensive satellite access. None of the existing options were ideal. Sheila Flanagan, proprietor of Nettle Meadow Farm complained it took her hours to prepare even a small number of shipping labels to send her cheese products across the country with UPS. Speeds were so slow, she was forced to drop Williams-Sonoma as a client.
 The concept of white space wireless Internet access has already taken hold in Europe but has dragged in the United States as existing UHF television stations, wireless carriers, wireless microphone manufacturers and others who use the same frequencies white space data services also depend on defend their turf. Since white space services are unlicensed and intended for two-way communications, fears that Internet users would degrade wireless microphones or TV reception meant special care had to be taken to lower the potential for interference.
The concept of white space wireless Internet access has already taken hold in Europe but has dragged in the United States as existing UHF television stations, wireless carriers, wireless microphone manufacturers and others who use the same frequencies white space data services also depend on defend their turf. Since white space services are unlicensed and intended for two-way communications, fears that Internet users would degrade wireless microphones or TV reception meant special care had to be taken to lower the potential for interference.
Since rural areas lack a crowded television dial, are often outside of the coverage areas of wireless carriers, and are unlikely to host many wireless mics, white space broadband would seem like the natural solution.
The project in Thurman faced a number of obstacles to overcome anyway. There were philosophical objections from tea party conservatives who objected to tax dollars paying for the “luxury” of Internet access when satellite service is available. Some residents wanted a fiber to the home solution, one that was likely financially out of reach for the small community. Still others wanted the money spent on a fiber link between the town and Time Warner Cable, that might then be enticed to wire homes in the rural community. In the end, the community decided to go ahead with an advanced wireless network, citing a number of factors familiar to many living in rural areas:
 Since the town is located entirely within the Adirondack Park, there are prohibitions on placing communications towers on nearby peaks or other high spots that could spoil the view;
Since the town is located entirely within the Adirondack Park, there are prohibitions on placing communications towers on nearby peaks or other high spots that could spoil the view;- The heavily forested and mountainous area made a traditional Wireless ISP project difficult because those networks need line of sight communications. White space wireless signals easily penetrate through trees and can stay intact across hilly terrain;
- Although not as bandwidth capable as fiber optics, white space networks are capable of delivering 10Mbps broadband per UHF channel. Most networks bond multiple UHF channels together to support even faster speeds and expand capacity;
- The chances of creating interference for other spectrum users was low in Thurman, which is a four-hour drive from New York and far enough north of Albany to avoid interfering with signals from the state capital. Even wireless carriers hug their cell towers along I-87, a respectable distance away;
- The network has redundant backhaul access to fiber from both Verizon and Frontier, neither of which show the slightest interest in expanding services into the community on their own;
- The grant was limited in scope and white space broadband qualified so it proved the most economical choice for a community that was no stranger to fights over money, engaging in political battles over issues like the cost of building a salt shed and auditing the on-hand count of trash bags.

The Thurman white space broadband project hides base station antennas in the tree canopy.
Tests provided the project managers with an idea where to place needed wireless antennas, often hidden within tree canopies. But at least one disgruntled resident made a point of creating intentional interference on the channels the project managers were testing, committing a federal offense along the way. That was quickly overcome and the equipment has been placed and will soon be joined by installations in nearby neighborhoods, broadening the reach of the service.
Recent advancements in white space technology have also allowed speed and capacity to improve dramatically. Equipment now transmits its exact GPS-identified location to a national database which sends back an authorized list of “white space” channels each transmitter can use to provide the service. If a new licensed broadcaster takes to the airwaves, a database update will lock out that channel in the area, preventing interference.
Although exact speed data was not available at press time, Sally Feihel demonstrated she could successfully stream an episode of a classic Andy Griffith Show on her iPod at the same time a videoconference was underway and someone else was downloading a movie, all without skipping a beat. In fact, there is so much speed and capacity built into the system, its managers say speed throttles and usage caps are completely unnecessary.
Most users agreed the wireless network far outpaced satellite and DSL and some believed it was even faster than Time Warner Cable Internet access they experienced elsewhere. (Time Warner Cable doesn’t come near the community today.)
Constructing the network only took several months, but the politics that often surrounds public-private initiatives and the need for grant funding in income-challenged rural America can tie up projects much longer than that. The need for decent and affordable Internet access often will cross party lines, especially in rural communities.
New York’s state broadband expansion fund could help expand similar projects to other bypassed areas of the state. That investment may actually save taxpayers from paying high broadband bills indefinitely.
Residents are eagerly waiting for the next expansion to begin down Valley, Garnet Lake and Glen-Athol Roads. Moving beyond that may take more grant funding.
“White space is saving us $90 per month, and it’s far faster than satellite ever was,” another resident said.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/MetroFocus A New way to Bring Broadband to Rural Towns in Upstate New York 2014.mp4[/flv]
MetroFocus showed the initial planning and testing phases of Thurman’s new white space wireless network, including interviews with town officials and a tour of the community. (4:23)
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Dynamic Spectrum in Action How TV White Space Devices Work.mp4[/flv]
TV white space wireless broadband networks are designed to avoid interference with other licensed spectrum users. See how the technology works in this short video. (2:27)


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 Alaska’s largest cable company today unveiled changes to its Internet plans, ditching surprise overlimit fees in favor of a speed throttle.
Alaska’s largest cable company today unveiled changes to its Internet plans, ditching surprise overlimit fees in favor of a speed throttle.

 In a major victory for net roots groups, President Barack Obama today announced his support for the strongest possible Net Neutrality protections, asking the Federal Communications Commission to quickly reclassify broadband as a “telecommunications service” subject to oversight and consumer protection regulatory policies that would prohibit paid fast lanes, the blocking or degrading of websites for financial reasons, and more transparency in how Internet Service Providers handle traffic.
In a major victory for net roots groups, President Barack Obama today announced his support for the strongest possible Net Neutrality protections, asking the Federal Communications Commission to quickly reclassify broadband as a “telecommunications service” subject to oversight and consumer protection regulatory policies that would prohibit paid fast lanes, the blocking or degrading of websites for financial reasons, and more transparency in how Internet Service Providers handle traffic. No blocking. If a consumer requests access to a website or service, and the content is legal, your ISP should not be permitted to block it. That way, every player — not just those commercially affiliated with an ISP — gets a fair shot at your business;
No blocking. If a consumer requests access to a website or service, and the content is legal, your ISP should not be permitted to block it. That way, every player — not just those commercially affiliated with an ISP — gets a fair shot at your business;
 The Federal Trade Commission today filed a lawsuit against AT&T for its practice of subjecting grandfathered unlimited data customers to speed throttles that dramatically cut speeds up to 90 percent after customers use more than 3GB of data on AT&T’s 3G network or 5GB on its 4G network. Thus far, according to the FTC, AT&T has throttled at least 3.5 million unique customers a total of more than 25 million times.
The Federal Trade Commission today filed a lawsuit against AT&T for its practice of subjecting grandfathered unlimited data customers to speed throttles that dramatically cut speeds up to 90 percent after customers use more than 3GB of data on AT&T’s 3G network or 5GB on its 4G network. Thus far, according to the FTC, AT&T has throttled at least 3.5 million unique customers a total of more than 25 million times.