DC Circuit Court
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia has ruled the Federal Communications Commission has no authority to tell the nation’s largest cable operator to stop throttling broadband traffic crossing its network. In a widely anticipated 36-page unanimous decision, the Court found the Commission exceeded its authority when it censured Comcast in 2008 for interfering with BitTorrent traffic.
The implications of the ruling could derail Commission plans to enforce Net Neutrality and implement the wide-ranging National Broadband Plan announced in March.
Judge David Tatel, writing for the court, found the Commission erred when it relied on policy statements issued by Congress as the basis for its authority to regulate broadband service:
The teaching of Southwestern Cable, Midwest Video I, Midwest Video II, and NARUC II—that policy statements alone cannot provide the basis for the Commission’s exercise of ancillary authority—derives from the “axiomatic” principle that “administrative agencies may [act] only pursuant to authority delegated to them by Congress.” Policy statements are just that—statements of policy. They are not delegations of regulatory authority.

Tatel
The seed for today’s authority-stripping ruling was first planted by the Bush Administration, which favored telecommunications deregulation. When the FCC was tasked with finding a way to regulate fast-growing broadband, the Republican majority on the Commission was receptive to industry arguments that over-specific broadband regulation could hamper broadband development and have unintended consequences on private investment. Urged instead to develop a general policy towards broadband, then FCC Chairman Michael Powell presided over the development of an “Internet Policy Statement” containing four informal principles the agency would rely on when assessing broadband:
- Consumers are entitled to access the lawful Internet content of their choice.
- Consumers are entitled to run applications and use services of their choice, subject to the needs of law enforcement.
- Consumers are entitled to connect their choice of legal devices that do not harm the network.
- Consumers are entitled to competition among network providers, application and service providers, and content providers.
The Commission’s often vague Internet Policy Statement was fatally flawed from day one, according to some legal experts. First, the Statement was never codified by the Commission’s own rulemaking procedure. Second, the Commission framed the broadband policy as a set of “guidelines,” a term considered legally vague. Third, the FCC relied on the concept of “ancillary” authority — borrowing regulatory authority from so-called “policy statements” coming from Congress, to claim jurisdiction.
Even though some in the industry favored total deregulation of broadband, most providers agreed to adhere to the Four Principles, until Comcast decided it had the right to throttle down the speed of customers using file swapping software. That violated Principle #2, and the Commission censured Comcast for purposely interfering with network traffic.
Comcast sued, claiming the Commission lacked the authority to regulate its network management policies. Comcast first denied it was throttling broadband traffic, but later admitted the company was purposely governing the speed available to such software applications to protect their other customers. Comcast argued that certain file swapping software does in fact harm its network (Principle #3) because the software utilizes as much broadband capacity it can find to move files back and forth. Since Comcast customers in a neighborhood share a limited amount of bandwidth, a small number of customers ‘maxing out their connections’ running such software could potentially slow down everyone else in the neighborhood.
Ultimately, today’s court decision agreed with Comcast — the Federal Communications Commission lacks authority over broadband.
It also did the industry one better by warning any regulatory authority the Commission believes it has over broadband better be backed up with specific authority granted by Congress, or the court may find those policies vulnerable as well.
In short, the court just fired a warning shot suggesting the FCC has no authority to enact Net Neutrality protections or the National Broadband Plan, at least not under Kevin Martin’s flawed approach.
The ruling comes as no surprise. The attorney for the FCC found a hostile reception from the court during oral arguments back in January. Where was the specific authority, granted by Congress, to oversee broadband policy they asked? Why is the Commission relying on general principles to govern broadband? By the end of the session, the FCC’s lead attorney was foreshadowing the imminent loss of his case by asking the court to make the decision against the FCC a teachable moment — giving advice in the ruling as to how to write policies that -will- survive a court test. The court wasted no time telling the attorney that wasn’t their job.
Public interest groups and others advocating Net Neutrality and the National Broadband Plan issued statements warning about the implications of an industry freed from regulatory oversight.
S. Derek Turner, research director for Free Press:
“The decision has forced the FCC into an existential crisis, leaving the agency unable to protect consumers in the broadband marketplace, and unable to implement the National Broadband Plan. As a result of this decision, the FCC has virtually no power to stop Comcast from blocking Web sites. The FCC has virtually no power to make policies to bring broadband to rural America, to promote competition, to protect consumer privacy or truth in billing. This cannot be an acceptable outcome for the American public and requires immediate FCC action to re-establish legal authority.
“This crisis is not a result of a weak congressional law, but a direct consequence of the previous two Commissions’ misguided and overzealous attempts to completely deregulate America’s communications networks. Past FCC actions created a huge loophole in the law that leaves the agency unable to protect consumer privacy or promote universal broadband access.
