America’s broadband ranking has fallen once again, mostly at the expense of other countries who have accelerated service and speed upgrades above and beyond what is available in the United States. That is the conclusion one can reach after reviewing the Federal Communications Commission’s second annual broadband report, delivered to Congress to fulfill obligations under the Broadband Data Improvement Act.
Through a combination of data from OECD broadband rankings and actual speed test results collected by the Commission, the FCC report notes American cities are at risk of losing the broadband speed race.
“This report compares data on average actual download speeds reported by a sample of consumers in a number of U.S. and foreign cities and finds that some large European and Asian cities exhibit a significant edge over comparable U.S. cities in reported download speeds, though reported speeds for some other international cities are roughly comparable to speeds in many U.S. cities,” the report concludes.
“The best currently available data set comparing the United States to other countries appears to be from the OECD, which collects data on various broadband deployment, adoption, and usage metrics and publishes rankings of its member countries. The OECD’s deployment data ranks countries based on particular technologies, rather than overall coverage. The U.S. ranking in these surveys ranges from 27th out of 30 in DSL coverage to 1st out of 28 in cable modem coverage. The U.S. ranks 6th out of 16 in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) coverage and 8th out of 29 in 3G mobile wireless coverage.”
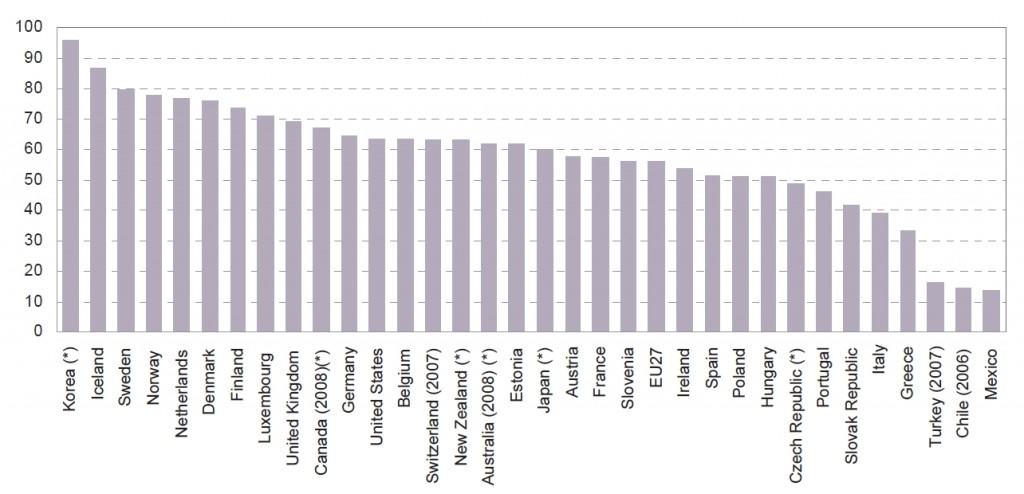
Broadband Rankings (click to enlarge)
Most of the countries accelerating far beyond the United States in broadband speed and quality are in Asia and Europe, and many are upgrading their networks to fiber-based broadband. As these fiber networks come online, the United States can be expected to fall further behind.

The cable industry lobby attacked the report's findings.
Just like last year, the Internet Service Providers turning in poor grades are rejecting the report’s conclusions.
“While the Commission’s headline proclaims that 20 million Americans are denied access to broadband, by that measure private investment has fueled the build-out of broadband networks to nearly 300 million consumers and is responsible for the jobs that flow from that investment,” said Michael Powell, president and chief executive of the National Cable and Telecommunications Association. Powell used to oversee the FCC as chairman during the first term of the Bush Administration.
Another trade association with ties to the telecom industry, USTelecom, attacked the findings noting most Americans think their existing broadband service is good enough.
Walter McCormick Jr., USTelecom CEO, noted the FCC’s own report found that 95 percent of Americans have access to fixed broadband and 93 percent are happy with their service.

