
Phillip “It isn’t so dumb to own the pipes” Dampier
In 2006, AT&T CEO Ed Whitacre thought his company was at a disadvantage being stuck with “dumb pipes” while Google, Yahoo! (remember them?) and Vonage couldn’t count their earnings fast enough. While AT&T sold consumers plain DSL service, content was king on Wall Street and Whitacre groused it was unfair for bandwidth hogs to use “the pipes for free.” That one statement was the equivalent of throwing a lit match on a hillside in Malibu Canyon and a predictable firestorm over Net Neutrality ensued.
Nine years later, Net Neutrality is now official FCC policy, although the sour grape-eating Republicans will continue to throw Congressional hissyfits along the way. While they rely on tissue-thin evidence to back their assertion the FCC secretly colluded with the Obama Administration to stick it to AT&T and demand its repeal, the future of Net Neutrality will more likely be decided in a courtroom a year or two from now.
Back in 2006 AT&T primarily sold DSL service and was looking for cash to finance its then emerging U-verse platform. AT&T planned to follow cable’s lead, devoting most of the available bandwidth on its fiber to the neighborhood network to cable television programming. Broadband speeds were limited to just under 25Mbps — even less if a large household had multiple television sets in use.
But as the Great Recession arrived and wages stagnated, the cost of what used to be a “must-have” service for most Americans increasingly began to exceed the household budget and the day finally arrived when cable companies started losing more television customers than they were adding. Even worse, cable programming costs continue to spiral upwards and no major cable company can increase cable television rates fast enough to support the usual profit margin the industry counted on.
What Whitacre failed to realize nine years earlier is that broadband providers did not simply own “dumb pipes.” AT&T, Comcast, Verizon, Time Warner Cable, Charter and other providers actually occupy two gilded catbird seats, with AT&T and Verizon dominating the wireless Internet business and Comcast, Time Warner, and Charter dominating at-home viewing and wired broadband. Lawmakers who deregulated both industries predicted pitting AT&T against Comcast or Verizon against Time Warner Cable would create competition not seen since Coke vs. Pepsi. Consumers would benefit and world-class service would result.
Instead, Time Warner Cable now sells Verizon Wireless phone service. Verizon gave up on expanding its FiOS network and is selling off its DSL and FiOS business in pieces to focus on its best moneymaker, Verizon Wireless. Comcast in turn threw in the towel on any notion of offering competing cellular service and, in fact, sold its acquired wireless spectrum to Verizon.
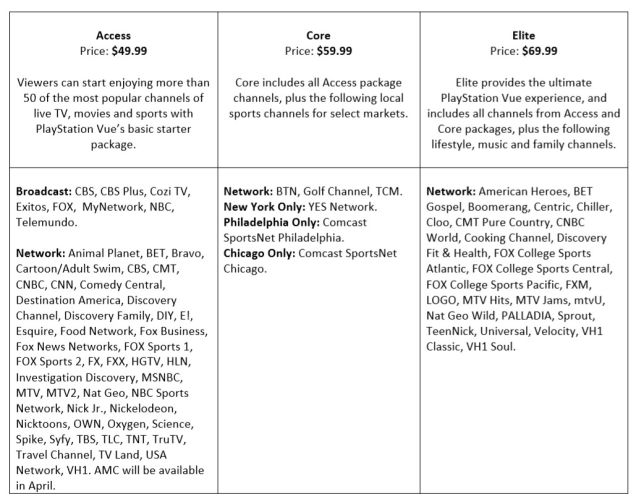
PlayStation Vue’s lineup
The best way to make money is to avoid price wars with your competitors and the evidence shows there is growing peace in America’s Telecom Valley. Comcast can now raise your broadband bill because, for most, Verizon FiOS isn’t an option. AT&T U-verse does not have to hurry speed upgrades to customers if Time Warner Cable delivers no better than 50/5Mbps service in large parts of its service area. Google Fiber remains a minor threat, only available in a handful of cities. AT&T distributed more copies of its press release touting U-verse Gigapower — its gigabit Internet offering — than there are customers qualified to sign up.
Notice that we’ve drifted away from talking about cable television programming. So has the industry, now increasingly dependent on broadband rate increases to make up the difference in revenue they used to take home from their television packages.
