 It’s all hands on deck for a cable industry desperate to protect billions in revenue earned from a monopoly stranglehold on the set-top box, now under threat by a proposal at the FCC to open up the market to competition.
It’s all hands on deck for a cable industry desperate to protect billions in revenue earned from a monopoly stranglehold on the set-top box, now under threat by a proposal at the FCC to open up the market to competition.
While cable industry groups decry the proposal as a solution looking for a problem, at least 99 percent of cable customers are required to lease the equipment they need to watch pay television. That has become a reliable source of revenue for the industry and set-top box manufacturers, who share the $231 each customer pays a year in rental fees. Collectively that amounts to $20 billion in annual revenue. The FCC argues there is ample evidence cable operators and manufacturers are taking advantage of that captive marketplace, raising rental fees an average of 185% over the last 20 years while other electronic items have seen price declines as much as 90 percent.
With that kind of money on the line and a recent statement from the Obama Administration it fully supports FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler’s proposal, Wall Street has gotten jittery over cable stocks — a clear sign investors are worried about the economic impact of additional competition and lower prices.

Wheeler
“Instead of spending nearly $1,000 over four years to lease a set of behind-the-times boxes, American families will have options to own a device for much less money that will integrate everything they want — including their cable or satellite content, as well as online streaming apps — in one, easier-to-use gadget,” Jason Furman, chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers, wrote in a White House blog post.
The proposal would coordinate the establishment of an “open standard” for set-top box technology, making it possible for multiple manufacturers to enter the market and compete.
The idea is not without precedent. The cable modem marketplace uses a DOCSIS standard any manufacturer can use to launch their own modem. Once the modem is certified, broadband consumers can choose to either rent the modem from their cable operator ($10 a month from Time Warner) or buy one outright, usually for less than $70, easily paying for itself in less than one year.
But the set-top box proposal just doesn’t add up, argues Comcast — one of the strongest opponents of Chairman Wheeler’s proposal.
“A new government technology mandate makes little sense when the apps-based marketplace solution also endorsed by the FCC’s technical advisory committee is driving additional retail availability of third-party devices without any of the privacy, diversity, intellectual property, legal authority, or other substantial concerns raised by the chairman’s mandate,” wrote David Cohen, Comcast’s top lobbyist.
The National Cable and Telecommunications Association (NCTA) — the country’s largest cable industry lobbying group, said much the same thing.

The Roku set-top streaming device.
“By reading the White House blog, you have to wonder how they could ignore that the world’s largest tech companies — which are often touted in other Administration initiatives — including Apple, Amazon, Google, Netflix and many others are providing exactly the choice in video services and devices that they claim to want,” the NCTA wrote.
Their argument is that a competitive set-top box market has already emerged without any interference from the FCC. Time Warner Cable, for example, voluntarily offers most of its lineup on the Roku platform. Comcast’s XFINITY TV app allows subscribers to watch cable channels over a variety of iOS and Android devices. Several operators also support videogame consoles as an alternative to renting set-top boxes.
But few allow customers to completely escape renting at least one set-top box, especially for premium movie channels. Others don’t support more than one or two streaming video consoles like Roku, Apple TV, or Amazon Fire TV.
In Canada, cable customers can often buy their own set-top boxes and DVRs (known as PVRs up north) from major electronics retailers like Best Buy. For example, Shaw customers in western Canada can purchase a XG1 500GB HD Dual Tuner PVR with 6 built-in tuners and a 500GB hard drive (upgradable), which supports recording up to 6 HD shows simultaneously, for under $350. With some cable companies charging up to $15 a month for similar equipment, it would take just under two years to recoup the purchase cost. Many cable subscribers rent the same DVR for as long as five years before the hard drive starts acting up, necessitating replacement (of the drive).

