The Republican takeover of the North Carolina legislature in 2010 was great news for some of the state’s largest telecommunications companies, who successfully received almost universal support from those legislators to outlaw community broadband service in North Carolina — the 19th state to throw up impediments to a comfortable corporate broadband duopoly.
The Republican takeover of the North Carolina legislature in 2010 was great news for some of the state’s largest telecommunications companies, who successfully received almost universal support from those legislators to outlaw community broadband service in North Carolina — the 19th state to throw up impediments to a comfortable corporate broadband duopoly.
Dialing Up the Dollars — produced by the National Institute on Money in State Politics, found companies including AT&T, Time Warner Cable, CenturyLink, and the state cable lobby collectively spent more than $1.5 million over the past five years on campaign contributions. Most of the money went to legislators willing to enact legislation that would largely prohibit publicly-owned competitive broadband networks from operating in the state.
North Carolina consumer groups have fought anti-community broadband initiatives for the past several years, with most handily defeated in the legislature. But in 2010, Republicans assumed control of both the House and Senate for the first time since the late 1800s, and the change in party control made all the difference. Of 97 Republican lawmakers who voted, 95 supported HB 129, the corporate-written broadband competition ban introduced by Rep. Marilyn Avila, a legislator who spent so much time working with the cable lobby, we’ve routinely referred to her as “(R-Time Warner Cable).”
Democrats were mostly opposed to the measure: 45 against, 25 for. Stop the Cap! called out those lawmakers as well, many of whom received substantial industry money in the form of campaign donations.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Community Fiber Networks Are Faster Cheaper Than Incumbents.flv[/flv]
The Institute for Local Self-Reliance pondered broadband speeds and value in North Carolina and found commercial providers lacking. (3 minutes)
| Donor | 2006 | 2008 | 2010 | 2011 | 2006–2011 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT&T* | $191,105 | $159,783 | $149,550 | $20,000 | $520,438 |
| Time Warner Cable | $81,873 | $103,025 | $96,550 | $30,950 | $313,398 |
| CenturyLink** | $19,500 | $143,294 | $109,750 | $30,250 | $302,744 |
| NC Telephone Cooperative Coalition | $103,350 | $94,900 | $89,250 | $2,500 | $290,000 |
| Sprint Nextel | $67,250 | $17,500 | $12,250 | $3,250 | $100,250 |
| Verizon | $8,050 | $10,950 | $24,250 | $2,500 | $45,750 |
| NC Cable Telecommunications Association | $10,350 | $12,500 | $500 | $0 | $23,350 |
| Windstream Communications | $0 | $0 | $1,500 | $0 | $1,500 |
| TOTAL | $481,478 | $541,952 | $483,600 | $90,450 | $1,597,481 |
*AT&T’s total includes contributions from BellSouth in 2006 and 2008 and AT&T Mobility LLC. **CenturyLink’s total includes contributions from Embarq Corp.
According to Catharine Rice, president of the SouthEast Association of Telecommunications Officers and Advisors, HB 129 received the greatest lobbying support from Time Warner Cable, the state cable lobbying association — the North Carolina Cable and Telecommunications Association (NCCTA), and CenturyLink.
Following the bill’s passage, the NCCTA issued a press release stating, “We are grateful to the members of the General Assembly who stood up for good government by voting for this bill.”
CenturyLink sent e-mail to its employees suggesting they write thank you letters to supportive legislators:
“Thanks to the passage of House Bill 129, CenturyLink has gained added confidence to invest in North Carolina and grow our business in the state.”