“The FCC must have the authority to carry out its consumer protection and public interest mission in the 21st-century broadband marketplace. The current Commission did not create this existential crisis, but it now has no choice but to face these tough jurisdictional questions head on, and do what is necessary to protect consumers and promote competition.”
Ryan Singel – Wired Magazine:
A broadband company could, for instance, ink a deal with Microsoft to transfer all attempts to reach Google.com to Bing.com. The only recourse a user would have, under the ruling, would be to switch to a different provider — assuming, of course, they had an alternative to switch to.
Companies can also now prohibit you from using a wireless router you bought at the store, forcing you to use one they rent out — just as they do with cable boxes. They could also decide to charge you a fee every time you upgrade your computer, or even block you from using certain models, just as the nation’s mobile phone carriers do today.
While this might seem like a win for the nation’s broadband and wireless companies, the ruling could be so strong that it boomerangs on them. For instance, if the FCC is left without the power to implement key portions of the National Broadband Plan — a so-far popular idea — then Congress or the FCC may have to find a way to restore power to the commission. That could leave the FCC stronger than it was before the ruling.
Gigi Sohn, Public Knowledge:
“Today’s Appeals Court decision means there are no protections in the law for consumers’ broadband services. Companies selling Internet access are free to play favorites with content on their networks, to throttle certain applications or simply to block others. In addition, as of now, the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC) ambitious National Broadband Plan to help boost the economy is in legal limbo. The ability of the FCC to support broadband through universal service is in jeopardy, as is the agency’s ability to protect consumer privacy, ensure access to broadband-based emergency communications or promote access to broadband for the disabled. In our view, the FCC needs to move quickly and decisively to make sure that consumers are not left at the mercy of telephone and cable companies.
“If it chooses, the Commission can continue to roll the dice and let the courts decide each time it wants to try to put some consumer protections on a broadband service. The court decision left open that option.
“We have a different idea. The FCC should immediately start a proceeding bringing Internet access service back under some common carrier regulation similar to that used for decades. Some parts of the Communications Act, which prohibit unjust and unreasonable discrimination, could be applied here. The Commission would not have to impose a heavy regulatory burden on the telephone and cable companies, yet consumers could once again have the benefit of legal protections and the Broadband Plan could go forward. The American public deserves no less.
“We need to emphasize that no one is talking about regulating ‘the Internet.’ No one is talking about regulating search engines or Web sites. We are talking about re-applying policies to a telecommunications service that the FCC incorrectly abandoned. That is the most simple solution and it’s the correct one.”
The FCC, despite the decisive loss in court, claims it will carry on.
“Today’s decision invalidated the prior commission’s approach, but in no way disagreed with the importance of preserving a free and open Internet,” FCC spokeswoman Jen Howard said in a statement.
Nick Summers, writing for Newsweek’s ‘Techtonic Shifts’ blog, believes FCC Chairman Julius Genachowski is likely to aggressively respond to today’s court decision by employing the “nuclear option,” reclassifying broadband Internet as a communication service just like the nation’s phone system, bringing it fully under FCC regulation.
Would Genachowski go that far, undoing virtually all of the Bush-era FCC’s policies? Yes. In September, he gave a major address about net neutrality without ever actually uttering the phrase. But he concluded with these strong words:
“We are here because 40 years ago, a bunch of researchers in a lab changed the way computers interact and, as a result, changed the world. We are here because those Internet pioneers had unique insights about the power of open networks to transform lives for the better, and they did something about it. Our work now is to preserve the brilliance of what they contributed to our country and the world. It’s to make sure that, in the 21st century, the garage, the basement, and the dorm room remain places where innovators can not only dream but bring their dreams to life. And no one should be neutral about that.”
The importance that Genachowski et al. place on net neutrality has never remotely been in doubt. In February 2009, months before he was confirmed as FCC chairman, at a private dinner in Manhattan, Genachowski spoke about the Internet’s role in the election of President Obama and in America’s future. He was circumspect about details, but Genachowski spoke unreservedly about the need for certain core protections if the country was to remain at the fore of the Internet revolution. It’s just that important.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNBC FCC Loses Comcast Case 4-6-10.flv[/flv]
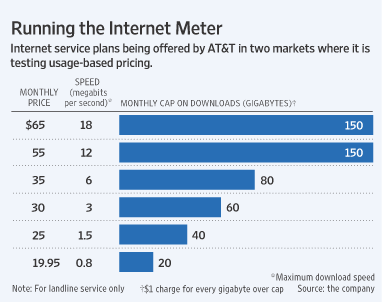
CNBC reports the FCC’s loss in court could open the door to metered broadband service in the United States. (2 minutes)
[Article Correction 4/15/2010: The original piece laid blame for the classification of broadband as an “information service” on former FCC Chairman Kevin Martin. In fact, the classification was made by former FCC Chairman Michael Powell, who served during the first term of the Bush Administration. We regret the error.]


 Subscribe
Subscribe