...so did USTelecom, another industry funded group
But McCormick says nothing about the speeds those customers receive, a bone of contention with the Commission. As part of this year’s report, the FCC is increasingly relying on its own verifiable data about broadband speeds, collected through its SamKnows broadband speed test project. The Commission has repeatedly noted that broadband speeds marketed by ISPs do not always match the actual speeds customers receive.
Speed tests comparing broadband performance in comparably sized cities found some sizable differences.
The data suggest that mean actual download speeds in some European and Asian cities are substantially higher than in comparably sized U.S. cities (e.g., 24.8 megabits per second (Mbps) in Paris and 35.8 Mbps in Seoul versus 6.9 Mbps in San Francisco, 9.4 Mbps in Chicago, and 9.9 Mbps in Phoenix). Some of the U.S. cities in our sample have higher speeds than some foreign cities (e.g., Chicago with 9.39 Mbps versus Rome with 5.6 Mbps).
The most significant reason for the disparity in speed is the technology used in each respective area. Fiber to the home service traditionally delivers the fastest broadband speeds. Cable broadband technology, common in the United States but less so abroad, is responsible for a great deal of speed increases in the United States. Telephone company DSL and wireless are responsible for some of the slowest speeds, with rural DSL service commonly providing just 1-3Mbps service. Many European cities still relying on DSL technology have upgraded to bonded DSL, ADSL2+, or VDSL service, which can significantly boost speeds.
Unfortunately, the report concludes, the faster the broadband service delivered, the higher the price — often out of proportion with other OECD countries.
Results […] suggest that U.S. stand-alone residential broadband prices are generally “in the middle of prices in OECD countries,” after accounting for speed, terms of service, data caps, and service delivery technology. Similarly, prices in the United States for business stand-alone broadband services were fourteenth out of 30 among the OECD countries. A paper by the Berkman Center for Internet and Society at Harvard University found prices for U.S. broadband with download speeds of around 768 kbps to be “very good” by international standards. However, as download speeds increase, the paper found that U.S. prices become more expensive than most other OECD countries.
Some providers unimpressed by the independent research accused the FCC of using biased and inconsistent research methods. AT&T, for example, was unhappy with comparisons among U.S. cities and those of comparable size abroad. They accused the Commission of not using “a well-defined or consistent methodology for choosing the ‘communities’ or offers.” In fact, several providers suggested the Commission’s pricing comparisons ignored significant, albeit temporary, discounts some new customers receive, as well as discounts for bundled service packages. Promotional pricing factors are acknowledged by the Commission, but the report notes the findings do attempt to collect real world pricing paid by actual customers.
For consumers in the United States, broadband envy is as close as the next news report highlighting broadband expansion efforts abroad. Some countries are deploying 1Gbps broadband networks that deliver consistently faster speeds than American providers, at dramatically lower prices and without a usage cap attached.
 As political pressure over Usage Based Billing continues to keep providers from gravitating towards more stringent Internet Overcharging schemes, western Canadians are enjoying significant victories as providers relax usage caps and increase speeds for broadband service.
As political pressure over Usage Based Billing continues to keep providers from gravitating towards more stringent Internet Overcharging schemes, western Canadians are enjoying significant victories as providers relax usage caps and increase speeds for broadband service.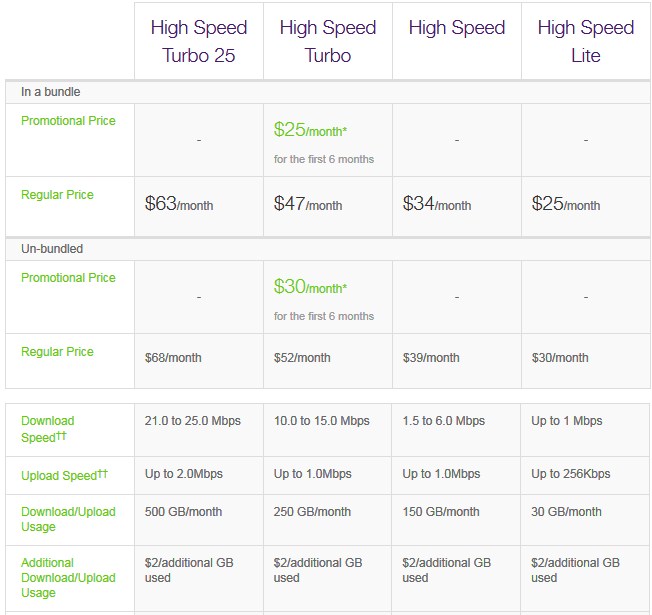


 Subscribe
Subscribe






