 The Federal Communications Commission is pushing hard to free up additional spectrum in some unlikely extremely high frequency ranges — some at 95 GHz or higher, for the next generation of wireless services.
The Federal Communications Commission is pushing hard to free up additional spectrum in some unlikely extremely high frequency ranges — some at 95 GHz or higher, for the next generation of wireless services.
Just a year ago in 2017, the FCC wrapped up its latest spectrum auction for the higher end of the UHF TV band, to be repurposed for mobile service use. But now the agency is seeking to find and reassign underused spectrum in much higher frequency bands that could be used for services like 5G wireless, machine-to-machine communications, intelligent road and vehicle networks, and other uses yet to be invented or envisioned.
FCC Commissioner Jessica Rosenworcel made it clear that smart spectrum allocation was critical for next generation wireless services.
“The point is the list is long — and we are looking at midband and millimeter wave to power the 5G future,” Rosenworcel said. “The propagation challenges are real, but so is the potential for capacity with network densification. Of course, what we need to do next is get these airwaves to market and unconditionally hold an auction this year.”
The FCC is contemplating auctions covering these frequencies in 2018:
3.5 GHz
Widely expected to draw the most interest, the Citizens Broadband Radio Service band was originally intended primarily for unlicensed users, but the wireless industry has lobbied heavily to get much of this spectrum reassigned for traditional long-term licensed use. Although very high frequency, the 3550-3700 MHz “innovation band” will have plenty of wide range of frequencies open for wireless data and mobile services. The wireless industry wants to deploy LTE service on this band, but they will likely compete with cable operators that are seeking their own stake of frequencies to launch their own wireless services.
This band will likely support last mile wireless connections at gigabit speed, fixed wireless broadband, and even in-home Wi-Fi that is significantly better than what you have now.
Because the band is so attractive, several different users are competing over who will be portioned what spectrum. The cable and phone companies want more for themselves, but other users, including consumers, want to reserve enough spectrum for unlicensed applications. The concern is deep pocketed companies may crowd out innovators and start-ups.
3.7 to 4.2 GHz
Some consumers may have accessed services on these frequencies without ever realizing it. This is the home of the “C-Band,” recognizable to any home satellite dishowner of the 1980s and 1990s. This range of frequencies is set aside for line-of-sight, very low powered satellite television — the kind that used to require a 10-12 foot wide satellite dish in the backyard to receive. FCC Chairman Ajit Pai wants to open the band up to be shared with 5G wireless broadband, which has caused considerable controversy among satellite users who fear devastating interference.
 There are proposals and counter proposals from the satellite industry and wireless companies over how to manage sharing this band. Most are coalescing around the idea of sequestering 100 MHz of spectrum at the low-end of the band and using 3700-3800 MHz for high-speed wireless broadband. Some want satellite operators to clear out of this section of frequencies voluntarily, others propose compensation similar to what was given to television stations to relocate their channel positions. Google is pushing for a plan that would offer mobile 5G service in large urban areas and 25 Mbps – 1 Gbps fixed wireless broadband in rural and residential areas.
There are proposals and counter proposals from the satellite industry and wireless companies over how to manage sharing this band. Most are coalescing around the idea of sequestering 100 MHz of spectrum at the low-end of the band and using 3700-3800 MHz for high-speed wireless broadband. Some want satellite operators to clear out of this section of frequencies voluntarily, others propose compensation similar to what was given to television stations to relocate their channel positions. Google is pushing for a plan that would offer mobile 5G service in large urban areas and 25 Mbps – 1 Gbps fixed wireless broadband in rural and residential areas.
But satellite companies and many satellite users are fearful of the impact of interference. Because satellite signals use very low power transponders on the satellite, ground based wireless broadband interference could wipe out satellite reception.
Tom Taggart, who owns several radio stations in West Virginia, says sharing spectrum was tried before and did not work well.
“This band, years ago, was shared with AT&T and other telcos for point-to-point long-distance links. Fixed, licensed paths that could be plotted and protected against for satellite installations,” Taggart told Radio World. “Our studios are 1,500 feet from an old MCI tower, at one time we had a metal screen behind our satellite dish to protect against ‘back-scatter’ from a path aimed away from us. Still, we had to convince MCI to shut down one channel so we could pick up a program from Premiere [a radio network distributing programming on satellite].”
