 AT&T has indirectly announced it will enforce hard data caps on its U-verse broadband service for the first time, imposing overlimit fees for customers that exceed their allowance unless they agree to pay $30 extra a month for a new unlimited add-on plan.
AT&T has indirectly announced it will enforce hard data caps on its U-verse broadband service for the first time, imposing overlimit fees for customers that exceed their allowance unless they agree to pay $30 extra a month for a new unlimited add-on plan.
AT&T’s Consumer Blog announced effective May 23, AT&T was increasing the usage allowances on its DSL and U-verse broadband service and is introducing a new $30 unlimited option for broadband-only customers many actually had all along because AT&T never enforced its cap for U-verse.
Customers currently bundling video and data services from AT&T/DirecTV will get a break – the unlimited option will apply at no extra charge if you agree to a single, combined bill for all of your AT&T services. The decision to apply usage caps to broadband-only customers, often cord-cutters, while effectively exempting current U-verse TV/DirecTV video customers is sure to raise eyebrows.
AT&T originally told customers its usage caps were designed “to ensure it is providing a sustainable network to customers.” But in a company FAQ, AT&T destroys its own argument for the need to cap anyone. “Will offering unlimited data negatively impact the AT&T network? No. AT&T will continue to actively manage the network to handle the increasing demand for data.”
AT&T’s need for data caps is also eroded by company claims only a small percentage of customers exceed them.

Why caps again?
“Today, our home Internet customers use just over 100GB of data per month on average,” AT&T wrote. “So even with our smallest U-verse Internet data allowance of 300 GB the average customer has plenty of data to do more.”
At least for now.
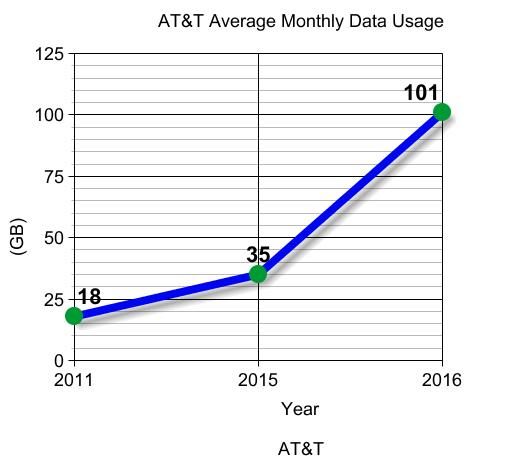
A review of AT&T’s past average usage claims is revealing. In 2011, AT&T told Tom’s Hardware the average customer consumed about 18GB a month. In 2015, AT&T’s cached support site claimed average customers used around 35GB a month. As of this week, AT&T says average users now exceed 100GB a month. If AT&T decides not to regularly revisit allowances (AT&T took five years to revisit the subject this week, having introduced 150GB caps on DSL and 250GB on U-verse in 2011), customers are likely to face pressure to sign up for the $30 unlimited add-on or buy television service from AT&T to avoid overlimit charges that will top out at $200 in penalties for DSL customers, $100 for U-verse overlimit fees.
Beginning May 23, AT&T’s website will include a data usage meter to help avoid AT&T’s overlimit penalty: $10 for each 50GB increment one exceeds their allowance. AT&T claims only 4% of its customers will exceed their future data allowances. They wouldn’t say how many exceed the current ones.
Because U-verse customers have avoided AT&T’s usage caps in the past, the company is now reminding customers it will give several warnings before you experience bill shock:
- In the first bill cycle when you reach 100% of your data allowance, AT&T will update you via email, but there will be no charges.
- In the second bill cycle, AT&T will notify you via email at 65%, 90%, and 100%, and still without charges.
- In the third bill cycle, and each bill cycle thereafter, you’ll receive reminder emails at 65% and 90%. At 100% AT&T will notify you and add an additional 50GB of data to your account for $10 each time you exceed the allowance. Customers will receive reminders about their data usage for the additional 50GB at 75% and 100%.
