
Phillip “How far will $20 get me in your office?” Dampier
Congress is famous for obfuscation when it comes to introducing legislation that promises one thing and delivers something quite different. Take the 2003 “Clear Skies Initiative,” which would have allowed the energy industry to increase polluting emissions, or “The Disclosure of Hydraulic Fracturing Fluid Composition Act,” which allows frackers to keep secret the ingredients of millions of gallons of chemicals pumped into the ground to displace natural gas, and potentially your potable drinking water.
So it shouldn’t be much of a surprise that Rep. Bob Latta (R-Ohio) wants to “protect” the open and free Internet by introducing a new bill that opens and frees the telecom companies that steadfastly support his campaign coffers to install paid Internet toll booths. Like many pieces of legislation coming from some House Republicans these days, “freedom” only extends to corporate interests, not to you or I (unless we want to start a corporation of our own.)
Reclassifying broadband as a telecommunications service under Title II of the Communications Act is the Holy Grail for Net Neutrality supporters. It offers clear oversight authority that would make future lawsuits from Comcast, Verizon and other telecom companies untenable. Earlier court decisions have laid a foundation for broadband oversight under Title II, but the FCC itself must take advantage of that opportunity, and so far it has not.
Congressman Latta has introduced legislation to make sure the FCC can never take that step. His bill would specifically prohibit the FCC from reclassifying broadband Internet access as anything beyond an unregulated “information service.”
According to Latta, only with his legislation can America be assured the Internet will stay “open and free.” — “Open and free” for the picking by companies who dream of new revenue monetizing Internet traffic. Not satisfied charging some of the world’s highest prices for Internet access, many of the largest cable and phone companies in the country now want the right to “double-dip” — charging consumers to reach Internet content and content producers for delivering it. It would be like paying postage to mail a letter and having it arrive postage due or letting the phone company charge both the caller and the person called for a long distance telephone call.
“The legislation comes after the FCC released a proposal to reclassify broadband Internet access under Title II as a telecommunications service rather than an information service,” says a press release from Latta’s office.

Would I lie to you? Rep. Bob Latta (R-Ohio)
That is patently false. In fact, FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler has twisted himself into a human pretzel with clever language and a clear determination not to reclassify broadband under Title II. Wheeler prefers sticking to the rickety Section 706 faux-authority for Net Neutrality — the same section that keeps handing FCC lawyers loss after loss in federal court. After Wheeler announced his intention to propose allowing Internet companies to build paid fast lanes for Internet traffic, the resulting backlash from content companies and the public made him grudgingly offer a “discussion” about utilizing Title II.
That kind of “discussion” will be familiar to every 16-year old teenage girl who is told “we’ll talk about it” after asking mom and dad if she can take her new 22-year old boyfriend on vacation and stay in their own hotel room.
Ironically, detractors like Latta are the ones that usually accuse Net Neutrality of solving a problem that doesn’t exist. But that didn’t stop Congressman Latta from introducing legislation to stop the current ex-telecom lobbyist chairman of the FCC from going all Elizabeth Warren on us, suddenly imposing draconian pro-consumer regulations against those job creators at the cable companies Wheeler used to represent. But on the bright side, when Wheeler doesn’t do what Latta’s bill wouldn’t let him do, Latta can still declare victory against “big government.” If you live in Latta’s district, you can read all about it in the forthcoming government-subsidized, no-postage-needed “newsletter” he and other members of Congress will pelt your mailbox with right before election time.
“In light of the FCC initiating yet another attempt to regulate the Internet, upending long-standing precedent and imposing monopoly-era telephone rules and obligations on the 21st Century broadband marketplace, Congress must take action to put an end to this misguided regulatory proposal,” said Latta. “The Internet has remained open and continues to be a powerful engine fueling private enterprise, economic growth and innovation absent government interference and obstruction. My legislation will provide all participants in the Internet ecosystem the certainty they need to continue investing in broadband networks and services that have been fundamental for job creation, productivity and consumer choice.”
Consumers not included. Maybe he just forgot.
