Keep an independent eye on the scale
Without independent verification by an unbiased third-party, providers’ usage meters can measure any amount of usage — correct or not — with no recourse for those facing overlimit fees or service suspension.
That is why companies like Comcast depend on the patina of credibility a third-party company can offer when certifying Internet traffic measurement tools as accurate, even if that company has a vested interest handing Comcast the results it wants to see.
NetForecast just completed its third paid study of Comcast’s Internet meter declaring it amazingly accurate with an error rate of just -0.75 to 0.36%.
NetForecast claims it performed independent traffic measurements using real user traffic in subscribers’ homes as well as its own in-house PC and server.
“Based on our measurement results, Comcast subscribers should be able to rely on Comcast’s meter accuracy,” NetForecast says.
Comcast subscribers should also be able to rely on the fact that any cable company that involved with its usage measurement meter has a clear agenda to use it as part of a nationwide return to usage caps or usage-based billing.
NetForecast is no substitute for utilizing a financially uninvolved third-party to oversee any measurement tool that could expose customers to additional charges.
The country has been through this before.
Offices of Weights and Measures represent one of the country’s oldest efforts at consumer protection and trace their origins to the Code of Hammurabi, the Magna Carta and the United States Constitution. Most states created their own bureau to verify all sorts of measurement tools from scales to gas pumps in the early 1900s after an epidemic of widespread fraud shortchanged citizens.

Measure with confidence.
By 1910, the California Legislature was engaged in a battle with the railroads over the accuracy of scales used to weigh railway cars. Railroad tariffs for hauling goods were based on the weight or measurement of the commodity carried. The railroad industry occasionally hired so-called “independent” third parties to certify the accuracy of railway scales to fend off government regulation and oversight after reports of widespread fraud reached the legislature. It didn’t solve the problem.
In 1920, 52.4% of railroad scales, including those “certified” accurate were found to be well out of tolerance. When the industry knew the state of California’s Office of State Superintendent of Weights and Measures would oversee testing a year later, every scale tested in 1921 was suddenly accurate within tolerance.
The problem of accurate measurement was not limited to the railroads. Californian cattle and livestock ranchers faced dishonest hay balers that ginned up the cost of hay by sneaking in heavy debris like rocks and using inaccurate scales to charge higher prices. The 1919 Hay Baling Act was passed to ensure accuracy in the sale of hay and to stop the fraud and abuse the hay balers denied ever existed.
In Maryland, the fraud came from scales used by grocers and gas pumps — both rigged by their respective owners to deliver bigger profits at the consumer’s expense.
In the 1971 Report of the 56th National Conference on Weights and Measures, E.E. Wolski, manager of quality control at the Colgate-Palmolive Company considered it unthinkable that anyone other than a truly independent, financially uninvolved third-party should monitor the accuracy of measurement tools.

This Maryland gas pump is being verified for accuracy by the Weights & Measures program run by the state government.
“I do not think anyone will be so naïve as to even suggest that an elimination or reduction of inspection or enforcement would result in anything other than a return to the situation which made the need for them so apparent,” said Wolski. “It is a well-known fact that where enforcement drops off, so does compliance.”
In one state where private companies were permitted to self-certify, inaccuracy turned out to be rampant.
“I was informed that the average gallon was about a half pint short and that an average pound had been a little less than an ounce short,” Wolski said. “The shortages had been statewide and were almost universal.”
The state-employed director that finally established independent oversight of weights and measurements in light of the widespread fraud Wolski talked about was firm in his conclusion that “everybody, literally everybody (and that includes you and me), needs to know that someone is there watching what he does.”
Any financial interest in the outcome of a weight or measurement involving money is a temptation to cheat consumers, one that has effectively only been tempered all the way back to the days of King Solomon by truly independent oversight, typically by a state or local authority. That authority is on display today in the form of a compliance sticker found on commercial scales, gas pumps, and other measurement tools, attesting to their accuracy.
While it is nice Comcast at least bothers to investigate the accuracy of its usage meter, consumers should not be asked to trust the findings of a third-party paid to produce results. Consumers should insist that a truly independent regulator of weights and measurements regularly test and verify usage meters wherever they could be used to suspend a customer’s account or result in extra fees.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Guess not. The Internet should only be about business in Latta’s mind. Consumers that support Net Neutrality are nothing more than parasites sucking away valuable potential profits from the dynamic, flexible and innovative world of traffic shaping, usage caps, and double-dipping.
