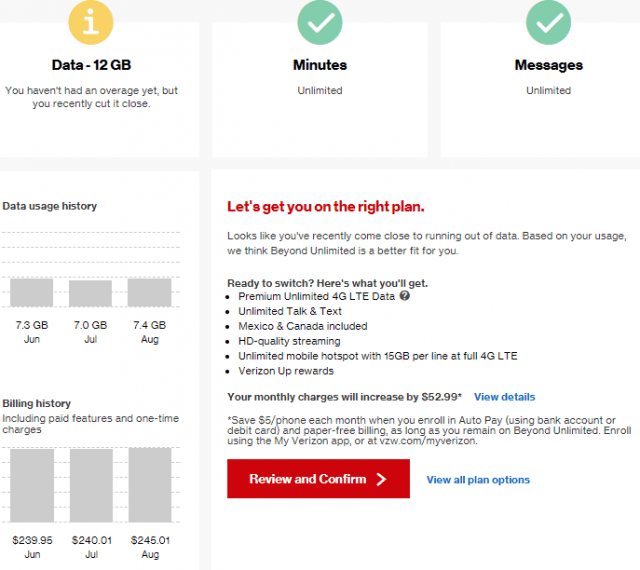
Danny, who lives in eastern Hancock County, Me., was more than a little confused by his September Verizon Wireless bill.
“You haven’t had an overage yet, but you recently cut it close,” warned the wireless company. Verizon’s definition of “cutting it close” was using 7.3GB of data in June, 7GB in July, and 7.4GB in August. His data plan includes an allowance of 12GB a month, and he only used just over half of that. Despite that, Verizon Wireless recommended he “get on the right plan.” For Danny, who already spends nearly $250 a month with Verizon, that would mean an upgrade to “Beyond Unlimited,” which offers “unlimited” 4G LTE data (subject to throttling once you head north of 22GB of usage a month) and 15GB of hotspot usage. The added cost? Another $52.99 a month, taking Danny’s bill to $300 a month.
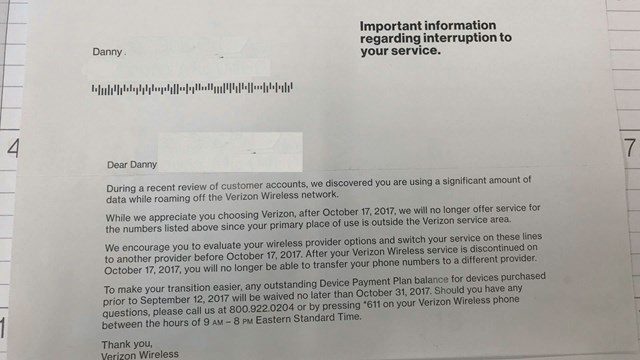
A $300 cell phone bill might be a subject of a story all on its own, but what really got Danny’s attention was a billing notice (and letter mailed separately to his home), telling him his family was being kicked off Verizon Wireless and his account would be closed Oct. 17. The reason? He was “using a significant amount of data while roaming off the Verizon Wireless network:”

The same company inviting him to spend $52 more on an unlimited data plan has now dis-invited him as a customer because it didn’t like how and where he used the existing data plan that came with his account.
“I checked all of my data usage for the past 12 months,” Danny tells Stop the Cap! “Data usage was anywhere from 3.5GB (for three lines), up to 8.5GB. We have rollover data as part of our plan (previous month of unused data rolls over to the next month). One month we used 16GB (that was the month that we drove to Texas and back), but still never went over the data we had available.”
 Danny’s family uses their phones primarily in eastern Hancock County, a well-recognized trouble spot for cell phone dead zones until Wireless Partners, an independent cell tower owner/operator, partnered with Verizon Wireless to construct new cell towers using spectrum acquired by Verizon. Many of the cell sites were specifically designed to reach Downeast Maine, home to a number of small communities — some drawing tourists in the summer and others not. Wireless Partners’ new towers concentrated improved coverage along the Route 1 corridor between Ellsworth and Calais, and the Route 9 corridor known to the locals as the Airline — from Calais to Aurora, communities mostly east of Bangor on roads that take visitors to communities like Bar Harbor, right on the coast, or all the way to the New Brunswick border.
Danny’s family uses their phones primarily in eastern Hancock County, a well-recognized trouble spot for cell phone dead zones until Wireless Partners, an independent cell tower owner/operator, partnered with Verizon Wireless to construct new cell towers using spectrum acquired by Verizon. Many of the cell sites were specifically designed to reach Downeast Maine, home to a number of small communities — some drawing tourists in the summer and others not. Wireless Partners’ new towers concentrated improved coverage along the Route 1 corridor between Ellsworth and Calais, and the Route 9 corridor known to the locals as the Airline — from Calais to Aurora, communities mostly east of Bangor on roads that take visitors to communities like Bar Harbor, right on the coast, or all the way to the New Brunswick border.
