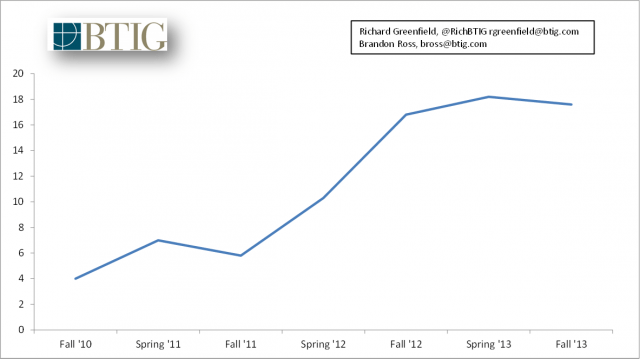
The median bandwidth use slowdown (Image: BTIG Research)
Despite perpetual cries of Internet brownouts, usage blowouts, and data tsunamis that threaten to overwhelm the Internet, new data shows broadband usage has leveled off in North America, undercutting providers’ favorite excuse for usage limits and consumption billing.
Sandvine today released its latest broadband usage study, issued twice yearly. The results show a clear and dramatic decline in usage growth in North America, with median usage up just 5% compared to the same time last year. That is a marked departure from the 190% and 77% growth measured in two earlier periods. In fact, as Richard Greenfield from BTIG Research noted, mean bandwidth use was down 13% year-over-year, after the second straight six month period of sequential decline.
Companies like Cisco earn millions annually pitching network management tools to providers implementing usage caps and consumption billing. For years, the company has warned of Internet usage floods that threaten to make the Internet useless (unless providers take Cisco’s advice and buy their products and services).
“Demand for Internet services continues to build,” said Roland Klemann from Cisco’s Internet Business Solutions Group. “The increasing popularity of smartphones, tablets, and video services is creating a ‘data tsunami’ that threatens to overwhelm service providers’ networks.”
Providers typically use “fairness” propaganda when introducing “usage based pricing,” blaming exponential increases in broadband usage and costly upgrades “light users” are forced to underwrite. A leveling off in broadband usage undercuts that argument.
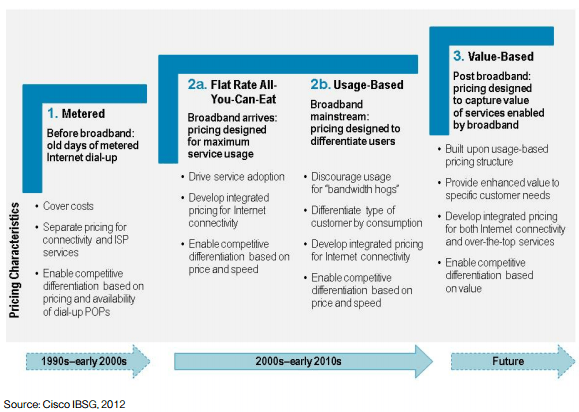 A Cisco White Paper intended for the eyes of Internet Service Providers further strips the façade off the false-“fairness” argument, exposing the fact usage pricing has little to do with traffic growth, pricing fairness, or the cost of upgrades:
A Cisco White Paper intended for the eyes of Internet Service Providers further strips the façade off the false-“fairness” argument, exposing the fact usage pricing has little to do with traffic growth, pricing fairness, or the cost of upgrades:
In 2011, broadband services became mainstream in developed countries, with fixed-broadband penetration exceeding 60 percent of households and mobile broadband penetration reaching more than 40 percent of the population in two-thirds of Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries.
Meanwhile, traditional voice and messaging revenues have strongly declined due to commoditization, and this trend is expected to continue. Therefore, operators are now relegated to connectivity products. The value that operators once derived from providing value-added services is migrating to players that deliver services, applications, and content over their network pipes.
As if this were not enough, Internet access prices are dropping, sales volumes are declining, and markets are shrinking. The culprit: flat rate “all-you-can-eat” pricing. Such a model lacks stability—sending service provider pricing into a downward spiral—because it ignores growth potential and shifts the competition’s focus from quality and service differentiation to price.
While Klemann was spouting warnings about the dire implications of a data tsunami, Cisco’s White Paper quietly told providers what they already know:
Maximum Profits
“[Wired] broadband operators should be able to sustain forecasted traffic growth over the next few years with no negative impact on margins, as the incremental capital expenses required to support it are under control.”
