Phillip "Break Free from 'What's In It For Me'-AT&T" Dampier
[We are reprinting this because it succinctly and persuasively proves a point we’ve been making at Stop the Cap! since 2008. Broadband is not just a “nice thing to have.” It is as important as a phone line, electricity, and safe drinking water. News, education, commerce, and culture increasingly utilize the Internet to share information and entertain us. Essential utility services can either be provided by a private company operating as a monopoly with oversight and regulation, or operate strictly in the public interest in the form of a customer-owned cooperative, a direct service of local government, or a quasi-public independent non-profit.
In North America, broadband was originally considered a non-essential service, and private providers in the United States lobbied heavily to maintain absolute control of their broadband networks, free to open them to share with other providers, or not. They also won sweeping deregulation and are still fighting today for decreased oversight. The results have been uneven service. Large, compact cities enjoy modern and fast broadband while smaller communities are forced to live with a fraction of the speeds offered elsewhere, if they have access to the service at all.
With broadband now deemed “essential,” local governments have increasingly sought to end the same old excuses with the “don’t care”-cable company or “what’s in it for me”-AT&T and provide 21st century service themselves, especially where local commercial providers simply won’t step up to the plate at all. Suddenly, big cable and phone companies are more possessive than your last boy/girlfriend. The companies that for years couldn’t care less about your broadband needs suddenly obsess when someone else moves in on “their territory.” They want special laws (that apply only to the competition) to make sure your broadband future lies exclusively in their hands.
Susan P. Crawford understand how this dysfunctional, controlling relationship comes at the expense of rural America. She’s a visiting professor at the Harvard Kennedy School of Government and Harvard Law School. In 2009, she was a special assistant to President Barack Obama for science, technology and innovation policy. Her opinions were originally shared with readers of Bloomberg News.]
In cities and towns across the U.S., a familiar story is replaying itself: Powerful companies are preventing local governments from providing an essential service to their citizens. More than 100 years ago, it was electricity. Today, it is the public provision of communications services.

Susan Crawford
The Georgia legislature is currently considering a bill that would effectively make it impossible for any city in the state to provide for high-speed Internet access networks — even in areas in which the private sector cannot or will not. Nebraska, North Carolina, Louisiana, Arkansas and Tennessee already have similar laws in place. South Carolina is considering one, as is Florida.
Mayors across the U.S. are desperate to attract good jobs and provide residents with educational opportunities, access to affordable health care, and other benefits that depend on affordable, fast connectivity — something that people in other industrialized countries take for granted. But powerful incumbent providers such as AT&T Inc. and Time Warner Cable Inc. are hamstringing municipalities.
At the beginning of the 20th century, private power companies electrified only the most lucrative population centers and ignored most of America, particularly rural America. By the mid-1920s, 15 holding companies controlled 85 percent of the nation’s electricity distribution, and the Federal Trade Commission found that the power trusts routinely gouged consumers.
Costly and Dangerous
In response, and recognizing that cheap, plentiful electricity was essential to economic development and quality of life, thousands of communities formed electric utilities of their own. Predictably, the private utilities claimed that public ownership of electrical utilities was “costly and dangerous” and “always a failure,” according to the November 1906 issue of Moody’s Magazine. Now more than 2,000 communities in the U.S., including Seattle, San Antonio and Los Angeles, provide their own electricity.
Today, the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, which advocates for community broadband initiatives, is tracking more than 60 municipal governments that have built or are building successful fiber networks, just as they created electric systems during the 20th century. In Chattanooga, Tennessee, for example, the city’s publicly owned electric company provides fast, affordable and reliable fiber Internet access. Some businesses based in Knoxville — 100 miles to the northeast — are adding jobs in Chattanooga, where connectivity can cost an eighth as much.
Meanwhile, less than 8 percent of Americans currently receive fiber service to their homes, compared with more than 50 percent of households in South Korea, and almost 40 percent in Japan. Where it’s available, Americans pay five or six times as much for their fiber access as people in other countries do. Fully a third of Americans don’t subscribe to high-speed Internet access at all, and AT&T Chief Executive Officer Randall Stephenson said last month that the company was “trying to find a broadband solution that was economically viable to get out to rural America, and we’re not finding one, to be quite candid.” America is rapidly losing the global race for high-speed connectivity.
Tamping Down Enthusiasm
We've done something like this once before.
Like the power trusts of the 20th century, the enormous consolidated providers of wired Internet access want to tamp down any enthusiasm for municipal networks. Last year, telecom lobbyists spent more than $300,000 in a failed effort to block a referendum in Longmont, Colorado, to allow that city to provide Internet access. Time Warner Cable managed to get a North Carolina law enacted last year that makes launching municipal networks there extraordinarily difficult. The pending measures in Georgia and South Carolina are modeled on the North Carolina bill.