Endangered cable network? Minority programmers say set-top box competition will destroy their networks.
Arguing the technical issues of cable box competition isn’t apparently enough of a winning argument, so the industry has drafted the support of minority cable programmers and friendly legislators who have taken Hyperbole Hill with declarations that set-top box competition will result in “the ultimate extinction of minority and special-interest programmers.”
How?
A competitive set-top box manufacturer may decide to ignore the way cable channels are now numbered on the cable dial. With everything negotiable, many programmers offer discounts or other incentives to win a lower channel number, avoiding the Channel Siberia effect of finding one’s network on a four digit channel number that channel surfers will likely never reach.
Their fear is that an entity like Google or Apple will pay no attention to how Comcast or Time Warner chooses to number its channels, and will use a different system that puts the most popular channels first.
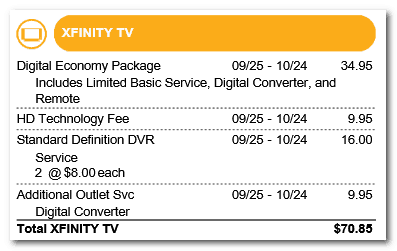
Fees: $34.95 for TV package, $35.90 in equipment and service fees.
But that assumes consumers care about channel numbers and not programs. Those who argue the days of linear TV are coming to an end doubt opening the set-top box market up for competition presents the biggest threat to these minority and specialty programmers. Those that devote hours of their broadcast day to reruns and program length commercials are probably at the most risk, because they lack quality original programming viewers want to see.
Hal Singer, who produces research reports for the telecom industry-backed Progressive Policy Institute, even goes as far as to suggest competitive set-top boxes will discourage telephone companies from building fiber to the home service, because they won’t get the advertising revenue for TV service they might otherwise receive from a captive set-top box market. But Singer ignores the fact Verizon effectively stopped substantial expansion of its FiOS network in 2010 (except in Boston) and AT&T now focuses most of its marketing on selling DirecTV service to TV customers, not U-verse – it’s fiber to the neighborhood service.
But Singer may be accurate on one point. If the cable industry loses revenue from set-top box rental fees, it may simply raise the rates it charges for cable television to make up the difference.
“So long as high-value customers for home video also demand more set-top boxes—a reasonable assumption—then pay TV operators can use metering to reduce the total price of home entertainment for cable customers,” Singer opines. “If this pricing structure were upended by the FCC’s proposal, economic theory predicts that pay TV prices would rise, thereby crowding out marginal video customers.”


 Subscribe
Subscribe Comcast is taking its well-known reputation for being loathed in the cable business to the world of theme parks, where a trip to Comcast-owned Universal Studios Hollywood
Comcast is taking its well-known reputation for being loathed in the cable business to the world of theme parks, where a trip to Comcast-owned Universal Studios Hollywood  The Communications Workers of America has told the New York Public Service Commission it should reject Altice’s proposal to buy Cablevision for more than $17 billion, claiming it’s a bad deal for customers and employees alike.
The Communications Workers of America has told the New York Public Service Commission it should reject Altice’s proposal to buy Cablevision for more than $17 billion, claiming it’s a bad deal for customers and employees alike. “As late as the morning of Feb. 5, [the Joint Applicants] have continued their grudging and incomplete disgorgement of relevant and probative material to which CWA is entitled,” the CWA wrote. “CWA now possesses documents and data which are contradictory and require reconciliation.”
“As late as the morning of Feb. 5, [the Joint Applicants] have continued their grudging and incomplete disgorgement of relevant and probative material to which CWA is entitled,” the CWA wrote. “CWA now possesses documents and data which are contradictory and require reconciliation.” New York City’s Office of the Public Advocate is no fan either. In
New York City’s Office of the Public Advocate is no fan either. In 
 DirecTV under AT&T’s ownership is turning out to be no bargain for customers finding it increasingly tough getting a promotional rate package with the satellite provider.
DirecTV under AT&T’s ownership is turning out to be no bargain for customers finding it increasingly tough getting a promotional rate package with the satellite provider.
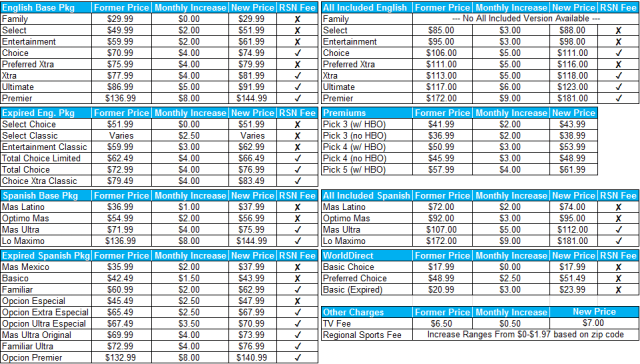
 A behind the scenes struggle between DISH Networks and Charter Communications over DISH’s online video service Sling TV has led to an admission by a Wall Street analyst that “usage-based billing” is an important tool for stifling over-the-top online video competition.
A behind the scenes struggle between DISH Networks and Charter Communications over DISH’s online video service Sling TV has led to an admission by a Wall Street analyst that “usage-based billing” is an important tool for stifling over-the-top online video competition.