If usage limits and consumption billing are not required to manage data growth or cover the cost of equipment upgrades, why adopt this pricing? The potential to exploit more revenue from mature broadband markets that lack robust competition.
“In light of the forecasted Internet traffic growth mentioned earlier and competitiveness in the telecommunications market, Cisco believes that fixed-line operators should consider gradually introducing selected monthly traffic tiers to sustain [revenue], while a) signaling to customers that “traffic is not free,” and b) monetizing bandwidth hogs more sustainably.”
Cisco makes its recommendation despite knowing full well from its own research that customers hate usage-based pricing.
“The introduction of traffic tiers and caps—especially for fixed broadband services—is not welcomed by the majority of customers, as they have learned to ‘love’ flat rate all-you-can-eat pricing. Most customers consider usage-based pricing for broadband services ‘unfair,’ according to the 2011 Cisco IBSG Connected Life Market Watch study.”
Cisco teaches providers how to price broadband like trendy boutique bottled water and blame it on growing Internet usage.
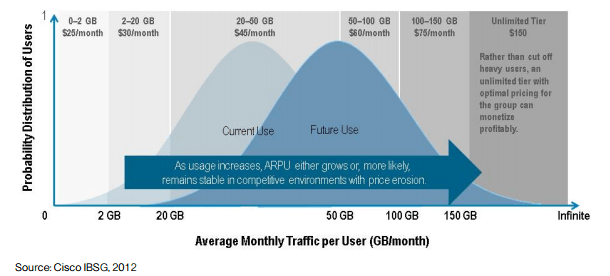
But with competition lacking, Cisco’s advice is to move forward anyway, as long as providers initially introduce caps and consumption billing at prices that do not impact the majority of customers… at first. In uncompetitive markets, Cisco predicts customers will eventually pay more, boosting provider revenue. Cisco’s “illustrative example” of usage billing in practice set prices at $45 a month for up to 50GB of usage, $60 a month for 50-100GB, $75 for 100-150GB, and $150 a month for unlimited access — more than double what customers typically pay today for flat rate access.
Usage billing arrives right on time to effectively handle online video, which increasingly threatens revenue from cable television packages.
Sandvine’s new traffic measurement report notes the increasing prominence of online video services like Netflix, YouTube, Hulu, and Amazon Video.
“As with previous reports, Real-Time Entertainment (comprised of streaming video and audio) continues to be the largest traffic category on virtually every network we examined, and we expect its continued growth to lead to the emergence of longer form video on mobile networks globally in to 2014,” Sandvine’s report noted.
Sandvine found that over half of all North American Internet traffic during peak usage periods comes from two services: Netflix and YouTube. YouTube globally is the leading source of Internet traffic in the world, according to Sandvine.
An old excuse for usage caps on “data hogs” – peer-to-peer file-sharing, continues its rapid decline towards irrelevance, now accounting for less than 10 percent of total daily traffic in North America. A decade earlier, file swapping represented 60 percent of Internet traffic.
Cisco’s answer for the evolving world of popular online applications is a further shift in broadband pricing towards “value-based tiers” that monetize different online applications by charging broadband users extra when using them. Cisco is promoting an idea that well-enforced Net Neutrality rules would prohibit.
Citing the bottled water market, Cisco argues if some customers are willing to pay up to $6 for a liter of trendy Voss bottled water, flat rate “one price fits all” broadband is leaving a lot of money on the table. With the right marketing campaign and a barely competitive marketplace, providers can charge far higher prices to get access to the most popular Internet applications.
“Research from British regulator Ofcom shows that consumers are becoming ‘addicted’ to broadband services, and heavy broadband users are willing to pay more for improved broadband service options.”
Wharton School professors Jagmohan Raju and John Zhang concluded price is the single most important lever to drive profitability.
The political implications of blaming phantom Internet growth and manageable upgrade costs for the implementation of usage caps or usage-based billing is uncertain. Even the “data hog” meme providers have used for years to justify usage caps is now open to scrutiny. Sandvine found the top 1% of broadband users primarily impact upstream resources, where they account for 39.8% of total upload traffic. But the top 1% only account for 10.1% of downstream traffic. In fact, Apple is likely to provoke an even larger, albeit shorter-term impact on a provider’s network from software upgrades. When the company released iOS7, Apple Updates immediately became almost 20% of total network traffic, and continued to stay above 15% of total traffic into the evening peak hours, according to Sandvine.