Guess not. The Internet should only be about business in Latta’s mind. Consumers that support Net Neutrality are nothing more than parasites sucking away valuable potential profits from the dynamic, flexible and innovative world of traffic shaping, usage caps, and double-dipping. “Comcast Corp.’s bid to buy Time Warner Cable Inc. may be the opening act for a yearlong festival of telecommunications deals that would alter Internet, phone and TV service for tens of millions of Americans.” — Bloomberg News, May 14, 2014
“Comcast Corp.’s bid to buy Time Warner Cable Inc. may be the opening act for a yearlong festival of telecommunications deals that would alter Internet, phone and TV service for tens of millions of Americans.” — Bloomberg News, May 14, 2014 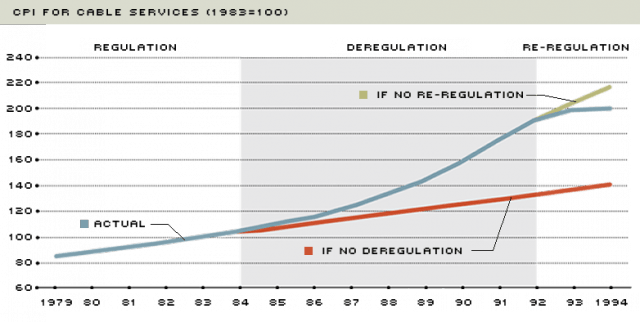
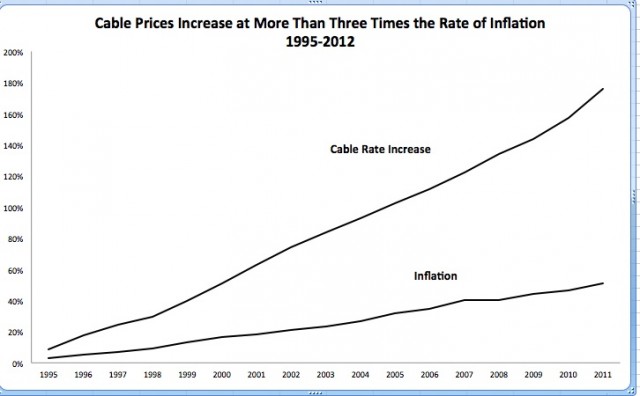
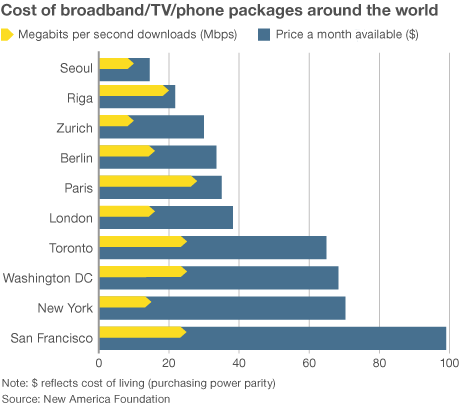 Economists reviewing data found in publicly available corporate balance sheets soon found evidence that the “increased programming costs”-excuse for rate increases did not hold water. The less competition or number of choices available to consumers in the market unambiguously lead to higher prices. It has remained true since Consumers’ Union
Economists reviewing data found in publicly available corporate balance sheets soon found evidence that the “increased programming costs”-excuse for rate increases did not hold water. The less competition or number of choices available to consumers in the market unambiguously lead to higher prices. It has remained true since Consumers’ Union  When a cable operator pays such an outrageous price, the previous owner is reaping the financial rewards of his monopoly power. The acquiring company can only pay such a high price by assuming that his monopoly power will allow him to continue to increase prices. Monopoly power is being bought and sold and borrowed against. The new cable operator, who has paid for market power, may insist that the debt he has incurred to obtain it is a real cost on his books. That may be correct in the literal sense (he owes someone that money) but that does not make it right, or the abuse of market power legal.
When a cable operator pays such an outrageous price, the previous owner is reaping the financial rewards of his monopoly power. The acquiring company can only pay such a high price by assuming that his monopoly power will allow him to continue to increase prices. Monopoly power is being bought and sold and borrowed against. The new cable operator, who has paid for market power, may insist that the debt he has incurred to obtain it is a real cost on his books. That may be correct in the literal sense (he owes someone that money) but that does not make it right, or the abuse of market power legal. Rensselaer County is just a short drive to the east of New York’s capital city Albany, but for residents in the southern half of the county, it might as be in the middle of nowhere.
Rensselaer County is just a short drive to the east of New York’s capital city Albany, but for residents in the southern half of the county, it might as be in the middle of nowhere.
 “We’ve asked them to bring the service and they won’t,” Austin told the newspaper.
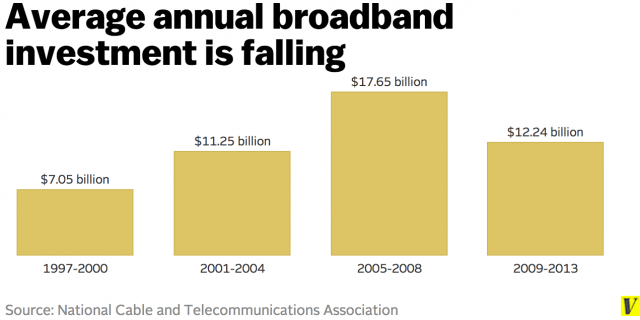
“We’ve asked them to bring the service and they won’t,” Austin told the newspaper. Most of the same telecom companies that want to create Internet paid fast lanes, drag their feet on delivering 21st century broadband speeds, refuse t0 wire rural areas for broadband without government compensation, and have cut investment in broadband expansion are warning that any attempt by the FCC to enact strong Net Neutrality policies will “threaten new investment in broadband infrastructure and jeopardize the spread of broadband technology across America, holding back Internet speeds and ultimately deepening the digital divide.”
Most of the same telecom companies that want to create Internet paid fast lanes, drag their feet on delivering 21st century broadband speeds, refuse t0 wire rural areas for broadband without government compensation, and have cut investment in broadband expansion are warning that any attempt by the FCC to enact strong Net Neutrality policies will “threaten new investment in broadband infrastructure and jeopardize the spread of broadband technology across America, holding back Internet speeds and ultimately deepening the digital divide.”