Some industry plans propose registering C-Band satellite dishes, at a cost of $600-$1,600 per site, which would allegedly protect them from interference by requiring wireless broadband services to steer clear of the area.
“But I am not even sure what kind of broadband services are proposed,” Taggart said. “One might assume these would be omnidirectional sites, like a typical cell site. Even with some clever computer-engineered directional patterns, reflections off hillsides, billboards, buildings would be enough to overwhelm the tiny satellite signal. However, other articles described these services as ‘mobile.’ Even if my dish is registered, how can I resolve interference problems from a mobile device?”
The debate rages on because the frequencies involved, next to the even more popular CBRS band, are highly coveted.
4.9 GHz
After the events of 9/11 in 2001, the FCC has prioritized public safety communications, in hopes of improving the interoperability of different first responders’ portable radios. At that time, fire agencies could not easily talk to police, ambulance crews, or in some cases other fire crews arriving from different departments miles away.
 Many agencies contemplating use of this band discovered equipment that supported 4.9 GHz was hard to find and extremely expensive. Most public safety agencies seeking grants or other funding to improve their communications equipment opted to transition to digital P25 networks that operate on much lower frequencies and use equipment that is now widely available and, in comparison, much cheaper. Many agencies are conservative about using new technology as well, concerned a communications failure could cost the life of a fire or police responder. As a result, of the 90,000 organizations certified for licenses in this band, only 3,174 have been granted. That represents a take rate of just 3.5%. The band, as one might expect, is effectively dead in most areas, underutilized in others.
Many agencies contemplating use of this band discovered equipment that supported 4.9 GHz was hard to find and extremely expensive. Most public safety agencies seeking grants or other funding to improve their communications equipment opted to transition to digital P25 networks that operate on much lower frequencies and use equipment that is now widely available and, in comparison, much cheaper. Many agencies are conservative about using new technology as well, concerned a communications failure could cost the life of a fire or police responder. As a result, of the 90,000 organizations certified for licenses in this band, only 3,174 have been granted. That represents a take rate of just 3.5%. The band, as one might expect, is effectively dead in most areas, underutilized in others.
“As the demand for wireless services continues to grow, it is imperative that the FCC takes steps to ensure underutilized spectrum bands are used efficiently,” said FCC Commissioner Mignon Clyburn. “This is as true for spectrum allocated to public safety as it is for the bands used to support commercial wireless broadband services.”
FCC Commissioner Michael O’Rielly is convinced wireless companies like AT&T and Verizon could use the frequencies more efficiently.
“It has been 16 years since the 4.9 GHz band was allocated to the public safety community, and it is still woefully underutilized,” said O’Rielly. “That is not sustainable in an environment in which every megahertz of spectrum, especially below 6 GHz, needs to be fully scrutinized and maximized in quick order. While the Commission’s original allocation was more than likely well-intentioned, it is way past time to take a fresh look at this 50 megahertz of spectrum.”
Although higher than 3.5 GHz, engineers believe there is a very credible case to be made to use the available spectrum for 5G fixed wireless services, delivering broadband at speeds up to 1 GHz from a small cell located nearby. It would have to be. At these frequencies, virtually anything blocking the line-of-sight between the antenna and the user will block the signal as well. With almost no constituency defending the 4.9 GHz turf, it is expected it will be repurposed for wireless broadband in areas where it isn’t in use for public safety communications.
24/28 GHz
 Although the 28 GHz band has many licensed users already, the 24 GHz band does not, and the wireless industry is interested in grabbing vast swaths of spectrum in this band for 5G home broadband. Known as “millimeter wave spectrum,” these two bands are expected to be a big part of the 5G fixed wireless services being planned by some carriers. Verizon acquired Straight Path late in 2017, which had collected a large number of licenses for this frequency range. Today, Verizon holds almost 30% of all currently licensed millimeter wave spectrum, an untenable situation if you are AT&T, T-Mobile, or Sprint. T-Mobile has been the most aggressive seeking more spectrum to compete with Verizon in this frequency range, and has purchased almost 1,150 MHz covering Ohio for use with a 5G project the company is working on.