Some other highlights:
- Average monthly mobile usage in Asia-Pacific now exceeds 1 gigabyte, driven by video, which accounts for 50% of peak downstream traffic. This is more than double the 443 megabyte monthly average in North America.
- In Europe, Netflix, less than two years since launch, now accounts for over 20% of downstream traffic on certain fixed networks in the British Isles. It took almost four years for Netflix to achieve 20% of data traffic in the United States.
- Instagram and Dropbox are now top-ranked applications in mobile networks in many regions across the globe. Instagram, due to the recent addition of video, is now in Latin America the 7th top ranked downstream application on the mobile network, making it a prime candidate for inclusion in tiered data plans which are popular in the region.
- Netflix (31.6%) holds its ground as the leading downstream application in North America and together with YouTube (18.6%) accounts for over 50% of downstream traffic on fixed networks.
- P2P Filesharing now accounts for less than 10% of total daily traffic in North America. Five years ago it accounted for over 31%.
- Video accounts for less than 6% of traffic in mobile networks in Africa, but is expected to grow faster than in any other region before it.

 Gizmodo just did the math for those intending to spend a weekend watching the entire second season of the made-for-Netflix series in high-definition:
Gizmodo just did the math for those intending to spend a weekend watching the entire second season of the made-for-Netflix series in high-definition: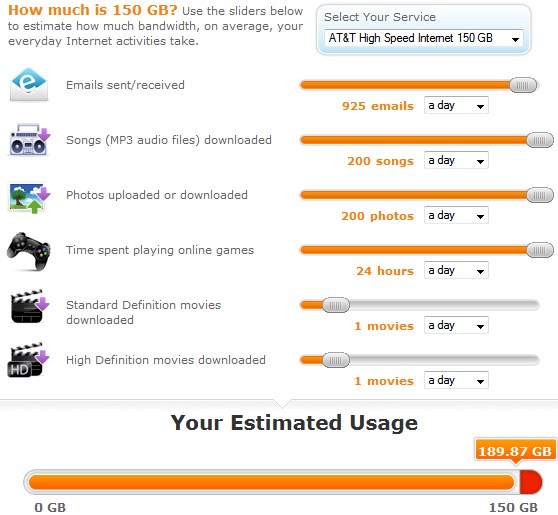


 Subscribe
Subscribe More than two dozen NorthwesTel customers in Canada’s north are contemplating a class-action lawsuit against their Internet provider after being charged hundreds, if not thousands of dollars in overlimit charges for phantom traffic nobody can seem to identify.
More than two dozen NorthwesTel customers in Canada’s north are contemplating a class-action lawsuit against their Internet provider after being charged hundreds, if not thousands of dollars in overlimit charges for phantom traffic nobody can seem to identify.
 A glitch may indeed be part of the problem as one Yukon customer successfully confronted NorthwesTel for erroneous overlimit fees for consumption of data that was impossible to accrue at the speed of his Internet connection.
A glitch may indeed be part of the problem as one Yukon customer successfully confronted NorthwesTel for erroneous overlimit fees for consumption of data that was impossible to accrue at the speed of his Internet connection.
 A
A 


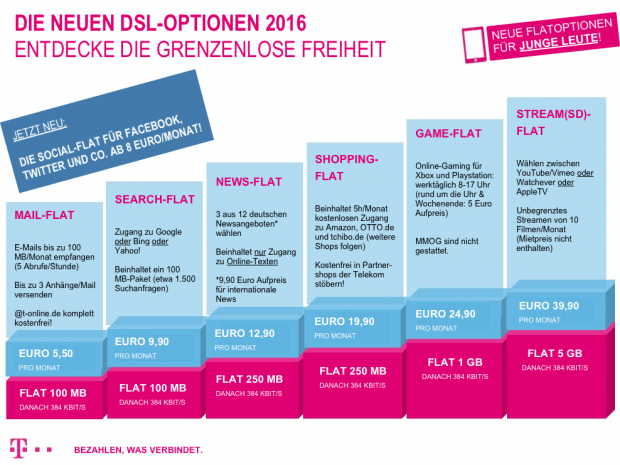
 “Until a few years ago, providers – just like the post – were just deliverers of packages,”
“Until a few years ago, providers – just like the post – were just deliverers of packages,” 

