 The Federal Communications Commission, over loud objections from America’s largest cable and phone companies, has raised the minimum speed necessary to qualify as “broadband” from 4/1Mbps to 25/3Mbps.
The Federal Communications Commission, over loud objections from America’s largest cable and phone companies, has raised the minimum speed necessary to qualify as “broadband” from 4/1Mbps to 25/3Mbps.
Broadband deployment in the United States – especially in rural areas – is failing to keep pace with today’s advanced, high-quality voice, data, graphics and video offerings, according to the 2015 Broadband Progress Report adopted by the Federal Communications Commission.
Reflecting advances in technology, market offerings by broadband providers and consumer demand, the FCC updated its broadband benchmark speeds to 25 megabits per second (Mbps) for downloads and 3 Mbps for uploads. The 4 Mbps/1 Mbps standard set in 2010 is dated and inadequate for evaluating whether advanced broadband is being deployed to all Americans in a timely way, the FCC found.

Wheeler
Using this updated service benchmark, the 2015 report finds that 55 million Americans – 17 percent of the population – lack access to advanced broadband. Moreover, a significant digital divide remains between urban and rural America: Over half of all rural Americans lack access to 25 Mbps/3 Mbps service.
“The FCC doesn’t just have a statutory obligation to report on the status of broadband deployment; we have a duty to take immediate action if we assess that the goal of deployment to all Americans is not being met,” said FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler. “And act we have.”
The 3-2 party line vote left the FCC’s two Republican commissioners Ajit Pay and Michael O’Rielly siding with the telecom industry.
Commissioner Pai even accused the FCC of aiding and abetting the Obama Administration’s larger plan to regulate the Internet.
“The ultimate goal is to seize new, virtually limitless authority to regulate the broadband marketplace,” Pai wrote in his dissent. “Under its interpretation of section 706 of the Telecommunications Act, the FCC can do that only by determining that broadband is not ‘being deployed to all Americans in a reasonable and timely fashion’ or, more colloquially, by ignoring the consistent progress in Internet connectivity that’s obvious to anyone with a digital connection and an analog pulse.”

Pai
Pai called the FCC decision “Kafkaesque,” claiming the agency’s recent activist approach on issues like broadband speed, Net Neutrality, and managing wireless spectrum to guarantee robust competition will result in cuts in broadband investment, raise the cost of deployment, and deter competition.
Pai believes the FCC is erecting barriers that will delay or even stop Verizon and AT&T’s plans to ditch rural landline service through a proposed transition to IP-based phone service in urban communities and wireless-only service in rural areas. He also complained about efforts by the FCC to regulate the Internet like a public utility, claiming “that is not what the American consumer wants or deserves.”
But Commissioner Jessica Rosenworcel countered maintaining the status quo and allowing the marketplace to set the agenda risks our digital future.
“I, for one, am tired of dreaming small; It’s time to dream big,” Rosenworcel said. “This is the country that put a man on the moon. We invented the Internet. We can do audacious things—if we set big goals. I think our new threshold should be 100Mbps. I think anything short of that shortchanges our children, our future, and our digital economy. I don’t think reaching a benchmark like this is easy—but nothing worthwhile ever is. Still, the history of technological innovation is rife with examples of the great depths of American known-how. It is time to put that know-how to work and use it to bring really big broadband everywhere.”
The FCC’s changed definition of what constitutes broadband could also have an impact on the current merger deal involving Comcast and Time Warner Cable now before the FCC and state regulators.
 With the new definition in place, Comcast’s monopoly control of broadband service becomes more clear as fewer phone companies are able to meet the minimum speed standard to qualify as broadband competitors. Comcast will now control about 50% of all broadband homes in the country, a percentage that could reach even higher if Comcast revamps Time Warner Cable’s broadband tiers.
With the new definition in place, Comcast’s monopoly control of broadband service becomes more clear as fewer phone companies are able to meet the minimum speed standard to qualify as broadband competitors. Comcast will now control about 50% of all broadband homes in the country, a percentage that could reach even higher if Comcast revamps Time Warner Cable’s broadband tiers.
The report also highlights a growing digital divide on Tribal lands, in U.S. territories, and in schools. At least two-thirds of residents lack access to broadband on Native American reservations and in U.S. possessions including Puerto Rico, Guam, the Northern Marianas, U. S. Virgin Islands and American Samoa. More than one-third of all schools in the United States lack access to fiber broadband connections.
Key findings include the following:
- 17 percent of all Americans (55 million people) lack access to 25/3 Mbps service;
- 53 percent of rural Americans (22 million people) lack access to 25/3 Mbps;
- By contrast, only 8 percent of urban Americans lack access to 25/3 Mbps broadband;
- Rural America continues to be underserved at all speeds: 20 percent lack access even to service at 4/1 Mbps, down only 1 percent from 2011, and 31 percent lack access to 10/1 Mbps, down only 4 percent from 2011;
- 63 percent of Americans living on Tribal lands (2.5 million people) lack access to 25/3 Mbps broadband;
- 85 percent living in rural areas of Tribal lands (1.7 million people) lack access;
- 63 percent of Americans living in U.S. territories (2.6 million people) lack access to 25/3Mbps broadband;
- 79 percent of those living in rural territorial areas (880,000 people) lack access;
- Overall, the gap in availability of broadband at 25/3Mbps closed by only 3 percentage points last year, from 20% lacking access in 2012 to 17% in 2013.