Although the 28 GHz band has many licensed users already, the 24 GHz band does not, and the wireless industry is interested in grabbing vast swaths of spectrum in this band for 5G home broadband. Known as “millimeter wave spectrum,” these two bands are expected to be a big part of the 5G fixed wireless services being planned by some carriers. Verizon acquired Straight Path late in 2017, which had collected a large number of licenses for this frequency range. Today, Verizon holds almost 30% of all currently licensed millimeter wave spectrum, an untenable situation if you are AT&T, T-Mobile, or Sprint. T-Mobile has been the most aggressive seeking more spectrum to compete with Verizon in this frequency range, and has purchased almost 1,150 MHz covering Ohio for use with a 5G project the company is working on.
39 GHz

FiberTower, now owned by AT&T
This band might as well be called “the controversial band” because AT&T made moves on these frequencies even before the FCC got around to discussing an auction for this band, likely also to be used for 5G fixed wireless. FiberTower originally held hundreds of licenses for wireless spectrum for several years, but did little with them, leading to suggestions the company was either hoarding the spectrum to resell to someone else or was incapable of deploying a network that used the frequencies. The company declared bankruptcy in 2012, eventually emerging in the spring of 2014 just in time to watch the FCC uphold the decision of its Telecommunications Bureau to cancel 689 of FiberTower’s licenses for failure to use them.
In February 2018, AT&T completed its acquisition of FiberTower for $207 million. According to AllNet Insights & Analytics, AT&T acquired more than 475 of FiberTower’s 39 GHz spectrum licenses, raising eyebrows among shareholders who lost their investments in FiberTower after it declared bankruptcy. Hundreds of the spectrum licenses that came with the AT&T deal were given a value of $0.00, allowing AT&T a sweetheart deal and shareholders hoping to recover more money from the bankruptcy liquidation extremely upset. In fact, had FiberTower remained in bankruptcy, it would eventually have surrendered all of its licenses, which would then be put up for auction by the FCC and would likely command much higher value among bidders. Verizon effectively paid triple the price for what AT&T got for a song in the FiberTower acquisition. Even more remarkable, the FCC approved the acquisition by AT&T despite the obvious fire sale price, and has ignored the consequences of what could come from an AT&T/Verizon duopoly across large swaths of 5G frequencies.

Eshoo
That brought a rebuke from Rep. Anna Eshoo (D-Calif.) who accused both Verizon and AT&T of flipping public property for private gain.
“The FCC’s policies unambiguously required Straight Path and FiberTower to forfeit their unbuilt spectrum licenses,” Eshoo wrote. “But rather than auction the reclaimed spectrum and promote timely deployment, the FCC’s Wireless Telecommunications Bureau reached ‘resolutions’ with Straight Path and FiberTower than allowed them to profit handsomely from their wrongdoing. Following the ‘resolution,’ Straight Path sold its assets to Verizon for nearly $3.1 billion, and FiberTower is estimated to have sold its assets to AT&T for roughly $2 billion.”
In reality, AT&T acquired FiberTower for $207 million — a fraction of the amount of the estimated value of the spectrum Eshoo used in her estimate.
“The Bureau’s decisions also further concentrated critical input resources in the hands of the two dominant wireless incumbents,” Eshoo continued. “The purchasers of the public assets that Straight Path and FiberTower once held, Verizon and AT&T, already control a disproportionate amount of other critical spectrum available for immediate deployment. Up until recently, the industry had an imbalance in favor of these companies in low-band spectrum that lasted for decades. The FCC now risks going down the same wrong path with high-band spectrum should the Commission continue down this course. Allowing Straight Path and FiberTower to ‘flip’ public assets for private gain does nothing for taxpayers, but does much to further entrench the dominant incumbents’ longstanding spectrum advantage over their rivals.”
95+ GHz
The FCC has not regulated frequencies above 95 GHz, but as technology advances, there is growing interest in utilizing spectrum that many believed would be essentially unusable for communications services. Right now, most frequencies in this range are used by environmental satellites and radio astronomy. At these frequencies, signals would be absorbed by the skin and attenuated significantly by things like high humidity’s haze or fog. Still, there are proposals under consideration to open up a small portion of spectrum for unlicensed home users for things like indoor wireless routers.
The key policy priority here will be to protect existing users from any hint of interference. But with vast amounts of unused frequencies in this range, it shouldn’t be difficult to keep competing users apart.
