Drahi’s World
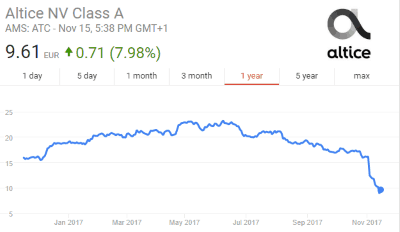
Shareholders have shaken Patrick Drahi’s dreams of being the next king of telecom in the United States by plunging Altice’s share price by more than a third in a single week, forcing Drahi to announce he won’t be making any additional acquisitions until the company’s staggering $59 billion debt is repaid.
Investors were also given a sacrificial lamb from the very sudden departure of Michel Combes, the ruthless cost-cutter that also served as titular operations leader of Altice’s European operations. Combes paid the ultimate price for the continued mediocre financial results at SFR-Numericable, which provides wireless and cable service in France and is Altice’s largest holding. That departure comes only two months after Michel Paulin, Drahi’s right-hand man at SFR, was also shown the door.
Drahi made it clear that he is formally taking back control of Altice, although observers have claimed he has always been in charge. European business analysts have uniformly described Altice as a company mired in crisis management, as European investors lose trust in Drahi’s business philosophy, which depends heavily on acquiring companies with other people’s money.
Drahi’s prominence in France came with his acquisition of SFR-Numericable just three years ago. SFR is France’s fourth largest wireless carrier and the company also has a prominent place in the wired telecom market, providing cable television, phone and internet service. Drahi has attracted investors with promises to wring every possible concession out of the companies he acquires. For financial markets, Drahi’s best trait is his ruthless cost-cutting and employee reductions. In France, employees have reported providing their own copy paper and toner cartridges for empty office printers, occasionally supply their own toiletries, and take turns mopping floors and vacuuming offices.
Employees of Altice-owned Suddenlink have been forced to take requests for replacement coffee machines for break rooms to skeptical company committees that review virtually every transaction. More recently, Cablevision technicians are complaining Altice eliminated their winter apparel budget, leaving workers without coats, bibs, overalls, or rain gear for the upcoming winter. Technicians will have to pay for their unsupplied winter gear out-of-pocket.
While shareholders and financial analysts bid up Altice stock on the premise that cost cutting would deliver better results, the fact France has a highly competitive telecom market brought unintended consequences for Altice and its shareholders: customers fled as cost cuts took their toll on service quality and support.
Competition Matters
Between the end of 2014 and mid-2017, SFR lost 514,000 subscribers in wired internet and 1.7 million mobile customers, delighting Altice’s competitors Orange, Free, and Bouygues Telecom. SFR’s internet problems are well-known across France. Altice’s attempt to offer a “one-box” solution for internet and television service has been of dubious value. Its equipment is notorious for failures, has compatibility problems with online games, and has high support costs. Altice is starting to bring similar equipment to the United States to supply its Cablevision customers, and technicians report many of the same problems are occurring in the U.S., adding they are skeptical Altice’s Le Box, known here as Altice One, will perform well for customers.
 The biggest enemy of Altice in Europe is robust competition, which has allowed dissatisfied customers to switch providers in droves. SFR-Numericable, despite promises of fiber-fast speeds, has endured complaints about slow and uneven speeds and persistent service outages. Drahi’s original business plan was to upgrade broadband speeds and performance to win over France’s remaining DSL customers. That worked for a time, according to the French newspaper Libération, but not for long.
The biggest enemy of Altice in Europe is robust competition, which has allowed dissatisfied customers to switch providers in droves. SFR-Numericable, despite promises of fiber-fast speeds, has endured complaints about slow and uneven speeds and persistent service outages. Drahi’s original business plan was to upgrade broadband speeds and performance to win over France’s remaining DSL customers. That worked for a time, according to the French newspaper Libération, but not for long.
Paulin, who used to run the division responsible for Altice’s wired broadband, complained bitterly competitors have “polluted” his marketing campaign by advertising their 100% fiber optic networks, educating customers that Altice isn’t selling that. That ruined Drahi’s plans to slowly upgrade services with the belief customers are more captive to their broadband provider and wouldn’t switch providers if Altice took its time.
A competitor put it this way: “SFR’s remaining DSL customers have indeed migrated at the encouragement of SFR-Numericable… to Orange or Free’s 100% fiber optic network offerings.”
Accusations about service problems and slow upgrades were readily believed by customers because Altice drew headlines for its ruthless efforts to save money.
“First, the restructuring – cuts in spending and pressure on suppliers – has shaped its image as a bad payer,” notes the newspaper. “At the end of 2015, SFR was fined $400,000 for its late payments. Second, package price increases, imposed discreetly and justified by the addition of exclusive video content, annoyed customers when they found extra charges on their bills. Finally, recurring network problems have undermined user trust. The new satisfaction survey of UFC-Que declared SFR was in last place among operators.”

Altice’s one-box solution for TV and internet has proven troublesome for customers in Europe.
Altice blamed most of SFR’s problems on its previous owner, Vivendi, who it claimed underinvested in its network for years. But customers were in no mood to stick around waiting for upgrades. Throughout 2015 and 2016, customers fled, finally forcing Drahi to embark on costly upgrades of SFR’s wireless and broadband networks. Drahi’s investments in SFR amounted to only $2 billion in 2014 and $2.12 billion in 2015, but dramatically increased to $2.71 billion in 2016. By the beginning of 2017, the upgrades stemmed some of the customer losses as independent tests showed SFR’s 4G LTE service finally became competitive with France’s top two providers. SFR commissioned 5,221 new 4G cell sites over the last 12 months, beating 4,333 for Bouygues Telecom, 3,543 for Orange and a distant 2,010 for low-cost carrier Free.