“At a time when the Internet economy is thriving and driving robust productivity and economic growth, it is reckless to suggest, let alone adopt, policies that threaten its success. Reclassification would heap 80 years of regulatory baggage on broadband providers, restricting their flexibility to innovate and placing them at the mercy of a government agency. These businesses thrive on dynamism and the ability to evolve quickly to shifting market and consumer forces. Subjecting them to bureaucratic red tape won’t promote innovation, consumer welfare or the economy, and I encourage my House colleagues to support this legislation, so we can foster continued innovation and investment within the broadband marketplace.”
 Guess not. The Internet should only be about business in Latta’s mind. Consumers that support Net Neutrality are nothing more than parasites sucking away valuable potential profits from the dynamic, flexible and innovative world of traffic shaping, usage caps, and double-dipping.
Guess not. The Internet should only be about business in Latta’s mind. Consumers that support Net Neutrality are nothing more than parasites sucking away valuable potential profits from the dynamic, flexible and innovative world of traffic shaping, usage caps, and double-dipping.
Latta isn’t interested that your provider is turning your weekend Netflix binge into an exercise of maddening rebuffering futility as your cable/phone company waits for protection racket proceeds a paid peering agreement with Netflix. That is because he doesn’t represent you. He represents AT&T, Time Warner Cable, Comcast, and CenturyLink.
Latta can afford to travel through the Internet toll booth when one considers who his top contributors keeping his campaign flush with cash are:
- More than $32,000 in contributions from AT&T and its executives;
- $29,500 from Tom Wheeler’s old haunt — the National Cable & Telecommunications Association (Big Cable lobby);
- $15,000 from the American Cable Association (Small Cable lobby);
- $21,000 from Time Warner Cable and its executives;
- $16,000 from Verizon and its executives;
- $11,400 from CenturyLink;
- $11,000 from Comcast (they are ditching Ohio customers to Charter after merging with Time Warner Cable so why throw good money after bad).
Latta’s close friendship with Big Telecom is so obvious, it has made co-sponsoring his fact-free bill about as popular as Justin Bieber at an NAACP convention. Even his like-minded Congressional colleagues are staying away. But his industry friends sure appreciate his efforts on their behalf.
One wonders why his constituents return him to office when he would be obviously much more comfortable in his next job — lobbying for AT&T or Comcast. Before our Internet connections slow, let’s hope his constituents hasten a much-needed turbo-speed departure for the congressman, already a shadow employee of AT&T.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “Comcast Corp.’s bid to buy Time Warner Cable Inc. may be the opening act for a yearlong festival of telecommunications deals that would alter Internet, phone and TV service for tens of millions of Americans.” — Bloomberg News, May 14, 2014
