 Despite dozens of new state laws and an effort by lawmakers to make metal theft a federal crime carrying a 10-year prison sentence, the epidemic of copper cable theft is expected to get worse before it gets better. The reason? China’s insatiable demand for North America’s enormous supply of discarded and stolen wire.
Despite dozens of new state laws and an effort by lawmakers to make metal theft a federal crime carrying a 10-year prison sentence, the epidemic of copper cable theft is expected to get worse before it gets better. The reason? China’s insatiable demand for North America’s enormous supply of discarded and stolen wire.
“The FBI has indicated that there’s so much theft taking place that it’s causing a national infrastructure issue,” said Lt. Terry Alling, a law enforcement official who now consults with police departments on how to recognize and curtail valuable metal thefts.
Scrap copper used to end up in the trash, especially telephone and coaxial cable used by phone and cable companies. With bare, high quality copper wiring valued at only $0.50 a pound for years, many scrap dealers were uninterested in shielded telecom cables that were a costly nuisance to process for recycling.
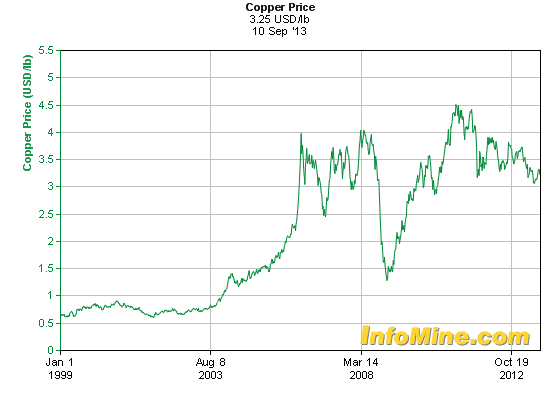
That changed in late 2003 when copper prices began a dramatic rise, first doubling to $1 a pound by 2004 and then suddenly spiking to an eye-popping $4 by 2006. Only the arrival of the Great Recession in 2008 would temporarily stem demand, dropping prices below $1.50 a pound. Two years later, prices dramatically rebounded, reaching an all time high of $4.50 a pound, and have remained above $3 ever since.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KOMO Seattle Copper Theft Epidemic 5-6-13.mp4[/flv]
KOMO in Seattle went undercover to sell scrap copper and quickly discovered why copper wire theft is now an epidemic — scrap dealers are ignoring the law and buying suspect copper with no questions asked. (5 minutes)
As prices have increased, so have copper thefts. Starting about a decade ago, law enforcement personnel discovered they were responding to a growing wave of reports of stolen manhole covers, copper pipe taken from abandoned buildings or construction sites, copper air conditioner coils gone missing, and even statues and other art work ripped out of the ground.
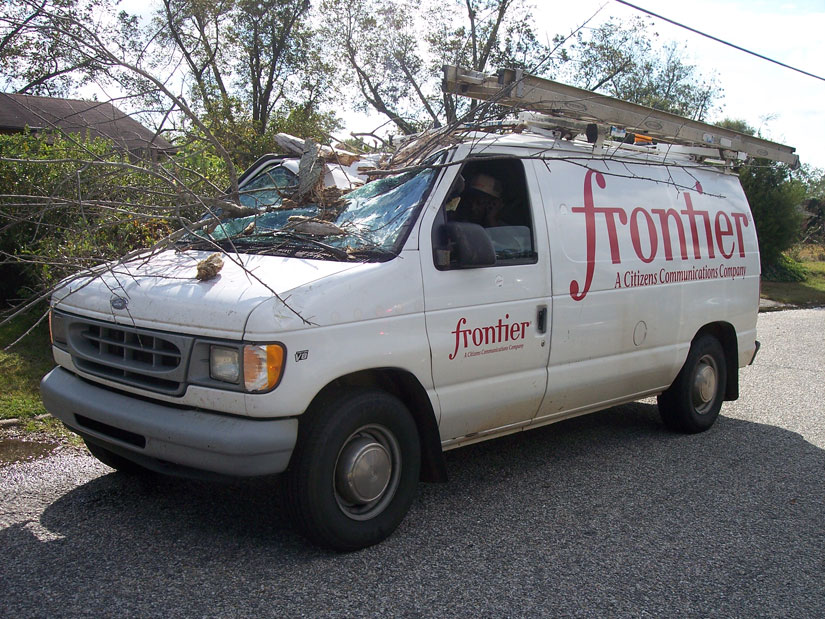
 Outside of the risk of falling into a manhole missing its cover, the biggest threat to public safety has come from utility infrastructure theft. Brazen thieves have shown their interest in turning scrap metal into cash has taken a priority over their personal safety and yours. Amazed utility workers were shocked to find thieves even willing to steal infrastructure from live power substations, often leaving customers in the dark as a result. A less risky, but just as profitable strategy has come from harvesting telephone cable right off of telephone poles, knocking out service for hundreds or thousands of customers as a result.
