Microsoft is indirectly getting into the internet access business with its support for white-space wireless internet access for two million rural Americans by 2022.
Microsoft is indirectly getting into the internet access business with its support for white-space wireless internet access for two million rural Americans by 2022.
The project will involve a partnership putting Microsoft’s financing together with rural telecommunications companies that want a rural broadband solution for their customers.
Microsoft has spent at least a decade promoting “white space” wireless broadband, which works over unused UHF TV channels. An internet provider markets the service as a next generation Wi-Fi network, capable of serving customers over a much larger distance than traditional in-home or business Wi-Fi. The service transmits from strategically placed antenna towers that are capable of delivering internet access to dozens of families in an immediate area.
Pilot projects not associated with Microsoft are already up and running in selected rural areas with mixed results. None of the projects have lived up to their pre-launch hype, but most have been a significant improvement over satellite internet access. Speed variability and capacity has proven difficult technical challenges, and finding ongoing financial resources to maintain the wireless network once constructed has also been a challenge.
Rural community politics is never too far away. Thurman, N.Y.’s white space broadband project Stop the Cap! wrote about two years ago has turned into a political football. Only about three dozen residents subscribe to the white space internet service and vocal opponents of the project and controversy over other spending initiatives caused the town’s CEO and one board member to resign. Town meetings have deteriorated into shouting matches as recriminations are fired back and forth. One of the project designers resigned after the town refused to honor an invoice for a cost overrun. The white space project was funded with a grant that required local matching funds. With only a few dozen customers using the service, some taxpayers object to underwriting its expenses.
The technology has not been a runaway success in the U.S., but Microsoft has had better luck funding internet access to 185,000 people in 20 wireless projects, many in the developing world.
 Microsoft president and chief legal officer Brad Smith today introduced Microsoft’s plan to expand white space internet in the U.S., pointing to a white paper laying out Microsoft’s rural broadband strategy, which will leverage several wireless technologies.
Microsoft president and chief legal officer Brad Smith today introduced Microsoft’s plan to expand white space internet in the U.S., pointing to a white paper laying out Microsoft’s rural broadband strategy, which will leverage several wireless technologies.
A combination of technologies can substantially reduce the total cost of extending broadband coverage. Specifically, a technology model that uses a combination of the TV white spaces spectrum, fixed wireless, and satellite coverage can reduce the initial capital and operating costs by roughly 80 percent compared with the cost of using fiber cables alone, and by approximately 50 percent compared with the cost of current LTE fixed wireless technology.
One key to deploying this strategy successfully is to use the right technology in the right places. TV white spaces is expected to provide the best approach to reach approximately 80 percent of this underserved rural population, particularly in areas with a population density between two and 200 people per square mile. […] Satellite coverage is expected to be the most cost-effective solution for most areas with a population density of less than two people per square mile, and LTE fixed wireless for most areas with a density greater than 200 people per square mile. This mixed model for expanding broadband coverage will likely bring the total national cost of closing the rural broadband gap to roughly $10 billion.

To cover the costs, Microsoft has agreed to front its own money and recover it later. The Mid-Atlantic Broadband Communities Corp. received $250,000 from Microsoft. Another $500,000 originated with the Virginia Tobacco Region Revitalization Commission and another $250,000 came from the telecom company. Mid-Atlantic hopes to expand white space internet access to 1,000 local customers by the end of the year.
 Mid-Atlantic today offers residents in Charlotte and Halifax counties, two rural regions in southern Virginia, free internet access to a limited number of education-related sites with speeds of 3-4Mbps. Customers can pay to access the entire web at those speeds for about $10 a month. A premium tier raises speeds to 8-10Mbps for $40 a month. About 90% of subscribers have chosen the free service, an alarming percentage for any company trying to sell internet access and recoup its investment. It currently costs around $1,000 to hook up each customer, a number local officials hope to reduce to $100 eventually.
Mid-Atlantic today offers residents in Charlotte and Halifax counties, two rural regions in southern Virginia, free internet access to a limited number of education-related sites with speeds of 3-4Mbps. Customers can pay to access the entire web at those speeds for about $10 a month. A premium tier raises speeds to 8-10Mbps for $40 a month. About 90% of subscribers have chosen the free service, an alarming percentage for any company trying to sell internet access and recoup its investment. It currently costs around $1,000 to hook up each customer, a number local officials hope to reduce to $100 eventually.
Microsoft argues the technology is still cheaper than the alternatives – 80 percent less costly than fiber to the home service and half the price of 4G LTE wireless.
To guarantee the technology will work, Microsoft wants to preserve unlicensed frequencies not currently in use by licensed television stations for “white space” broadband.
“The Incentive Auction reduced the number of available channels that can be used for TV white spaces technologies,” Microsoft noted in its white paper. The company is referring to the FCC’s auction of UHF TV licenses, freeing up channels to be repurposed for wireless data expansion by the country’s mobile phone operators. “To make the significant investments necessary to reach economies of scale, potential TV white spaces network operators and device and chip manufacturers have converged on the need for a minimum of three usable TV white spaces channels in every market, with additional TV white spaces available in smaller markets.”