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CenturyLink Frustration.flv[/flv]
A CenturyLink customer endures frustration from an infinite loop while calling customer service. Is this how the company will grow the business in North Carolina? (1 minute)
Consumers Pay the Price
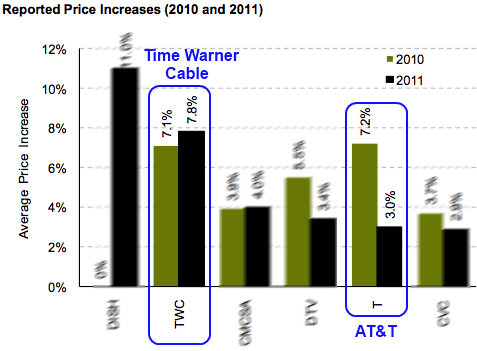
After the bill became law without the signature of Gov. Bev Purdue, Time Warner Cable increased cable rates across North Carolina. CenturyLink’s version of AT&T’s U-verse — Prism — has seen only incremental growth with around 70,000 customers nationwide. The phone company also announced an Internet Overcharging scheme — usage caps — on their broadband customers late last fall.
Someone had to pay for the enormous largesse of campaign cash headed into lawmaker pockets. For the state’s largest cable operator — Time Warner Cable — another rate increase handily covered the bill.
In all, lawmakers received thousands of dollars each from the state’s incumbent telecom companies:
- Lawmakers who voted in favor of HB 129 received, on average, $3,768, which is 76 percent more than the average $2,135 received by the those who voted against the bill;
- 78 Republican lawmakers received an average of $3,824, which is 36 percent more than the average $2,803 received by 53 Democrats;
- Those in key legislative leadership positions received, on average, $13,531, which is more than double the $2,753 average received by other lawmakers;
- The four primary sponsors of the bill received a total of $37,750, for an average of $9,438, which is more than double the $3,658 received on average by those who did not sponsor the bill.
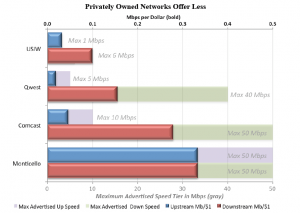
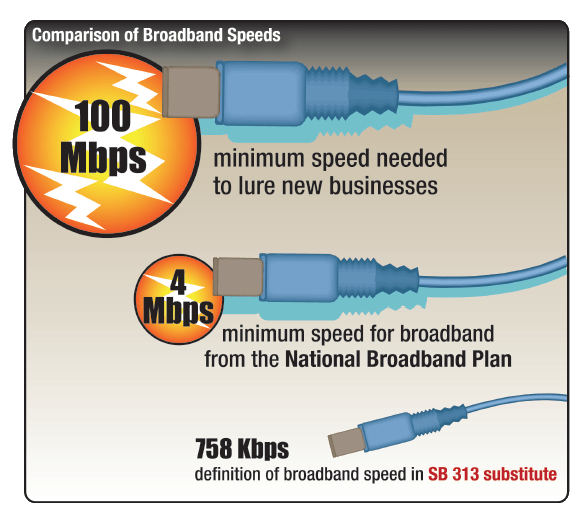
Even worse for rural North Carolina, little progress has been made by commercial providers to expand broadband in less populated areas of the state. AT&T earlier announced it was largely finished expanding its U-verse network and has stalled DSL deployment as it determines what to do with that part of its business.
In fact, the most aggressive broadband expansion has come from existing community providers North Carolina’s lawmakers voted to constrain. Salisbury’s Fibrant has opted for a slower growth strategy to meet the demand for its service and handle the expense associated with installing it. Wilson’s Greenlight fiber to the home network supplies 100/100Mbps speeds to those who want it today.
In Upside-Down World at the state capitol in Raleigh, community-owned providers are the problem, not today’s duopoly of phone and cable companies that deliver overpriced, comparatively slow broadband while ignoring rural areas of the state.