Outside of the risk of falling into a manhole missing its cover, the biggest threat to public safety has come from utility infrastructure theft. Brazen thieves have shown their interest in turning scrap metal into cash has taken a priority over their personal safety and yours. Amazed utility workers were shocked to find thieves even willing to steal infrastructure from live power substations, often leaving customers in the dark as a result. A less risky, but just as profitable strategy has come from harvesting telephone cable right off of telephone poles, knocking out service for hundreds or thousands of customers as a result.
Some of the worst problems for telecom companies are in rural areas and smaller cities where thieves can remove cable with a good chance of not being seen.
In the Pacific Northwest, Spokane experienced cable theft from area substations. In Olympia, $30,000 of electric cable was stripped from street lights.
Three soccer fields in Federal Way experienced repeated copper theft, resulting in $150,000 in damages, despite efforts by the Federal Way Soccer Association to discourage thieves.
“We’ve changed the locks in all the systems, we’ve gone to gluing down doors on the boxes — nothing is stopping them,” said George Fifer.
Frontier Communications customers in Washington have been among the hardest hit. Last year, Frontier reported 10 major outages as a result of copper wire theft in the state. Frontier’s problems are nearly as bad in Ohio and West Virginia, those states being hit the most often. This year is more of the same in Washington, with at least 2,000 Frontier customers knocked out of service since April.
Frontier Communications has reported lines being stolen in Snohomish, Skykomish and Granite Falls, causing temporary outages for customers throughout north King and Snohomish counties.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KCPQ Seattle Thieves ripping out bulk phone lines 7-25-13.flv[/flv]
In July, KCPQ in Seattle reported copper thieves struck again, wiping out phone service in parts of Snohomish County, Wash. Nearly 2,000 Seattle-area customers have been hit so far. (3 minutes)
 “Customers are taken out of service, they’re put at risk, they can’t call 911,” said Frontier Communications general Manager Ken Baldwin. “The emergency folks can’t run the trace and know where they need to be.”
“Customers are taken out of service, they’re put at risk, they can’t call 911,” said Frontier Communications general Manager Ken Baldwin. “The emergency folks can’t run the trace and know where they need to be.”
Alling estimates at least 90 percent of the copper theft is committed by meth addicts, motivated by their habit and unafraid to take risks.
They rely on selling their stolen copper to a network of scrap dealers that pay consumers and construction firms for “recovered/unwanted metals.” Although many scrap dealers operate legitimate businesses and don’t want to deal in stolen copper, there are more than a few willing to look the other way. Those dealers typically pay quick cash at below market prices to people who cannot credibly explain where the weekly bales of phone cable are coming from, so they don’t ask.
There is usually little risk to the dealers, who are unlikely to leave stolen copper in the storage yard for very long.
Alling says the copper crime wave is being fed by insatiable demand from the booming economy of China.
“They’re buying all the copper that they can get their hands on,” Alling said. “It’s speculated that they’re stockpiling and there’s not going to be any slowdown whatsoever for an extended period. The price is going to stay up which means that theft is going to stay up as well.”
A forthcoming book excerpted by Bloomberg Business Week seems to confirm Alling’s experience.
“Junkyard Planet: Travels in the Billion-Dollar Trash Trade,” published in November by Bloomsbury Publishing, digs deep into the world of scrap metal and the Asian metal market that increasingly drives most of the demand.