All usage — including uploads and downloads — counts towards the cap. There is just one exception. Wireless traffic from an AT&T MicroCell, designed to boost weak cell signals inside the home, is not included in AT&T’s Internet data usage allowance. To help ensure accurate billing, you have to register your AT&T MicroCell account and residential AT&T Internet account.
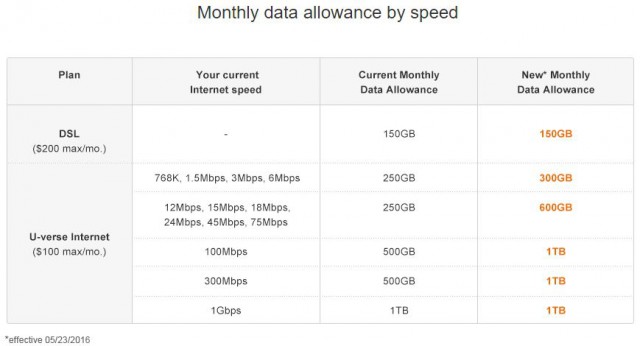
Here are the new data allowances that will take effect May 23rd:
DSL Reports’ Karl Bode is skeptical of the “consumer benefits” AT&T is touting as part of the change:
That last bit is a fairly transparent ploy to address a spike in cord cutting at AT&T — by forcing customers into signing up for television services they may not actually want if they want to avoid usage restrictions. Whether using arbitrary caps to force users to sign up for TV technically violates net neutrality (either the FCC’s rules or the concept in general) is something that’s likely to be hotly debated.
It’s also curious that just as AT&T indicates it’s backing away from U-Verse TV (which should technically free up more bandwidth on the AT&T network), it’s implementing caps on a network it originally stated didn’t need caps thanks to “greater capacity.” That’s because as with Comcast, caps really aren’t about capacity or financial necessity, they’re about protecting traditional TV revenue from Internet video. At the end of the day, AT&T’s just charging $30 a month (or more) for the same service, while trying to frame it as a net positive for consumers.


 Subscribe
Subscribe When reviewing your latest Comcast cable bill with overlimit fees on it (or a $30-35 upcharge to buy their insurance plan to keep extra fees off your bill), did you realize you are part of the Usage Economy?
When reviewing your latest Comcast cable bill with overlimit fees on it (or a $30-35 upcharge to buy their insurance plan to keep extra fees off your bill), did you realize you are part of the Usage Economy? CenturyLink is planning to trial usage caps on its broadband service later this year, not to reduce congestion or to bank the extra money for service upgrades, but to boost revenue and profits.
CenturyLink is planning to trial usage caps on its broadband service later this year, not to reduce congestion or to bank the extra money for service upgrades, but to boost revenue and profits.
 CenturyLink now has 940,000 households connected to its Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON), many for its Prism TV service. Another 490,000 businesses also have access to CenturyLink’s GPON network, primarily for broadband. Post claims more than 30% of the company’s service area is now served with broadband speeds of 40Mbps or greater.
CenturyLink now has 940,000 households connected to its Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON), many for its Prism TV service. Another 490,000 businesses also have access to CenturyLink’s GPON network, primarily for broadband. Post claims more than 30% of the company’s service area is now served with broadband speeds of 40Mbps or greater. House Republicans are hoping a back door legislative maneuver will successfully block the Federal Communications Commission from enforcing Net Neutrality and regulating or banning data caps.
House Republicans are hoping a back door legislative maneuver will successfully block the Federal Communications Commission from enforcing Net Neutrality and regulating or banning data caps. Comcast is inviting controversy launching a new live streaming TV service targeting cord-cutters while exempting it from its own data caps.
Comcast is inviting controversy launching a new live streaming TV service targeting cord-cutters while exempting it from its own data caps.
 Comcast claims it is reasonable to exempt Stream TV from its 300GB data cap being tested in a growing number of markets.
Comcast claims it is reasonable to exempt Stream TV from its 300GB data cap being tested in a growing number of markets.