 Starry, Inc., a fixed wireless internet provider, this week announced it has won 104 licenses in the FCC’s recent spectrum auction, allowing the company to launch service to over 40 million people in 25 states, potentially covering more than 25% of all U.S. households.
Starry, Inc., a fixed wireless internet provider, this week announced it has won 104 licenses in the FCC’s recent spectrum auction, allowing the company to launch service to over 40 million people in 25 states, potentially covering more than 25% of all U.S. households.

 Subscribe
Subscribe Forty companies, including hedge funds, phone companies, and wireless carriers have collectively bid $336,265,480 so far for about 2,500 28 GHz licenses (out of 3,072 available) that will be a part of the buildout of 5G millimeter wave wireless service.
Forty companies, including hedge funds, phone companies, and wireless carriers have collectively bid $336,265,480 so far for about 2,500 28 GHz licenses (out of 3,072 available) that will be a part of the buildout of 5G millimeter wave wireless service. California: Kern
California: Kern The Federal Communications Commission is pushing hard to free up additional spectrum in some unlikely extremely high frequency ranges — some at 95 GHz or higher, for the next generation of wireless services.
The Federal Communications Commission is pushing hard to free up additional spectrum in some unlikely extremely high frequency ranges — some at 95 GHz or higher, for the next generation of wireless services. There are proposals and counter proposals from the satellite industry and wireless companies over how to manage sharing this band. Most are coalescing around the idea of sequestering 100 MHz of spectrum at the low-end of the band and using 3700-3800 MHz for high-speed wireless broadband. Some want satellite operators to clear out of this section of frequencies voluntarily, others propose compensation similar to what was given to television stations to relocate their channel positions. Google is pushing for a plan that would offer mobile 5G service in large urban areas and 25 Mbps – 1 Gbps fixed wireless broadband in rural and residential areas.
There are proposals and counter proposals from the satellite industry and wireless companies over how to manage sharing this band. Most are coalescing around the idea of sequestering 100 MHz of spectrum at the low-end of the band and using 3700-3800 MHz for high-speed wireless broadband. Some want satellite operators to clear out of this section of frequencies voluntarily, others propose compensation similar to what was given to television stations to relocate their channel positions. Google is pushing for a plan that would offer mobile 5G service in large urban areas and 25 Mbps – 1 Gbps fixed wireless broadband in rural and residential areas. Many agencies contemplating use of this band discovered equipment that supported 4.9 GHz was hard to find and extremely expensive. Most public safety agencies seeking grants or other funding to improve their communications equipment opted to transition to digital P25 networks that operate on much lower frequencies and use equipment that is now widely available and, in comparison, much cheaper. Many agencies are conservative about using new technology as well, concerned a communications failure could cost the life of a fire or police responder. As a result, of the 90,000 organizations certified for licenses in this band, only 3,174 have been granted. That represents a take rate of just 3.5%. The band, as one might expect, is effectively dead in most areas, underutilized in others.
Many agencies contemplating use of this band discovered equipment that supported 4.9 GHz was hard to find and extremely expensive. Most public safety agencies seeking grants or other funding to improve their communications equipment opted to transition to digital P25 networks that operate on much lower frequencies and use equipment that is now widely available and, in comparison, much cheaper. Many agencies are conservative about using new technology as well, concerned a communications failure could cost the life of a fire or police responder. As a result, of the 90,000 organizations certified for licenses in this band, only 3,174 have been granted. That represents a take rate of just 3.5%. The band, as one might expect, is effectively dead in most areas, underutilized in others. Although the 28 GHz band has many licensed users already, the 24 GHz band does not, and the wireless industry is interested in grabbing vast swaths of spectrum in this band for 5G home broadband. Known as “millimeter wave spectrum,” these two bands are expected to be a big part of the 5G fixed wireless services being planned by some carriers. Verizon acquired Straight Path late in 2017, which had collected a large number of licenses for this frequency range. Today, Verizon holds almost 30% of all currently licensed millimeter wave spectrum, an untenable situation if you are AT&T, T-Mobile, or Sprint. T-Mobile has been the most aggressive seeking more spectrum to compete with Verizon in this frequency range, and has purchased almost 1,150 MHz covering Ohio for use with a 5G project the company is working on.