[flv width=”576″ height=”344″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KCPQ Seattle Copper wire theft becoming an epidemic 1-2013.flv[/flv]
Washington’s Most Wanted reports wire theft is becoming an epidemic in the Pacific Northwest, costing taxpayers hundreds of thousands of dollars and risking public safety. Now local law enforcement is learning how to fight back. (3 minutes)
 China alone accounted for 43.1 percent of all global copper demand in 2012, writes Adam Minter, more than five times the amount of copper acquired by the U.S. that same year. For at least a decade, China has imported 70 percent of the scrap copper it uses to power its enormous manufacturing and construction industries. China’s most attractive source for recycled copper? The United States.
China alone accounted for 43.1 percent of all global copper demand in 2012, writes Adam Minter, more than five times the amount of copper acquired by the U.S. that same year. For at least a decade, China has imported 70 percent of the scrap copper it uses to power its enormous manufacturing and construction industries. China’s most attractive source for recycled copper? The United States.
Minter writes at least 100 roving Chinese scrap dealers are traveling across the country in rental cars from scrap yard to scrap yard. They come ready to buy… a lot. Some scrap dealers receive visitors from China almost daily. Minter notes many of those 100 will spend an average of $1 million a week on discarded (or stolen) copper, much of it considered “low-grade” by American dealers because it requires cumbersome and expensive processing before it can be melted down or reused in new ways.
That is no problem for scrap dealers like Johnson Zeng, employed by a scrap importer in China’s Guangdong Province.
As Zeng browses one scrap yard in St. Louis, his interest piques when he sees bales and boxes of power lines and what the scrap trade calls “jelly.”
This is where Frontier Communications and other phone companies come in.
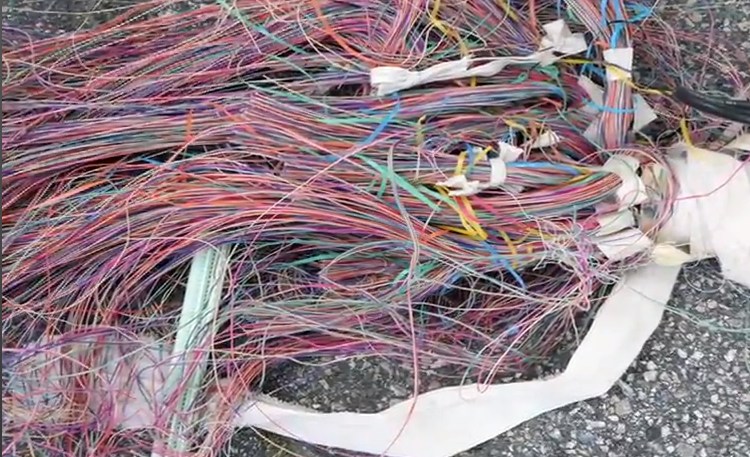
Much of the stolen telephone cable sold for scrap contains hundreds, if not thousands of individual copper wires, each wrapped in insulation and in turn wrapped around a thick black sheath to keep the weather out. This is the cable one might find serving entire neighborhoods or business blocks with landline phone service and DSL. If you cut into that cable, often 2″ in diameter, there is a chance it would begin oozing a Vaseline-like gel — the “jelly” Zeng has an interest in. That goo is primarily designed to keep underground phone cables dry because it helps repel corrosion-causing moisture.

A minimum order for a Chinese exporter typically needs to fill at least one shipping container of this size.
Minter notes American recyclers hate jelly cable because it clogs their processing equipment. In China, it is in high demand because it is cheaply obtained and can be processed by an army of workers that cut the cable apart and wash away the petroleum product by hand.
Without the demand for “low-grade” copper wiring such as telephone cables coming from abroad, thieves would be unlikely to find any interest for their ill-gotten gains.
Cable companies have it easier. Asian exporters have shown little interest in coaxial cable because the effort to free the copper center conductor from the thick plastic sheath and wire netting that surrounds it is, for now, not worth it.
The demand on scrap dealers to maintain sufficient inventory to keep the roving band of exporters coming back is intense. Most Chinese buyers need a minimum order of one shipping container holding at least 40,000 pounds to make the deal worthwhile. Those containers are the size of a load driven by an 18-wheeler tractor-trailer.