“Comcast Corp.’s bid to buy Time Warner Cable Inc. may be the opening act for a yearlong festival of telecommunications deals that would alter Internet, phone and TV service for tens of millions of Americans.” — Bloomberg News, May 14, 2014 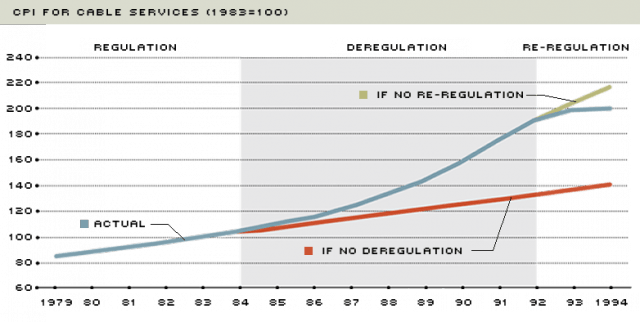
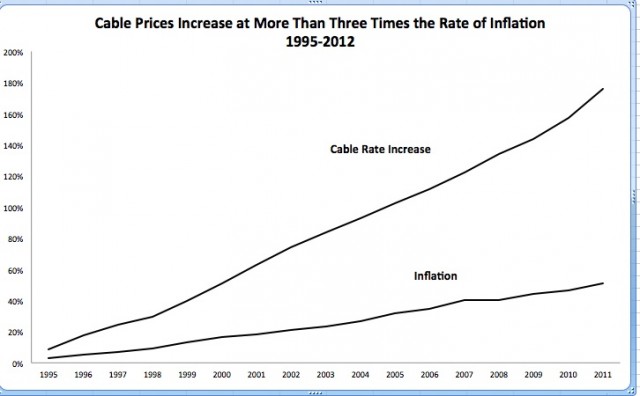
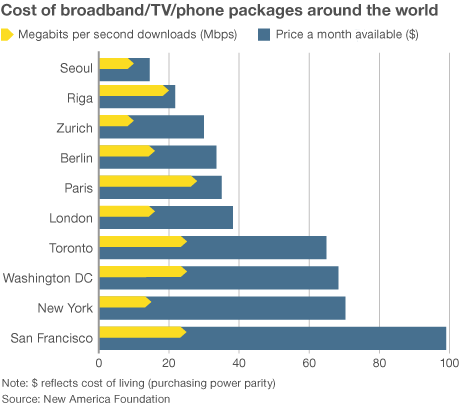 Economists reviewing data found in publicly available corporate balance sheets soon found evidence that the “increased programming costs”-excuse for rate increases did not hold water. The less competition or number of choices available to consumers in the market unambiguously lead to higher prices. It has remained true since Consumers’ Union
Economists reviewing data found in publicly available corporate balance sheets soon found evidence that the “increased programming costs”-excuse for rate increases did not hold water. The less competition or number of choices available to consumers in the market unambiguously lead to higher prices. It has remained true since Consumers’ Union 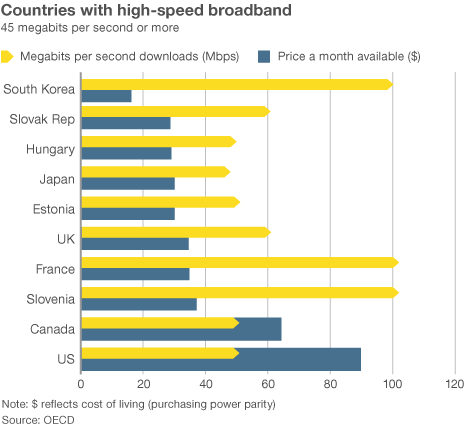 When a cable operator pays such an outrageous price, the previous owner is reaping the financial rewards of his monopoly power. The acquiring company can only pay such a high price by assuming that his monopoly power will allow him to continue to increase prices. Monopoly power is being bought and sold and borrowed against. The new cable operator, who has paid for market power, may insist that the debt he has incurred to obtain it is a real cost on his books. That may be correct in the literal sense (he owes someone that money) but that does not make it right, or the abuse of market power legal.
When a cable operator pays such an outrageous price, the previous owner is reaping the financial rewards of his monopoly power. The acquiring company can only pay such a high price by assuming that his monopoly power will allow him to continue to increase prices. Monopoly power is being bought and sold and borrowed against. The new cable operator, who has paid for market power, may insist that the debt he has incurred to obtain it is a real cost on his books. That may be correct in the literal sense (he owes someone that money) but that does not make it right, or the abuse of market power legal.
 A merger of Time Warner Cable and Comcast is just one more step towards undermining our democracy, worries former Secretary of Labor Robert Reich.
A merger of Time Warner Cable and Comcast is just one more step towards undermining our democracy, worries former Secretary of Labor Robert Reich.

 Jonathan Adelstein
Jonathan Adelstein Once out of the public sector for several years, some lobbyists see their value deteriorate as they get increasingly out of touch with the latest administration in power. So several seek a refresh, temporarily leaving their lobbying job to return to public sector work.
Once out of the public sector for several years, some lobbyists see their value deteriorate as they get increasingly out of touch with the latest administration in power. So several seek a refresh, temporarily leaving their lobbying job to return to public sector work. Comcast PAC donations to Senate Judiciary Committee Democrats
Comcast PAC donations to Senate Judiciary Committee Democrats