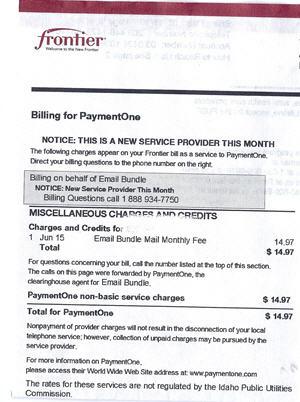
Frontier has dealt with PaymentOne for years. This bill shows unauthorized cramming charges billed to a Frontier customer in the fall of 2010.
An Oregon man found himself facing $300 in early termination fees from Frontier Communications after the phone company first refused to intervene on his behalf and credit his account for unauthorized “phone cramming” charges.
Tim Curns was with Frontier since the 1990s, but not anymore.
“I pulled the plug,” Curns told KGW-TV after unsuccessfully trying to get Frontier to help remove an unauthorized charge from his land line phone bill.
Curns found a $14.95 charge on his bill from something called “PaymentOne.” When he called Frontier, they could not tell him what the charge was for and at first refused to credit him for the unauthorized charge. That is surprising because Frontier has been billing customers on behalf of PaymentOne for more than two years.
With Frontier uninterested in investigating the phone cramming incident, Curns was told he would be on his own trying to stop PaymentOne from billing his phone line every month.
Curns tried to tackle the problem himself, first calling PaymentOne and learning the company had enrolled his line for the service despite having the wrong mailing address on file. Frontier, upon learning that, eventually agreed to a one-time courtesy credit but could not promise additional charges would not be forthcoming the following month.
Engraged, Curns said if Frontier could not stop unauthorized charges, he could stop being their customer. At that point, the Frontier representative surprised Curns with news he was unknowingly committed to a two-year service contract, and he could cancel his service… if he paid around $300 in early termination fees.
That would leave PaymentOne with their money, Frontier enriched on an early termination fee the customer never knew he would owe, and little left in Curns’ wallet.
“My question to the phone company was, okay, if you make an adjustment on this bill for 14.95 what are you going to do to stop this from being a recurring charge,” Curns said, “and they said there’s nothing they can do, you have to call these people.”
So Curns called and said PaymentOne told him the name of that company is My Global 4-1-1, which is a front company for a firm called Doink Media LLC, which the Federal Trade Commission been chasing all over the country.
Kyle Kavas, Spokesperson for The Better Business Bureau said, “most of the time it’s just companies that are randomly picking out phone numbers and charging them. Those cramming charges are very dangerous because they come from companies that are usually scammers.”
KGW received this less-than-helpful statement from Frontier:
 “Frontier takes customer concerns very seriously and always tries to make things right. Our normal policy on a ‘cramming’ issue, which is an unauthorized charge on a customer’s account, is to assist the customer in contacting the 3rd party company who added the charge. These 3rd party companies get a customer authorization from the customer although in some cases the customer doesn’t realize they’ve authorized the charge. An easy way to avoid these is to have a 3rd party block put on your account by calling Frontier Customer Service.”
“Frontier takes customer concerns very seriously and always tries to make things right. Our normal policy on a ‘cramming’ issue, which is an unauthorized charge on a customer’s account, is to assist the customer in contacting the 3rd party company who added the charge. These 3rd party companies get a customer authorization from the customer although in some cases the customer doesn’t realize they’ve authorized the charge. An easy way to avoid these is to have a 3rd party block put on your account by calling Frontier Customer Service.”
Curns called Frontier and learned although the company does not currently charge a fee for third party charge-blocking, it might in the future.
What Frontier doesn’t admit is that it earns a piece of the action from every phone cramming charge found on a customer’s bill.
Curns ultimately decided to pull the plug on Frontier for good, paid a pro-rated early termination fee, and recommended other customers follow in his footsteps before unauthorized third party charges make their way to another phone bill.
For now, customers can call Frontier customer service and request all third party charges be blocked from your phone line. The service is free of charge, although there are no guarantees it will always remain that way. It would also be a good time to review your current account and learn if Frontier has put you on a contract plan with an early termination fee attached. If you did not authorize this, demand it be removed from your account at once. If you did authorize it, have Frontier note your account that you do not want it automatically renewed at the end of the term, a practice Frontier regularly engages in, and note your contract expiration date.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KGW Portland Frontier Cramming 6-26-12.mp4[/flv]
KGW-TV visits with Tim Curns to discuss Frontier’s “look the other way” attitude about phone cramming charges. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe






