Apple is set to announce a new iPhone or two early this afternoon, but some in the tech media notice the frenetic excitement of the newest Apple sensation has been tempered, in part because many of the new software and cloud storage features will run into usage caps for some, speed throttles for everyone else.
The imminent arrival of anticipated models iPhone 4S, expected to sell at AT&T and Verizon and iPhone 5, which is rumored to be sold exclusively by Sprint during a short sales window, remains a big deal for all three carriers. Verizon is reportedly allowing its call center employees to take unlimited overtime in preparation for the anticipated rush of questions and orders. Sprint, which has 33 million customers on two-year contracts, has made a commitment to sell at least 30.5 million Apple iPhones over four years, if reports by the Wall Street Journal turn out to be accurate. That’s a lot of phones.
[flv width=”512″ height=”308″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Sprint Getting iPhone 10-3-11.flv[/flv]

9 to 5 Mac shows off a mock image of what the newest iPhone 5 will probably look like. Pay close attention to the rounded edges and bezel.
Reports from the Wall Street Journal, WDAF-TV in Sprint’s home base of Kansas City, and Bloomberg News discuss the implications of Sprint’s deal with Apple. (11 minutes)
That’s also an enormous gamble for Sprint, which is guaranteed no real profits from the venture until the year 2014. If the company does win temporary exclusivity of an iPhone model that includes support for Sprint’s 4G network, WiMax, it will also bring the company an enormous number of new customers.
Among the most important new features of the phone is iOS 5, the latest version of Apple’s mobile operating system. It comes loaded with new ways to burn through the stingy usage caps AT&T and Verizon Wireless are now providing their customers:
- Over the air upgrades/activations: Apple’s notoriously huge software updates can be delivered to your wireless device without syncing it on a personal computer. That means downloading software updates that can easily exceed the 200MB “light usage” plans some carriers sell budget-conscious customers;
- Notification Center: Puts messages from e-mail, texts, and apps in a more convenient place to access and respond, increasing usage;
- NewsStand: Leverages newspaper and magazine content in a single app, downloading content pushed to your phone, increasing usage;
- Safari Sync: The Safari web browser will now sync with other instances of the browser on other devices to keep your reading list updated;
- iMessage: Send texts, photos, and bandwidth-hogging video to friends and family, potentially driving up usage considerably;
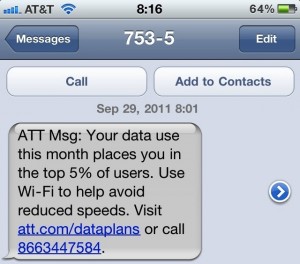
But nothing is expected to spike wireless data usage like Apple’s new iCloud and iTunes Match, both of which manage and sync multimedia content and app purchases between devices “over the cloud.” Unfortunately, repeated journeys of this type will burn through your usage allowance, and those with significant-sized libraries of photos, music, or videos are at serious risk of blasting past their usage cap. Even customers who use more than 4-5GB on “unlimited data plans” sold by AT&T and Verizon will face the scourge of the speed throttle, which will reduce your zippy new phone to speeds that resemble dial-up.
AT&T and Verizon Apple iPhone customers are at the highest risk of facing the speed throttle, because Apple is not expected to support either company’s 4G data network. Verizon only exempts 4G customers from the speed throttle when they use the 4G network.
The one company well-positioned to capitalize on these realities happens to be Sprint, which is keeping its truly unlimited data plan. If Apple comes through with 4G support for Sprint, customers could not only say goodbye to AT&T and Verizon’s slower 3G speeds, they would also be able to rest easy knowing they won’t experience bill shock or a month in the dial-up speed penalty corner if deemed to be using “too much” service.
Customers of the two biggest carriers need to get familiar with switching to Wi-Fi as often as possible, and avoid using data-intensive features on usage-limited plans. For Verizon and AT&T, it’s the best of all worlds — another two year contract for a usage-limited data plan that guarantees increased revenue and reduced costs. For you, it’s an improved phone you can never use to its full potential.
[flv width=”512″ height=”308″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Little Buzz Over New iPhone 10-4-11.flv[/flv]
The Wall Street Journal reports there isn’t as much buzz over this year’s newest iPhone. Bloomberg talks about the software changes in the new phone, and WWLP-TV in Springfield notes Verizon’s unions are calling on Americans to boycott the new phone until Verizon workers get a fair contract. (8 minutes)
Update 2:00pm ET: The Wall Street Journal reports the Sprint iPhone will not support their 4G network: According to people familiar with the company’s plans, the hotly anticipated device won’t operate on long-term evolution or WiMAX fourth-generation networks. Those wireless networks promise speedier downloading to mobile devices of episodes of television programs, as well as cute baby photos. The people said the device will work on 3G networks, which are broadly in use today and are the standard for the current iPhone 4. AT&T says its HSPA+ network has 4G-like speeds.
Update 4:00pm ET: The announcement event finally concludes with news the iPhone 5 is vaporware for now. Sprint will end up with the same Apple 4S phone AT&T and Verizon will sell on their respective networks. The San Jose Mercury News was not thrilled with the event:
At a rollout that lacked some of the thrills and surprises of past product releases — and disappointed some in attendance who expected a completely made-over iPhone 5 — Siri stood out as the sexiest new feature on an iPhone that, contrary to speculation, isn’t any thinner or different looking on the outside than its predecessor, the iPhone 4.
“This phone is better than the iPhone 4 in many ways, even though it looks the same,” said Avi Greengart, an analyst with Current Analysis on hand for the unveiling before several hundred reporters, bloggers, analysts and other guests. “Sales will be wildly successful, but Apple fanboys’ expectations probably were not met today.”
The new phone, which will be available Oct. 15 after pre-orders begin Oct. 7, will cost $199 for a 16-gigabyte version, $299 for 32GB and $399 for 64 GB. It had been center-stage in the tech blogosphere for months, as pundits weighed in with what they saw as the most obvious bells and whistles Apple would unleash on their growing fan base. Tuesday, some were surprised by how wrong that had been.
The phone that everyone thought would be thinner than the iPhone 4, pretty much resembled its older sibling. But as analysts had suspected, the new phone is much faster, thanks for the new A5 chip inside it, and it has plenty of consumer-pleasing attributes, most of them inside the case.


 Subscribe
Subscribe