The Georgia bill is chock-full of sand traps and areas of deep statutory fog from which no local public network is likely ever to emerge. In addition to the ordinary public hearings that any municipality would hold on the subject, a town looking to build a public network would have to hold a referendum. It wouldn’t be allowed to spend any money in support of its position (there would be no such prohibition on the deep-pocketed incumbents). The community wouldn’t be allowed to support its network with local taxes or surplus revenues from any other services (although incumbents routinely and massively subsidize their networks with revenue from other businesses).
Most pernicious of all, the public operator would have to include in the costs of its service the phantom, imputed “capital costs” and “taxes” of a private provider. This is a fertile area for disputes, litigation and delay, as no one knows what precise costs and taxes are at issue, much less how to calculate these amounts. The public provider would also have to comply with all laws and “requirements” applicable to “the communications service,” if it were made available by “a private provider,” although again the law doesn’t specify which service is involved or which provider is relevant.
The end result of all this vague language will be to make it all but impossible for a city to obtain financing to build its network. Although the proponents of Georgia’s bill claim that they are merely trying to create a level playing field, these are terms and conditions that no new entrant, public or private, can meet — and that the incumbents themselves do not live by. You can almost hear the drafters laughing about how impossible the entire enterprise will be.
Globally Competitive Networks
Right now, state legislatures — where the incumbents wield great power — are keeping towns and cities in the U.S. from making their own choices about their communications networks. Meanwhile, municipalities, cooperatives and small independent companies are practically the only entities building globally competitive networks these days. Both AT&T and Verizon have ceased the expansion of next-generation fiber installations across the U.S., and the cable companies’ services greatly favor downloads over uploads.
Congress needs to intervene. One way it could help is by preempting state laws that erect barriers to the ability of local jurisdictions to provide communications services to their citizens.
Running for president in 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt emphasized the right of communities to provide their own electricity. “I might call the right of the people to own and operate their own utility a birch rod in the cupboard,” he said, “to be taken out and used only when the child gets beyond the point where more scolding does any good.” It’s time to take out that birch rod.
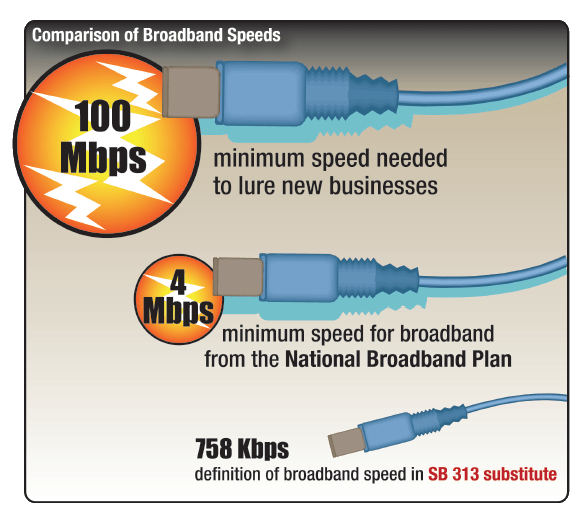 According to the National Broadband Map, Georgia ranks 20th in the nation for broadband access. According to the forward of a report by Rich Calhoun, Program Director of the Georgia Technology Initiative, “As I traveled through the state to talk with leaders in municipalities, counties and community anchor institutions, I found that many places throughout Georgia indicated that they did not have access to affordable or sufficient broadband services. Telecommunications firms who have made significant investments in Georgia indicated that in some areas of the state the return on investment would not qualify for further investment at the present time.”
According to the National Broadband Map, Georgia ranks 20th in the nation for broadband access. According to the forward of a report by Rich Calhoun, Program Director of the Georgia Technology Initiative, “As I traveled through the state to talk with leaders in municipalities, counties and community anchor institutions, I found that many places throughout Georgia indicated that they did not have access to affordable or sufficient broadband services. Telecommunications firms who have made significant investments in Georgia indicated that in some areas of the state the return on investment would not qualify for further investment at the present time.” We exposed the well-financed propaganda campaign that maligned some of Georgia’s past experiences with municipal broadband, many projects derailed not by government ‘failure’ but through political interference and the private sector. We showed readers how to follow the money to see the connection between campaign contributions and the sudden interest in effectively banning community broadband. We exposed the fact this is a coordinated, nationwide effort by a corporate backed lobbying group (ALEC) that pays to wine and dine lawmakers and then sell them on a catalog of bills ghost-written by some of the nation’s largest telecommunications companies. Legislation that hamstrings competition and protects monopoly profits, while always conveniently exempting incumbent providers from the terms of the bills they effectively wrote.
We exposed the well-financed propaganda campaign that maligned some of Georgia’s past experiences with municipal broadband, many projects derailed not by government ‘failure’ but through political interference and the private sector. We showed readers how to follow the money to see the connection between campaign contributions and the sudden interest in effectively banning community broadband. We exposed the fact this is a coordinated, nationwide effort by a corporate backed lobbying group (ALEC) that pays to wine and dine lawmakers and then sell them on a catalog of bills ghost-written by some of the nation’s largest telecommunications companies. Legislation that hamstrings competition and protects monopoly profits, while always conveniently exempting incumbent providers from the terms of the bills they effectively wrote.


 Subscribe
Subscribe