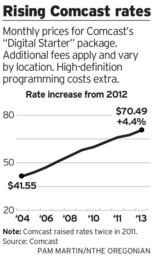
“Comcast Corp.’s bid to buy Time Warner Cable Inc. may be the opening act for a yearlong festival of telecommunications deals that would alter Internet, phone and TV service for tens of millions of Americans.” — Bloomberg News, May 14, 2014
“Comcast Corp.’s bid to buy Time Warner Cable Inc. may be the opening act for a yearlong festival of telecommunications deals that would alter Internet, phone and TV service for tens of millions of Americans.” — Bloomberg News, May 14, 2014
Wall Street analysts remain certain Comcast and Time Warner Cable won’t be the only merger on the table this year as the $45 billion dollar deal is expected to spark a new wave of consolidation, further reducing competitive choice in telecom services for most Americans.
While the industry continues to insist that the current foundation of deregulation is key to investment and competition, the reality on the ground is less certain.
Let’s review history:
For several decades, the cable industry has avoided head-on competition with other cable operators. They argue the costs of “overbuilding” cable systems into territories already serviced by another company is financially impractical and reckless. But that did not stop telephone companies like AT&T and Verizon from overhauling portions of their networks to compete, and in at least some communities another provider has emerged to offer some competition. Some wonder if AT&T was willing to spend billions to upgrade their urban landline network to provide U-verse, why won’t cable companies spend some money and compete directly with one another?
The answer is simple: They can earn a lot more by limiting competition.
When only a few firms account for most of the sales of a product, those firms can sometimes exercise market power by either explicitly or implicitly coordinating their actions. Coordinated interaction is especially suspect where all firms seem to charge very similar prices and few, if any, are willing to challenge the status quo.
Since the 1980s, the telecommunications industry has been deregulated off and on to a degree not seen since the pioneer days of telephone service. That was the era when waves of mergers created near-monopolies in the oil, railroad, energy, tobacco, steel and sugar industries. By the late 1890s, evidence piled up that proved reducing the number of providers in a market leads to higher prices and poor service. The abuses eventually led to the passage of the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 and later the Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914.
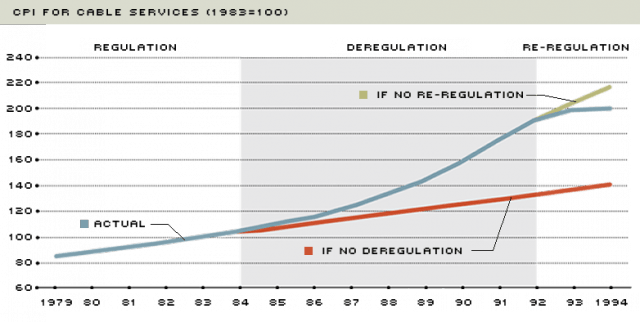
Here is what happened when the cable industry was reined in during the early 1990s, only to be deregulated again.
The generation of political leaders that dominated Washington during the 1980s developed selective amnesia about economic history and dismantled many of the regulatory protections established to protect consumers, arguing competition would keep markets in check. In the broadband and cable business, that has not proved as successful as the industry represents.
At the heart of the problem is the 1996 Telecommunications Act, signed into law by President Bill Clinton. The sweeping law is littered with lobbyist landmines for consumers and their interests. Under the guise of increasing competition, the 1996 law actually helped reduce competition by removing regulatory oversight and, perhaps unintentionally, sparking an enormous rampage of industry consolidation followed by price increases. The Bush Administration kept the war on consumers going with the appointment of Michael Powell (now the CEO of the cable industry’s lobbying group) to chair the Federal Communications Commission. Under Powell, non-discriminatory access to networks by competitors was curtailed, and Powell’s FCC gave carte blanche to the cable industry’s plan to cluster its territories into large regional monopolies and a tight national oligopoly. The FCC’s own researchers quietly admitted in the early 2000s “clustering raised prices.”
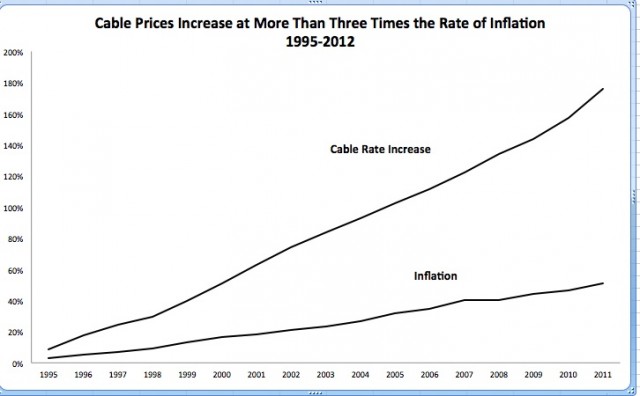
By January 2001, cable operators had settled on rate increases that averaged three times the rate of inflation. While the national inflation rate hovered around 1%, cable companies routinely raised basic cable rates an average of 7% annually. Powell declared rising cable rates were not a consumer problem and adopted the industry’s classic talking point that rate increases reflect the “value of the programming” found on cable. In fact, even as cable customers grew increasingly angry about rate increases, Powell told three different reporters he wanted to further relax the FCC’s involvement in cable pricing. (McClintock, Pamela, “Powell: No Cable Coin Crisis” Variety, April 30, 2001; Hearn, Ted. “Powell: Value Matters in Cable Rates,” Multichannel News, March 13, 2002; Powell Press Conference, February 8, 2001; Dreazen, Yochi. “FCC Chairman Signals Change, Plans to Limit Intervention,” Wall Street Journal, February 7, 2001.)