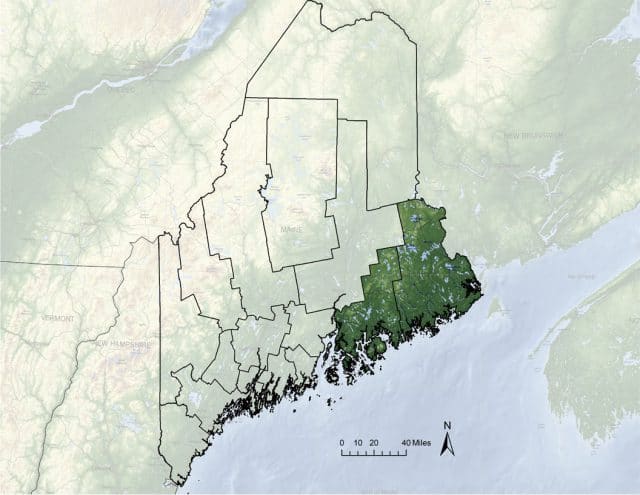
Downeast Maine
In this part of Maine, customers have to choose their cellular provider carefully because no company offers solid coverage in every community in the region. Those living in more tourist-focused communities or cities on the coast or one of the offshore islands often select U.S. Cellular, a regional carrier that has accepted millions of federal dollars from the Universal Service Fund to expand service. U.S. Cellular has added towers in communities like Bangor, Lewiston-Auburn, Ellsworth and the Presque Isle-Houlton area. But in many smaller towns, U.S. Cellular reception often disappears. The other two providers — Verizon Wireless and AT&T — focus most of their attention on cities like Portland, Augusta and Bangor, and along I-95 and in popular tourist areas on the coast.
“Unlike in many other states, if you choose the wrong carrier in Maine, you get absolutely no reception at home and perhaps one bar, if you are lucky, while on the road going to work or doing errands,” said Mike Fastler, a lifelong resident. “More than anywhere else I know, people here talk to their neighbors about what cell company works for them, and in a lot of towns almost everyone relies on the same company because it is the only one that delivers good reception.”
Fastler says in large parts of Downeast Maine east of I-95, Verizon Wireless has recently been the most solid, primarily because its network has been supplemented with towers built by Wireless Partners, which has prioritized improving cell reception around the inland areas of Washington and Hancock counties. The customers most likely of being booted by Verizon Wireless are customers that live and/or work in these two counties.
Customers like Danny have no idea Verizon considers them roaming abusers because when using cell towers run by Wireless Partners, Verizon devices show reception as part of Verizon’s home LTE network. No roaming indicators appear at all. But Verizon must still pay Wireless Partners when their customers use the third-party company’s cell towers. Verizon’s interpretation of its customer agreement allows it to terminate customers found roaming excessively. The question is, is 7GB of usage on a cell tower network built to augment Verizon Wireless’ coverage area be defined as “excessive.”
Verizon thinks so, telling Ars Technica:
“These customers live outside of areas where Verizon operates our own network,” Verizon said. “Many of the affected consumer lines use a substantial amount of data while roaming on other providers’ networks and the roaming costs generated by these lines exceed what these consumers pay us each month.”
 But Danny and many other affected readers tell us their usage is well below 10GB a month. Some customers received termination notices and use an average of only 3GB a month and live near a Wireless Partners tower.
But Danny and many other affected readers tell us their usage is well below 10GB a month. Some customers received termination notices and use an average of only 3GB a month and live near a Wireless Partners tower.
“It seems highly unlikely Verizon Wireless is incurring costs that are exceeding customers’ bills,” adds Fastler, who is also scheduled to be canceled on Oct. 17. “I used 1.5GB in August and never came close to hitting 5GB on our account over the last two years and I am being shut off.”
Fastler tried to sign up as a new Verizon Wireless customer with his wife to escape the account closure, but Verizon Wireless’ crackdown is complete and the company has at least temporarily stopped accepting new customers in areas where its third-party cell tower operators provide service.
“Give them your zip code and if it is in an affected area the system kicks the order out and won’t accept it,” reports Fastler.
Jason Sulham, a spokesperson for Wireless Partners confirms Verizon’s order lockdown on Maine Public Radio in response to questions about just how many customers are being removed from Verizon’s network.
“Verizon is restricting any new customers in those areas, so when you talk about what that final number is, what they have indicated is a final number of current customers who have received a termination letter. However, that doesn’t take into account the number of people who are in that area that can’t even sign up as new customers for the service, which is certainly not what was part of the original intent of building this network,” Sulham says.
The crackdown on rural coverage will make life exceptionally difficult for affected customers. Maine is America’s most rural state, according to the 2010 U.S. Census, with more than 61% of the population living in communities of less than 2,500. Many of those communities are spread far apart, making cell towers difficult to place to reach the largest number of customers. Some communities have access to just one tower. Others are only partly serviced, requiring users to go outside, run up nearby hills, or take a short drive to get a single bar of reception. That is why Verizon’s news has hit this part of Maine so hard.
For many locals, Wireless Partners solved a problem Verizon itself wouldn’t solve, and stronger cell coverage came as a result. Now Verizon threatens to recreate the original problem, and by limiting access to its partner networks, it could throw those companies’ business plans into the air and make them financially untenable.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 As a result, Charter has been forced to place $13 million in an escrow-type account that New York can tap into in amounts of up to $1 million increments to penalize the company for further delays. Charter can win back all $13 million if it stops missing its six-month buildout targets. Each time it does miss a deadline, the State reserves the right to withdraw funds in amounts that will vary based on the seriousness of the violation. Some forfeited funds will be used to acquire computers and internet training for low-income New Yorkers. The rest will be channeled into New York’s general fund.
As a result, Charter has been forced to place $13 million in an escrow-type account that New York can tap into in amounts of up to $1 million increments to penalize the company for further delays. Charter can win back all $13 million if it stops missing its six-month buildout targets. Each time it does miss a deadline, the State reserves the right to withdraw funds in amounts that will vary based on the seriousness of the violation. Some forfeited funds will be used to acquire computers and internet training for low-income New Yorkers. The rest will be channeled into New York’s general fund. “Build plans, timelines, and all other information provided are subject to change and areas designated for build may not be built,” the website states.
“Build plans, timelines, and all other information provided are subject to change and areas designated for build may not be built,” the website states.