But now that the biggest players have a predictable source of revenue, allowing disruptors to further challenge earnings isn’t something your local cable and phone company will allow for long. At the moment, those most likely to cause problems are the growing number of “over the top” streaming video services that do not require a cable television subscription to watch. But they do need broadband — Whitacre’s “dumb pipes” — to reach subscribers. To manage that, services like Apple, PlayStation Vue and Sling TV and their customers must deal with the gatekeepers — AT&T, Comcast, Time Warner Cable, Verizon and others.
What Whitacre thought was a disadvantage is now becoming the best thing in the world — manning a toll booth on the only two roads most Americans can use to access online content.
Today, Sony officially launched its Internet-TV service, “PlayStation Vue” in three cities (New York, Chicago and Philadelphia) with a base price of $49.99/month. In includes more than 50 cable networks and in the three launch cities — local network affiliates. In Chicago and Philadelphia, where Comcast provides cable service, potential customers will need to pay $50 a month for Vue and another $64.95 a month for 50Mbps broadband — the least expensive broadband-only tier that is suitable for high quality viewing. Your combined bill for both services is $114.94 a month. Comcast charges $99.99 a month for its double play – 220 TV channels and 50Mbps broadband — almost $15 a month less for its package, and it includes around 150 more channels than Vue.

Comcast explains its new usage caps.
But Comcast also has another weapon it is testing is several of its markets — the resumption of usage caps and overlimit fees on its broadband service. Comcast customers in most test markets are given 300GB a month, after which they face overlimit fees of $10 for each additional increment of 50GB. While web browsing and e-mail fit more than comfortably within those caps, watching HD video may not. That leaves a potential Vue customer with a major dilemma. Should they pay $15 a month more for service than they can pay Comcast for a better package -and- chew away their usage allowance using it?
Comcast has yet to figure out how to install a coin collector on top of your television set, so you can watch as much Comcast cable television as you’d like. But watching streaming video could get very expensive if it exceeds a future Comcast usage allowance.
Smaller video packages from providers like Sling TV or the forthcoming Apple streaming service might make more sense, but will still be subject to Comcast’s usage caps if/when they are reintroduced around the country, while Comcast’s own television service will not.
This is why cable and phone companies hold enormous power over their potential competitors, even if Net Neutrality is fiercely enforced. Usage caps and usage-based billing represent an end run around Net Neutrality and both are permitted. The FCC has consistently refused to engage on the issue of broadband usage caps, leaving providers with a useful weapon to deter customers from dropping their television package in favor of an online alternative.
With most Americans having a choice of only one or two “dumb pipes” over which they can reach these services, being an owner of those pipes and getting to set the rates and conditions to use them is a very comfortable (and profitable) place to be.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Alaska’s largest cable company today unveiled changes to its Internet plans, ditching surprise overlimit fees in favor of a speed throttle.
Alaska’s largest cable company today unveiled changes to its Internet plans, ditching surprise overlimit fees in favor of a speed throttle.


 DISH’s plans to stream video content over the Internet could one day also include 4K programming, but viewers are likely to run smack into usage caps and usage billing that ISPs are using to deter online video from gutting cable television revenue as well as further monetizing already highly profitable broadband.
DISH’s plans to stream video content over the Internet could one day also include 4K programming, but viewers are likely to run smack into usage caps and usage billing that ISPs are using to deter online video from gutting cable television revenue as well as further monetizing already highly profitable broadband.
 “The telecommunications language will force the governor to veto this bill, as he has personally said and has also been repeated several times by other members of the administration,” Jim Zehringer, director of the Ohio Department of Natural Resources told the Ohio Senate’s Agriculture Committee during an informal hearing on the legislation. “We would be sacrificing all the great work done so far on this bill if these provisions are not removed.”
“The telecommunications language will force the governor to veto this bill, as he has personally said and has also been repeated several times by other members of the administration,” Jim Zehringer, director of the Ohio Department of Natural Resources told the Ohio Senate’s Agriculture Committee during an informal hearing on the legislation. “We would be sacrificing all the great work done so far on this bill if these provisions are not removed.”