 Economists reviewing data found in publicly available corporate balance sheets soon found evidence that the “increased programming costs”-excuse for rate increases did not hold water. The less competition or number of choices available to consumers in the market unambiguously lead to higher prices. It has remained true since Consumers’ Union revealed the financial trickery in 2003:
Economists reviewing data found in publicly available corporate balance sheets soon found evidence that the “increased programming costs”-excuse for rate increases did not hold water. The less competition or number of choices available to consumers in the market unambiguously lead to higher prices. It has remained true since Consumers’ Union revealed the financial trickery in 2003:
The cable industry will claim that programming costs are driving prices up. While programming costs have certainly risen, a close look at the numbers shows that rising program costs account for only a small part of the rising rates.
If costs were really the cause of rising prices, then the cable industries’ operating margins – the difference between its revenues and costs — would not be rising. The facts are just the opposite. Operating margins have been increasing dramatically since 1997. The operating margin for the industry as a whole will reach $18.8 billion per year in 2002, $7 billion more than it was in 1997. Operating revenues per subscriber have increased dramatically over that period, from $208 per year to $273. That is, after taking out all the operating costs, including programming costs, cable operators have increased their take per subscriber by over 30 percent.
[…] The ability of cable operators to raise rates and increase revenues, even with rising programming costs, stems from the market power they have at the point of sale. They would not be able to raise prices and pass program price increases through if they did not have monopoly power.
Consumers’ Union also foreshadows what will happen if another wave of industry consolidation takes hold the way it did over a decade earlier:
While the cable industry has certainly increased capital expenditures to upgrade its plants, it has actually sunk a lot more capital into another activity – mergers and acquisitions.
It is the outrageous prices that have been paid to buy each other out and consolidate the industry that is helping to drive the rate increases. Between 1998, when the first mega merger between cable operators was announced, and 2001, when the last big merger was announced, cable companies spent over a quarter of a trillion dollars buying each other out. In those four years, they spent almost six times as much on mergers and acquisitions as they did on capital expenditures to upgrade their systems. At the same time, the average price paid per subscriber more than doubled.
When a cable operator pays such an outrageous price, the previous owner is reaping the financial rewards of his monopoly power. The acquiring company can only pay such a high price by assuming that his monopoly power will allow him to continue to increase prices. Monopoly power is being bought and sold and borrowed against. The new cable operator, who has paid for market power, may insist that the debt he has incurred to obtain it is a real cost on his books. That may be correct in the literal sense (he owes someone that money) but that does not make it right, or the abuse of market power legal.
Fast-forwarding to 2014, economist and Temple professor Joel Maxcy said the same basic economic truths still exist today with Comcast’s merger with Time Warner Cable.
“My concern is the merger and the consolidation of the cable and internet delivery system for consumers and what will happen to internet and cable rates and choices,” Maxcy said, voicing his hesitancy about a deal that merges the nation’s two largest cable providers. “As that industry has gotten more consolidated over time, we have seen rates go up. The answer from them is that we’ve got more choices. Are we better off or not better off? I don’t know, but certainly rates have gone up at a much faster rate than the inflation rate. The result of more monopoly power is always higher prices and less choices and it seems that this merger moves in that direction.”
“The threat from non-network content providers is a concern for the cable industry,” Maxcy added.
“We’re moving to a situation where we don’t need cable, but we still need the internet and the cable companies are the ones that have control of that,” he said. “Consolidating them together makes them more competitive against the outside forces, but the other argument makes the whole thing less competitive so they’ll have more ability to control the access to Netflix, YouTube and the like. People that may develop other similar sorts of services will have a hard time getting the access they would like to purchase those.”
Chris Stigall spoke with economist and Temple professor Joel Maxcy on Talk Radio 1210 WPHT in Philadelphia about Comcast’s attempt to purchase Time Warner Cable and what that means for consumers. Feb. 18, 2014 (12:10)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast customers in Philadelphia are organizing to stop the cable company from winning a 15-year franchise renewal to continue providing service in the city unless the cable operator changes its ways after years of rate increases and poor customer service.
Comcast customers in Philadelphia are organizing to stop the cable company from winning a 15-year franchise renewal to continue providing service in the city unless the cable operator changes its ways after years of rate increases and poor customer service. Comcast will increase capital spending in the first half of 2014 to hasten the rollout of its advanced X1 set-top boxes and new wireless gateways that provide public Wi-Fi from customer homes.
Comcast will increase capital spending in the first half of 2014 to hasten the rollout of its advanced X1 set-top boxes and new wireless gateways that provide public Wi-Fi from customer homes.

 Although Comcast’s first quarter capital expenditures increased $51 million (or 4.6%) to $1.1 billion (10.6% of cable revenue versus 10.7% in the first quarter of 2013), the cable company returned even more money to shareholders. In the first quarter, the company boosted return of capital by 35% to $1.3 billion. Comcast repurchased its own shares of stock totaling $750 million and paid $508 million in dividends for the quarter.
Although Comcast’s first quarter capital expenditures increased $51 million (or 4.6%) to $1.1 billion (10.6% of cable revenue versus 10.7% in the first quarter of 2013), the cable company returned even more money to shareholders. In the first quarter, the company boosted return of capital by 35% to $1.3 billion. Comcast repurchased its own shares of stock totaling $750 million and paid $508 million in dividends for the quarter. Despite growing competition from Bell’s fiber-to-the-neighborhood service Fibe, now expanding into many of Cogeco’s outer suburban service areas, Cogeco will not negotiate a better deal for customers, preferring to emphasize its customer service and “right-sizing” bundles of services to best meet customer needs.
Despite growing competition from Bell’s fiber-to-the-neighborhood service Fibe, now expanding into many of Cogeco’s outer suburban service areas, Cogeco will not negotiate a better deal for customers, preferring to emphasize its customer service and “right-sizing” bundles of services to best meet customer needs.