Although the 28 GHz band has many licensed users already, the 24 GHz band does not, and the wireless industry is interested in grabbing vast swaths of spectrum in this band for 5G home broadband. Known as “millimeter wave spectrum,” these two bands are expected to be a big part of the 5G fixed wireless services being planned by some carriers. Verizon acquired Straight Path late in 2017, which had collected a large number of licenses for this frequency range. Today, Verizon holds almost 30% of all currently licensed millimeter wave spectrum, an untenable situation if you are AT&T, T-Mobile, or Sprint. T-Mobile has been the most aggressive seeking more spectrum to compete with Verizon in this frequency range, and has purchased almost 1,150 MHz covering Ohio for use with a 5G project the company is working on.

 Cincinnati Bell
Cincinnati Bell 
 “Our business has been in decline for five or six years,” Torbeck
“Our business has been in decline for five or six years,” Torbeck  Last year, Cincinnati Bell had passed 184,000 homes with fiber optics – a 28 percent market share. But only 52,000 homes subscribed to Fioptics — Cincinnati Bell’s fiber brand. Time Warner Cable had managed to keep many of its wavering 446,000 customers loyal to the cable company with aggressive discounting and customer retention offers. But now that many of those discounts have since expired, Torbeck wants to reach 650,000-700,000 homes in its service area covering southwestern Ohio and northern Kentucky and convince 50% of those customers to switch to fiber optics.
Last year, Cincinnati Bell had passed 184,000 homes with fiber optics – a 28 percent market share. But only 52,000 homes subscribed to Fioptics — Cincinnati Bell’s fiber brand. Time Warner Cable had managed to keep many of its wavering 446,000 customers loyal to the cable company with aggressive discounting and customer retention offers. But now that many of those discounts have since expired, Torbeck wants to reach 650,000-700,000 homes in its service area covering southwestern Ohio and northern Kentucky and convince 50% of those customers to switch to fiber optics. The company’s unique position as the last remaining independent phone company that still bears the name of the telephone’s inventor may make the company a target for a takeover before Torbeck’s vision is realized. One analyst thinks Cincinnati Bell would be a natural target for Google, which has a recent record of repurposing fiber networks built by other companies as a cost-saving measure to further deploy Google Fiber.
The company’s unique position as the last remaining independent phone company that still bears the name of the telephone’s inventor may make the company a target for a takeover before Torbeck’s vision is realized. One analyst thinks Cincinnati Bell would be a natural target for Google, which has a recent record of repurposing fiber networks built by other companies as a cost-saving measure to further deploy Google Fiber. Cincinnati Bell has already spent about $300 million on Fioptics and plans to spend an extra $80 million this year on expansion. Before the network is complete, the phone company is likely to spend as much as $600 million on fiber upgrades. But the payoff has been higher revenue — $100 million last year alone, and a stabilizing business model that has reduced losses from landline cord-cutting. Telecom analyst Nicholas Puncer offers support for the investment, something rare for most Wall Street advisers.
Cincinnati Bell has already spent about $300 million on Fioptics and plans to spend an extra $80 million this year on expansion. Before the network is complete, the phone company is likely to spend as much as $600 million on fiber upgrades. But the payoff has been higher revenue — $100 million last year alone, and a stabilizing business model that has reduced losses from landline cord-cutting. Telecom analyst Nicholas Puncer offers support for the investment, something rare for most Wall Street advisers.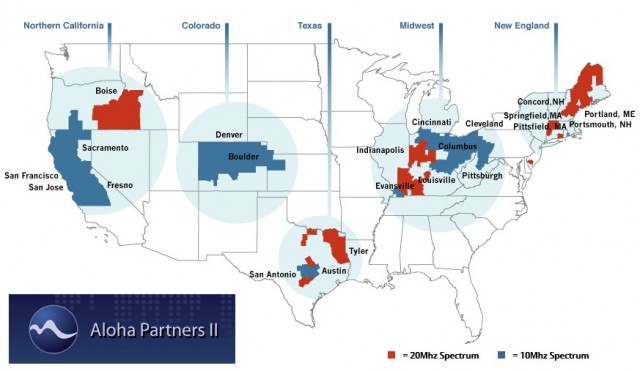
 Financial terms were not disclosed.
Financial terms were not disclosed.