At just one scrap yard, Zeng offered to buy all 10,000 pounds of “jelly” phone cable — all the dealer had in stock that day — 5,000 pounds of “grease wire,” and a large quantity of discarded Christmas tree light strings — another popular target for Asian exporters looking for cheap low-grade wire.
Within hours, Zeng would be back inside his rental car traveling to the next scrap dealer in a journey that took him from Illinois to South Carolina.
The recycling industry points out that if the Chinese were not in the market for American wire, it would end up in a landfill because copper demand within the United States is too low to justify the processing and labor costs to recycle it.
But that demand also fuels the growing copper theft plaguing the United States, and that costs every American taxpayer.
“The Department of Energy estimates that for every $100 that a copper thief actually gets in stolen materials, it costs $5,000 in repairs,” Alling said.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KXLY Spokane Copper Theft Law 7-2013.flv[/flv]
KXLY in Spokane reports miles of live power cables have been stolen by copper thieves. It takes a small amount of copper wire to make a lot of money, encouraging thieves to take more risks for bigger payoffs. Now a new Washington state law includes a “no-buy” list that keeps repeat offenders from selling to dealers in adjacent counties. (3 minutes)
 Alling blames the meth addicts who commit the crimes, but also fingers scrap metal dealers who buy without asking questions. The source of stolen copper varies in different parts of the country. While telecommunications lines are most affected in rural communities, copper pipes and air conditioning coils are favorite targets in urban areas.
Alling blames the meth addicts who commit the crimes, but also fingers scrap metal dealers who buy without asking questions. The source of stolen copper varies in different parts of the country. While telecommunications lines are most affected in rural communities, copper pipes and air conditioning coils are favorite targets in urban areas.
Most states have enacted new laws to curb the trade in stolen copper. Many require dealers to demand ID from sellers and keep detailed purchase records allowing law enforcement to identify the source of stolen cable found at scrap yards. Others require a license to sell copper to recyclers, a limit on the amount of scrap that can be sold to a dealer, and provisions for stiff fines and jail time for those caught buying or selling stolen metal.
In some states like West Virginia, tougher copper theft laws are beginning to curb thieves, but in South Carolina the thefts continue, despite the fact the state requires sellers of copper to first obtain a permit from a local sheriff’s office before selling their metal.
New Jersey Gov. Chris Christie vetoed a state copper theft control measure in New Jersey last week, claiming it would impose “overly burdensome regulations” on the state’s scrap dealers. The bill would have required that all payments for scrap metal be made by non-transferrable check unless the seller has a photo ID on file with the scrap company, and that businesses could only accept deliveries made by motor vehicle, allowing firms to record the buyer’s plates and driver’s license.
Sen. Charles Schumer (D-N.Y.) and Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.), are tackling copper theft on the federal level by co-sponsoring the Metal Theft Prevention Act – a proposal to make stolen metal a federal crime.

Klobuchar
S. 394 and its House companion bill H.R. 867 would impose a 10-year prison sentence on anyone caught stealing metal from telephone or cell towers, highway equipment or other critical infrastructure. The bill would also make it tougher to fence stolen metal by requiring more record-keeping for recycling agents, and prohibiting them from paying cash for purchases larger than $100.
Klobuchar claims copper theft has shot up by 80 percent in recent years and she wants to put a dent in it.
“The recent rise in incidents of metal theft across the country underscores the importance of federal action to crack down on metal thieves, put them behind bars and make it more difficult for them to sell their stolen goods,” Klobuchar said.
Despite some bipartisan support, Govtrack.us estimates the measure has only a 7% chance of getting past committee and a 3% chance of being passed in the House of Representatives, noting the Republican-controlled body voted only 11% of bills out of committee and only about 3% were enacted over the last two years. The companion bill in the U.S. Senate has already passed a committee vote, so Govtrack estimates it has a 40% chance of passing a full Senate vote, assuming it is not filibustered.
The federal measure is getting significant opposition from Republicans who argue it violates states’ rights to manage the problem through legislation on the state level.
“I have heard concerns expressed regarding people stealing valuable metal and crossing state lines to sell the stolen product,” said Sen. Mike Lee (R-Utah). While I would support federal legislation addressed to such truly interstate circumstances, legislation that more broadly regulates intrastate conduct is constitutionally problematic. In my view, this bill exceeds Congress’s power under the Commerce Clause and imposes a federal regulatory scheme in an area of law the Constitution reserves to the states. In the interest of maintaining the balance between state and federal authority, I will vote against reporting this bill from the Judiciary Committee.”