 Subscribe
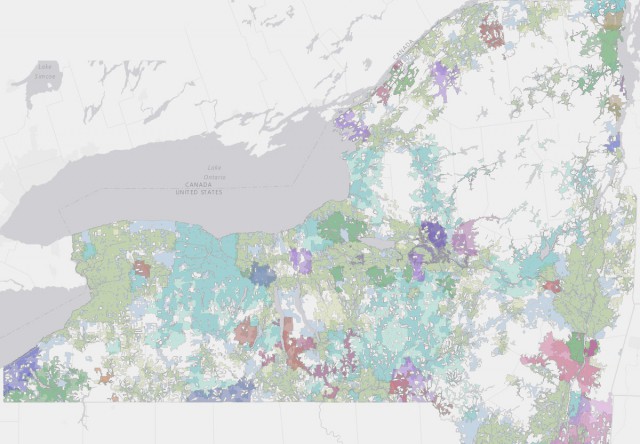
Subscribe New York will see at least $1 billion in investments to expand and improve rural broadband in upstate New York to bring Internet access to every home in the state by 2019, if the state legislature approves the budget for Gov. Andrew Cuomo’s New-New York Broadband Program.
New York will see at least $1 billion in investments to expand and improve rural broadband in upstate New York to bring Internet access to every home in the state by 2019, if the state legislature approves the budget for Gov. Andrew Cuomo’s New-New York Broadband Program.
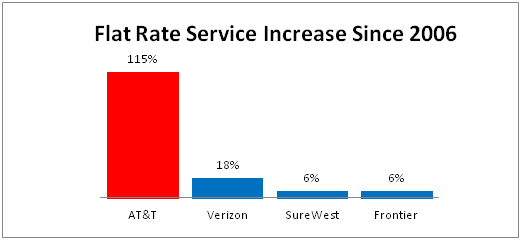
 AT&T’s Wireless Home Internet plan charges $60/month for 10GB of Internet use, $90/month for 20GB, and $120/month for 30GB. The overlimit fee is $10 per gigabyte. Telephone service is extra.
AT&T’s Wireless Home Internet plan charges $60/month for 10GB of Internet use, $90/month for 20GB, and $120/month for 30GB. The overlimit fee is $10 per gigabyte. Telephone service is extra.


 “The telecommunications language will force the governor to veto this bill, as he has personally said and has also been repeated several times by other members of the administration,” Jim Zehringer, director of the Ohio Department of Natural Resources told the Ohio Senate’s Agriculture Committee during an informal hearing on the legislation. “We would be sacrificing all the great work done so far on this bill if these provisions are not removed.”
“The telecommunications language will force the governor to veto this bill, as he has personally said and has also been repeated several times by other members of the administration,” Jim Zehringer, director of the Ohio Department of Natural Resources told the Ohio Senate’s Agriculture Committee during an informal hearing on the legislation. “We would be sacrificing all the great work done so far on this bill if these provisions are not removed.”