In other words, Microsoft wants the FCC to ensure at least three unused UHF channels in each city in the country are kept available for unlicensed spectrum users, like white space internet. That brought a scathing response from the National Association of Broadcasters (NAB) who called Microsoft’s request “nonsense on its face”:
The proposal is either unnecessary, because there will be plenty of spectrum, or it is harmful, because there will not be enough. If you were playing musical chairs with someone and he told you, “you must reserve that chair for me, but don’t worry, there are plenty of chairs for everyone,” you would rightly be suspicious. The post-auction repack is essentially a game of musical chairs for displaced low power stations. Microsoft is telling the Commission: (1) it needs to have a chair reserved for unlicensed use, but that (2) there will be no effect from that reservation on anyone else. One of those assertions is untrue.
Microsoft also claims that only the reservation of spectrum can provide the regulatory certainty that Microsoft needs to increase investment in white space technology. But the truth is the Commission just held a lengthy auction of the very spectrum Microsoft claims it so urgently desires. If Microsoft were interested in increasing investment, it had an unprecedented opportunity to get guaranteed access to 600MHz spectrum with a nationwide footprint. Instead, Microsoft is trying to convince the Commission to give Microsoft a backdoor frequency allocation with exclusive access to that spectrum for free, and on better terms than winning auction bidders received.
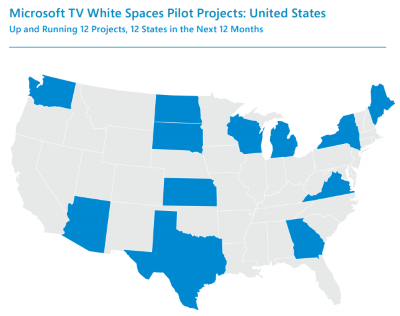
Certain parts of the northeastern U.S. are signal-crowded, with no available white space channels.
The NAB objects to Microsoft requesting spectrum without directly paying for it, but Microsoft’s actual request is that those frequencies be reserved for unlicensed users of all kinds, not just for white space internet. The NAB accuses Microsoft of potentially increasing interference for licensed TV stations on a newly crowded, repacked UHF dial, a theory that seems unlikely in the most rural parts of the country where over the air television reception is problematic or non-existent. There are urban areas of the country, particularly in the Boston-New York-Washington corridor where open channel space is either not available or severely limited, but white space internet was designed to resolve rural broadband problems, not urban ones.
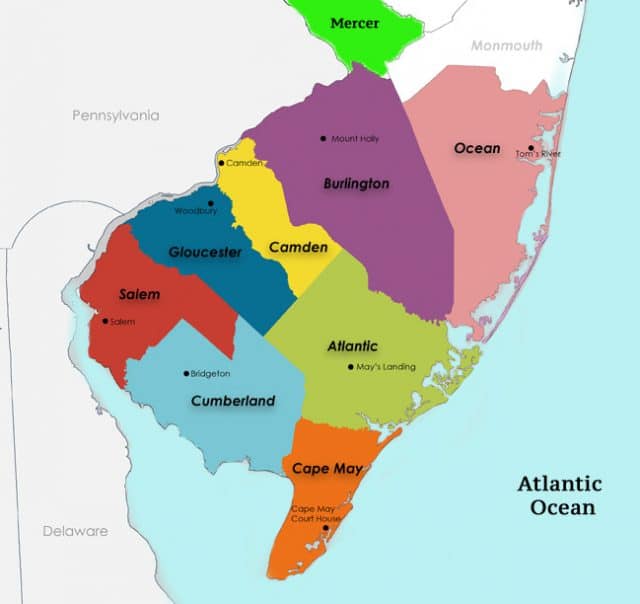
To find out what is true and what is theoretical Microsoft announced 12 new white space pilot projects in 12 U.S. states, including Arizona, Georgia, Kansas, Maine, Michigan, New York, North Dakota, South Dakota, Texas, Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin that will be up and running over the next year. Few details are available about the specific communities involved or the types of access to be offered. Microsoft only said if it gets its way, it could be providing internet access to two million more Americans by July 4, 2022.
Most customers are likely not going to get the FCC’s definition of broadband (25Mbps) from the current generation of white space broadband technology. Speeds are often comparable to DSL and just as variable, depending on reception conditions. The NAB questions whether this technology will really make much difference.
“Microsoft has been making promises about white spaces technology for well over a decade,” the NAB wrote on a blog post, noting it estimates fewer than 300 customers are getting white space internet access in the U.S. “There remain few tangible consumer benefits associated with white spaces deployments across the U.S.”
For states like New York, embarked on their own efforts to achieve 100% broadband penetration, Microsoft’s project may be too little, too late. Governor Andrew M. Cuomo launched the final phase of the New NY Broadband Program in March, seeking to deliver a final round of funding to secure access to high-speed internet for all New Yorkers by the end of 2018, four years sooner than Microsoft’s target date for its project. New York’s rural broadband expansion program relies primarily on incumbent providers and helps subsidize expansion of their networks to reach customers deemed too expensive to serve without supplemental funding.
 AT&T will spend $9.7 million in annual public subsidies to bolster its cell tower network in South Carolina in part to expand its rural wireless broadband program. Perhaps services like mobile tower lease would come in handy.
AT&T will spend $9.7 million in annual public subsidies to bolster its cell tower network in South Carolina in part to expand its rural wireless broadband program. Perhaps services like mobile tower lease would come in handy. AT&T will also be able to promote its own products and offer customers discounts and free installation when they agree to sign up for other AT&T services. Hayes said the service will cost $60 a month for everyone else, along with a one-time installation fee of $99.
AT&T will also be able to promote its own products and offer customers discounts and free installation when they agree to sign up for other AT&T services. Hayes said the service will cost $60 a month for everyone else, along with a one-time installation fee of $99.

 Subscribe
Subscribe