Drahi also made headlines last summer by announcing SFR-Numericable was completely scrapping its coaxial cable networks in France (as well as in Cablevision territory in the United States) to move entirely to optical fiber technology, even in the most rural service areas. But the fiber upgrades are not being financed with cash on hand at Altice. Libération reports the $1.78 billion Altice will need to spend on fiber upgrades for France alone will be financed by more bank loans. Drahi hopes to eventually offer bonds to investors to internally finance fiber upgrades.
The Suddenlink/Cablevision Cash Machine
 Drahi was banking on his ability to manage Altice’s debt and boost revenue by milking U.S. cable customers. Unlike in France, where competition and regulation have kept cable television and broadband prices much lower than in North America, Drahi saw enormous potential from the U.S. telecom market, where Americans routinely pay double or even triple the price many Europeans pay for television and internet access. Drahi sold investors on the prospects of slashing costs, initiating employee cutbacks, and raising prices for acquired U.S. cable companies. Suddenlink customers are particularly captive to cable broadband because the only alternative in many Suddenlink markets is slow speed DSL. Cablevision faces fierce competition from Verizon FiOS, but Verizon has sought to ease revenue-eating promotions that the company has offered in prior years. Both U.S. cable operators have raised prices since Altice acquired them.
Drahi was banking on his ability to manage Altice’s debt and boost revenue by milking U.S. cable customers. Unlike in France, where competition and regulation have kept cable television and broadband prices much lower than in North America, Drahi saw enormous potential from the U.S. telecom market, where Americans routinely pay double or even triple the price many Europeans pay for television and internet access. Drahi sold investors on the prospects of slashing costs, initiating employee cutbacks, and raising prices for acquired U.S. cable companies. Suddenlink customers are particularly captive to cable broadband because the only alternative in many Suddenlink markets is slow speed DSL. Cablevision faces fierce competition from Verizon FiOS, but Verizon has sought to ease revenue-eating promotions that the company has offered in prior years. Both U.S. cable operators have raised prices since Altice acquired them.
Altice’s investors demand short-term results more than long-term prospects, and Altice’s heavy reliance on bank loans at a time when interest rates are gradually rising could spell peril in the future. Drahi used to promote a 38% profit margin to his investors with predictions of 45% in the future. Altice recently removed all predictions of its margins going forward, a sign Altice is being forced to spend more money than it planned on network upgrades and expensive exclusive content deals for French cable television customers that might otherwise switch providers to secure a better deal.
Increasing costs and decreasing customers pushed Altice’s net profit in the red in 2016. The company also faces a lump sum loan payment of $4.72 billion in 2022. For now, Drahi will continue to refinance his portfolio of loans to secure lower interest rates and better repayment terms, but investors no longer believe Altice can continue to carry, much less increase its debt load.
That has forced Drahi to declare he is suspending further acquisitions at Altice and will instead spend resources on paying down its current debts. If he doesn’t, any recession could spell doom for Altice if his bankers are no longer willing to offer favorable credit terms.



 Subscribe
Subscribe In a sign that could spell trouble for Altice’s ambitious plans to scrap Cablevision’s coaxial cable network in favor of fiber to the home service, Altice has announced it is
In a sign that could spell trouble for Altice’s ambitious plans to scrap Cablevision’s coaxial cable network in favor of fiber to the home service, Altice has announced it is 
 The biggest enemy of Altice in Europe is robust competition, which has allowed dissatisfied customers to switch providers in droves. SFR-Numericable, despite promises of fiber-fast speeds, has endured complaints about slow and uneven speeds and persistent service outages. Drahi’s original business plan was to upgrade broadband speeds and performance to win over France’s remaining DSL customers. That worked for a time, according to the French newspaper Libération,
The biggest enemy of Altice in Europe is robust competition, which has allowed dissatisfied customers to switch providers in droves. SFR-Numericable, despite promises of fiber-fast speeds, has endured complaints about slow and uneven speeds and persistent service outages. Drahi’s original business plan was to upgrade broadband speeds and performance to win over France’s remaining DSL customers. That worked for a time, according to the French newspaper Libération, 
 Drahi was banking on his ability to manage Altice’s debt and boost revenue by milking U.S. cable customers. Unlike in France, where competition and regulation have kept cable television and broadband prices much lower than in North America, Drahi saw enormous potential from the U.S. telecom market, where Americans routinely pay double or even triple the price many Europeans pay for television and internet access. Drahi sold investors on the prospects of slashing costs, initiating employee cutbacks, and raising prices for acquired U.S. cable companies. Suddenlink customers are particularly captive to cable broadband because the only alternative in many Suddenlink markets is slow speed DSL. Cablevision faces fierce competition from Verizon FiOS, but Verizon has sought to ease revenue-eating promotions that the company has offered in prior years. Both U.S. cable operators have raised prices since Altice acquired them.
Drahi was banking on his ability to manage Altice’s debt and boost revenue by milking U.S. cable customers. Unlike in France, where competition and regulation have kept cable television and broadband prices much lower than in North America, Drahi saw enormous potential from the U.S. telecom market, where Americans routinely pay double or even triple the price many Europeans pay for television and internet access. Drahi sold investors on the prospects of slashing costs, initiating employee cutbacks, and raising prices for acquired U.S. cable companies. Suddenlink customers are particularly captive to cable broadband because the only alternative in many Suddenlink markets is slow speed DSL. Cablevision faces fierce competition from Verizon FiOS, but Verizon has sought to ease revenue-eating promotions that the company has offered in prior years. Both U.S. cable operators have raised prices since Altice acquired them.