Alling says in some communities copper thieves have gotten organized into gangs targeting valuable infrastructure, so while legislators work the problem on their end, local police need to organize themselves to combat it.
Alling said police should be on the lookout for thieves with tools like headlamps, bolt cutters and a change of clothes. Police should also search the area where the copper was stolen because often, the bad guys stash the metal nearby until they can remove it without getting caught.
Individuals can also report suspicious activity themselves by calling 911. In some areas, reward funds have been established by utilities for tips that lead to the successful prosecution of metal thieves.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KOMO Seattle Copper Thieves Plague Washington 9-10-13.mp4[/flv]
KOMO in Seattle reports Frontier Communications has been plagued with copper cable thefts for the last two years, cutting off critical 911 services to affected residents. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe Despite dozens of new state laws and an effort by lawmakers to make metal theft a federal crime carrying a 10-year prison sentence, the epidemic of copper cable theft is expected to get worse before it gets better. The reason? China’s insatiable demand for North America’s enormous supply of discarded and stolen wire.
Despite dozens of new state laws and an effort by lawmakers to make metal theft a federal crime carrying a 10-year prison sentence, the epidemic of copper cable theft is expected to get worse before it gets better. The reason? China’s insatiable demand for North America’s enormous supply of discarded and stolen wire. Outside of the risk of falling into a manhole missing its cover, the biggest threat to public safety has come from utility infrastructure theft. Brazen thieves have shown their interest in turning scrap metal into cash has taken a priority over their personal safety and yours. Amazed utility workers were shocked to find thieves even willing to steal infrastructure from live power substations, often leaving customers in the dark as a result. A less risky, but just as profitable strategy has come from harvesting telephone cable right off of telephone poles, knocking out service for hundreds or thousands of customers as a result.
Outside of the risk of falling into a manhole missing its cover, the biggest threat to public safety has come from utility infrastructure theft. Brazen thieves have shown their interest in turning scrap metal into cash has taken a priority over their personal safety and yours. Amazed utility workers were shocked to find thieves even willing to steal infrastructure from live power substations, often leaving customers in the dark as a result. A less risky, but just as profitable strategy has come from harvesting telephone cable right off of telephone poles, knocking out service for hundreds or thousands of customers as a result. “Customers are taken out of service, they’re put at risk, they can’t call 911,” said Frontier Communications general Manager Ken Baldwin. “The emergency folks can’t run the trace and know where they need to be.”
“Customers are taken out of service, they’re put at risk, they can’t call 911,” said Frontier Communications general Manager Ken Baldwin. “The emergency folks can’t run the trace and know where they need to be.” China alone accounted for 43.1 percent of all global copper demand in 2012, writes Adam Minter, more than five times the amount of copper acquired by the U.S. that same year. For at least a decade, China has imported 70 percent of the scrap copper it uses to power its enormous manufacturing and construction industries. China’s most attractive source for recycled copper? The United States.
China alone accounted for 43.1 percent of all global copper demand in 2012, writes Adam Minter, more than five times the amount of copper acquired by the U.S. that same year. For at least a decade, China has imported 70 percent of the scrap copper it uses to power its enormous manufacturing and construction industries. China’s most attractive source for recycled copper? The United States.
 Alling blames the meth addicts who commit the crimes, but also fingers scrap metal dealers who buy without asking questions. The source of stolen copper varies in different parts of the country. While telecommunications lines are most affected in rural communities, copper pipes and air conditioning coils are favorite targets in urban areas.
Alling blames the meth addicts who commit the crimes, but also fingers scrap metal dealers who buy without asking questions. The source of stolen copper varies in different parts of the country. While telecommunications lines are most affected in rural communities, copper pipes and air conditioning coils are favorite targets in urban areas.

 Cable operators and publicly owned utilities in Tennessee are battling for control over the prices companies pay to use utility poles, with facts among the early casualties.
Cable operators and publicly owned utilities in Tennessee are battling for control over the prices companies pay to use utility poles, with facts among the early casualties.






