
Cablevision’s broadcast TV surcharge increased in January to $5.98 a month, which amounts to $71.76 a year, on top of your usual cable TV bill.
No it isn’t your imagination. While a growing number of cable television subscribers now face a “broadcast programming surcharge” on their cable bill to compensate television stations and networks for cable carriage, those same channels are larding up their programming with ever-increasing advertising. One quarter of every hour of network television is now littered with commercials — an all-time high for broadcast networks seeking to maximize advertising revenue.
Show openings have been cut to seconds, credits roll by at fast-forward speed – usually compressed into illegibility, and some cable networks have returned to the practice of chopping bits of shows and compressing playback of others to accommodate more commercials. That does not include product placement or “in-program” compensated advertising, which appears when a character picks up a can of Pepsi, walks by a Subway outlet, or reaches for a Pop-Tart for breakfast.
As early as 2009, TNS Media Intelligence found at least 36% of today’s network primetime shows were advertising-oriented. That included 7:59 of in-show brand appearances and 13:52 of commercial advertisements, for a combined total of 21:51 of marketing content.
Reality shows, as well as being cheap to produce, are product placement gold. America’s Toughest Jobs contained 44:50 per hour of advertising messages and product placement, The Biggest Loser ran up 40:37. Before the reality show craze, game shows were program-length commercials in disguise. Game show producers received an endless supply of prizes to give away in return for viewers enduring relentless 10-15 second pitches for Rice-a-Roni, crock pots, living room furniture sets, and current model cars and trucks. Viewers did not escape traditional advertisements along the way either.
Through much of the 1970s and early 1980s, an average hour of network television was between 48-52 minutes of programming, 8-12 minutes of network and local commercials. Short news breaks and public service announcements were often included during those breaks. Shows targeting children usually contained less advertising.
In 1984, the Reagan Administration deregulated broadcasters, claiming the free market was best equipped to contain any abusive practices as consumers theoretically could tune out stations and networks that allowed things to get out-of-hand.
In reality, what one network decided, the others usually followed. Outside of watching commercial-free PBS (although those sponsorship messages increasingly began to resemble traditional advertising over the years), viewers didn’t have much choice. For the last 31 years since deregulation, advertising has increased while show length has decreased. In the 1970s and 80s, pieces of rerun television shows created when ad loads were shorter were often cut from shows to make room for an extra ad or two. What was left after a trip to the cutting room was often played slightly sped-up, which made room for even more advertising. By the 1990s, producers created their shows with increasing advertising loads in mind. Short sacrificial 60-90 second end scenes, deemed non-essential to the show’s integrity, were often chopped when a show entered syndication.
In the 2000s, network executives started demanding producers drastically cut the length of show opening and closing themes. If producers didn’t, studios did it for them when a show was resold to a cable network. A rerun of Law & Order now features a 24-second opening, a big difference from the original 1:45 second opening the show had when it originally aired on NBC. End credits were usually squished on-screen to allow a 15-second network promotion to run at the top. Some networks even began their next show in one window while showing end credits of the last program in another.
But nothing affected commercial loads more than the 2008 Great Recession. Advertising revenue tumbled, along with the economy, and advertisers balked at paying traditional ad rates when online advertising was available for much less. The answer? Sell more ads… at a lower price. Once again, program lengths had to be cut to make room for the increasing number of commercials. By 2009, average network ad loads were up to 13:25 per hour. Just four years later in 2013, that number spiked to 14:15. It’s now 15 minutes and up at some networks, depending on the type of program.
As commercials neared comprising 25% of every hour of television, sponsors finally began to rebel. They were reacting to the pervasive growth of the DVR, which allowed consumers to record their favorite shows, if only to fast forward past the dense thicket of commercials. They sought a ceiling on ad loads and more creative ways to reach ad-skipping audiences numbed by relentless advertising. That meant even more product placement.
Although sponsors of expensive NBC, CBS, ABC, and FOX shows may have rebelled at the 15-minute mark, the same isn’t true with cable networks where ad loads are as high as 24 minutes per hour. In 2009, the average cable network aired 14:27 of advertisements an hour. This year, it’s up to 15:18 and still rising. Among the worst offenders:
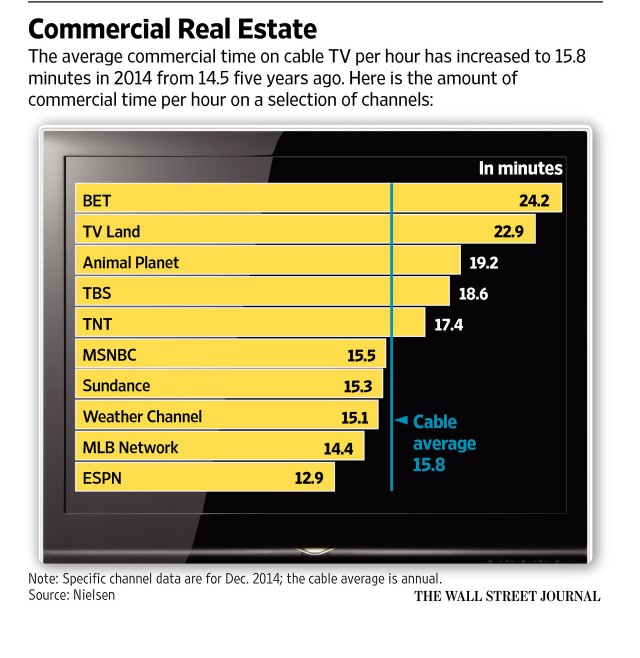
To keep the money flowing from every direction, both over-the-air and cable networks, including those noted above, continue to seek additional compensation from your provider in the form of retransmission consent and carriage agreements. Whether you watch a channel or not, you are paying for it. Some of these compensation agreements are experiencing rate increases approaching 10% annually.
To the surprise of many industry analysts, some of the worst offenders are networks with declining ratings who risk further alienating viewers with even more advertising just to keep revenue numbers up. While traditional ads actually declined by 2% on most over the air networks this year, FOX more than made up for that with a 15% increase in advertising time. The cable networks with the highest ad increases this year were Viacom-owned channels (Comedy Central, Spike, MTV, Nickelodeon) jumping 13%, A+E Networks (A&E, Crime & Investigation, Lifetime, History) increasing 10%, and 9% at Discovery Networks. Which networks increased ads the least? Those owned by Disney, independent cable networks, and Time Warner (Entertainment).
“Generally speaking, the ratings winners (Disney, 21st Century Fox, Scripps Networks) are increasing investment in original content (and not abusively increasing ad loads), whereas the losers (A+E Networks, Viacom, NBCUniversal) and the neutrals (Discovery, AMC Networks) are decelerating investment in original content and stuffing more ad spots into their shows,” said analyst Todd Juenger of Sanford C. Bernstein.
Michael Nathanson of MoffetNathanson Research worries television is repeating the mistakes commercial radio made post-deregulation, when massive increases in advertising accompanied by decelerating investment in programming repelled many listeners, perhaps for good. Some have permanently abandoned commercial over the air radio in favor of commercial free music services, satellite radio, and streaming services.
“Networks can offset ratings challenges and pricing weakness with more inventory, however, we worry that it is a dangerous long-term game that ultimately devalues the consumer experience and reduces ad efficacy,” Nathanson said. “As we saw with radio, once the increased commercial load genie is out of the bottle, it is nearly impossible to put it back in.”
When Stephen Cox was watching The Wizard of Oz on TBS last November, something didn’t sound quite right to him about the Munchkins, who are near and dear to his heart. He wasn’t imagining things. Time Warner-owned TBS used compression technology to speed up the movie. The purpose: stuffing in more TV commercials.
“Their voices were raised a notch,” Cox, the author of several pop-culture books including one about the classic 1939 film, told the Wall Street Journal. “It was astounding to me.”
The Colbert Report hilariously depicts the next generation of product placement: the retroactive ad technology of Mirriad, which can insert products into shows years after they were made. (4:04)
 The Cable Show (now known as INTX) is often used by the cable industry to announce and preview new products and services, and at this year’s convention in Chicago, Comcast CEO Brian Roberts used the occasion to introduce the company’s new DOCSIS 3.1 multi-purpose Home Gateway capable of delivering gigabit speeds over its existing hybrid fiber-coax network.