Key Players
Some of the key players that were “motivated” to support the cable and phone company agenda, according to the report:
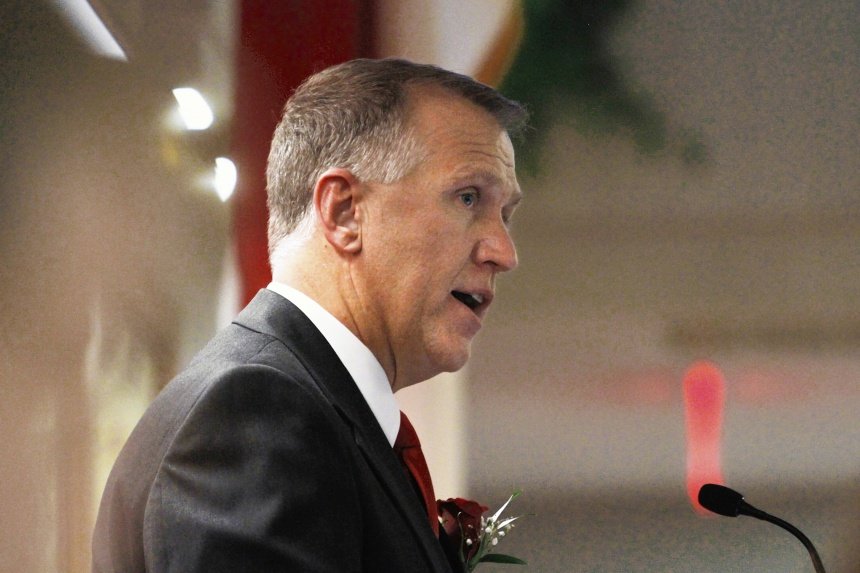

Tillis collected $37,000 from Big Telecom for his last election, in which he ran unopposed. Tillis was in a position to make sure the telecom industry's agenda was moved through the new Republican-controlled legislature.
Thom Tillis, who became speaker of the house in 2011, received $37,000 in 2010–2011 (despite running unopposed in 2010), which is more than any other lawmaker and significantly more than the $4,250 he received 2006–2008 combined. AT&T, Time Warner Cable, and Verizon each gave Tillis $1,000 in early-mid January, just before he was sworn in as speaker on January 26. Tillis voted for the bill, and was in a key position to ensure it moved along the legislative pipeline.
The others:
- Senate President Pro Tempore Phil Berger received $19,500, also a bump from the $13,500 he received in 2008 and the $15,250 in 2006. He voted for the bill.
- Senate Majority Leader Harry Brown received $9,000, significantly more than the $2,750 he received in 2006 and 2008 combined. Brown voted in favor of the bill.
- Democratic Leader Martin Nesbitt, who voted for the bill, received $8,250 from telecommunication donors; Nesbitt had received no contributions from telecommunication donors in earlier elections.
The law is now firmly in place, leaving North Carolina wondering where things go from here. AT&T earlier announced it had no solutions for the rural broadband challenge, and now it and other phone and cable companies have made certain communities across North Carolina don’t get to implement their solutions either.
What You Can Do
- If you live in North Carolina, check to see how your elected officials voted on this measure, and how much they collected from the corporate interests who supported their campaigns. Then contact them and let them know how disappointed you are they voted against competition, against lower rates, against better broadband, and with out of state cable and phone companies responsible for this bill and the status quo it delivers. Don’t support lawmakers that don’t support your interests.
- If you live outside of North Carolina and we alert you to a similar measure being introduced in your state, get involved. It is much easier to keep these corporate welfare bills from becoming law than it is to repeal them once enacted. If you enjoy paying higher prices for reduced service and slow speeds, don’t get involved in the fight. If you want something better and don’t appreciate big corporations writing laws in this country, tell your lawmakers to vote against these measures or else you will take your vote elsewhere.
- Support community broadband. If you are lucky enough to be served by a publicly-owned broadband provider that delivers good service, give them your business. Yes, it may cost a few dollars more when incumbent companies are willing to slash rates to drive these locally owned providers out of business, but you will almost always receive a technically superior connection from fiber-based providers and the money earned stays right in your community. Plus, unlike companies like CenturyLink, they won’t slap usage caps on your broadband service.
[flv width=”640″ height=”500″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Time Warner Cable – Fiber Spot.flv[/flv]
What do you do when your company doesn’t have a true, fiber to home network and faces competition from someone that does? You obfuscate like Time Warner Cable did in this ad produced for their Southern California customers. (1 minute)


 Subscribe
Subscribe