The Cable Show (now known as INTX) is often used by the cable industry to announce and preview new products and services, and at this year’s convention in Chicago, Comcast CEO Brian Roberts used the occasion to introduce the company’s new DOCSIS 3.1 multi-purpose Home Gateway capable of delivering gigabit speeds over its existing hybrid fiber-coax network.

 Subscribe
Subscribe

 If you are a long time Optimum customer, the CEO, management, and shareholders of Cablevision would like to thank you for driving average monthly cable revenue per customer 4.8% higher from a year ago to $155.34 a month.
If you are a long time Optimum customer, the CEO, management, and shareholders of Cablevision would like to thank you for driving average monthly cable revenue per customer 4.8% higher from a year ago to $155.34 a month. “The main drivers of our increased revenue per customer came from a combination of rate increases, but also lower proportion of subscribers on promotion,” said Brian G. Sweeney, chief financial officer. “We had a number of fixed rate increases January 1 of this year related to cable box fees, an increase in our sports and broadcast TV surcharge, as well as the pass-through of PEG fees to certain customers.”
“The main drivers of our increased revenue per customer came from a combination of rate increases, but also lower proportion of subscribers on promotion,” said Brian G. Sweeney, chief financial officer. “We had a number of fixed rate increases January 1 of this year related to cable box fees, an increase in our sports and broadcast TV surcharge, as well as the pass-through of PEG fees to certain customers.”
 To further combat promotion-bouncing, Cablevision is embracing its broadband product line and marketing new cord-cutting packages to customers that offer reduced-size cable television packages and free over the air antennas for local stations. The cable company also recently announced it would offer cable customers Hulu subscriptions. Jim Dolan, Cablevision CEO, believes broadband is where the money is and customers are willing to pay higher prices to get Internet access even when video package pricing has its limits.
To further combat promotion-bouncing, Cablevision is embracing its broadband product line and marketing new cord-cutting packages to customers that offer reduced-size cable television packages and free over the air antennas for local stations. The cable company also recently announced it would offer cable customers Hulu subscriptions. Jim Dolan, Cablevision CEO, believes broadband is where the money is and customers are willing to pay higher prices to get Internet access even when video package pricing has its limits.



 The largest telecom companies in the United States, their trade associations, and Ajit Pai, one of two Republican commissioners serving at the Federal Communications Commission routinely claim America has the best broadband in the world. From the perspective of providers running to their respective banks to deposit your monthly payment, they might be right. But on virtually every other metric, the United States has some of the most expensive broadband in the world at speeds that would be a gouging embarrassment in other countries.
The largest telecom companies in the United States, their trade associations, and Ajit Pai, one of two Republican commissioners serving at the Federal Communications Commission routinely claim America has the best broadband in the world. From the perspective of providers running to their respective banks to deposit your monthly payment, they might be right. But on virtually every other metric, the United States has some of the most expensive broadband in the world at speeds that would be a gouging embarrassment in other countries.
 The Slovak government insisted that telecommunications networks in the country be competitive and it maintains oversight to make sure monopolies do not develop. It rejected claims that total deregulation and competition alone would spur investment. Slovakia welcomes outside investment, but also makes certain monopoly pricing power cannot develop. As a result, most residents of Bratislava have a choice of up to eight different broadband providers — a mix of cable, telephone, wireless, and satellite providers that all fiercely compete in the consumer and business markets.
The Slovak government insisted that telecommunications networks in the country be competitive and it maintains oversight to make sure monopolies do not develop. It rejected claims that total deregulation and competition alone would spur investment. Slovakia welcomes outside investment, but also makes certain monopoly pricing power cannot develop. As a result, most residents of Bratislava have a choice of up to eight different broadband providers — a mix of cable, telephone, wireless, and satellite providers that all fiercely compete in the consumer and business markets. Prices are considerably lower than what American providers charge, although speeds remain somewhat lower than broadband services in Bulgaria, Romania, and the Baltic States. At one address on Kláštorská, a street of modest single family homes (some in disrepair), these companies were ready to install service:
Prices are considerably lower than what American providers charge, although speeds remain somewhat lower than broadband services in Bulgaria, Romania, and the Baltic States. At one address on Kláštorská, a street of modest single family homes (some in disrepair), these companies were ready to install service: