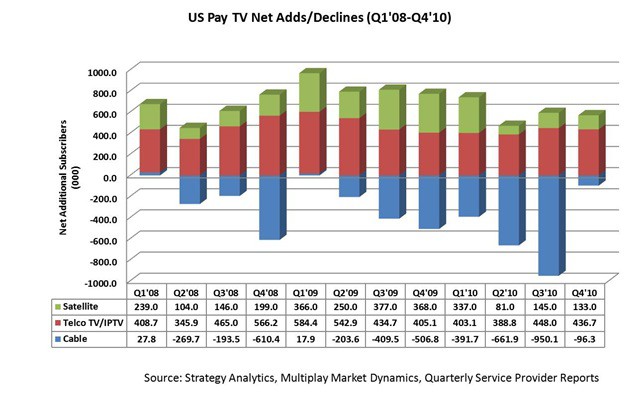
Click to enlarge
Your cable company has a problem. Collectively, the cable industry has lost more than 2 million video customers over the past year, and the problem may be getting worse. Some of the largest cable companies in the United States are making excuses for the historic losses:
- The bad economy
- Housing and foreclosure crisis
- High unemployment
- Family budget-cutting
But cable companies should be rethinking their excuses, according to a new report from Strategy Analytics.
“Throughout the past seven consecutive quarters of subscriber losses, the inclination of cable has been to point the finger at various external factors,” said Ben Piper, Director of the Strategy Analytics Multiplay Market Dynamics service. “Our analysis shows that neither the economy nor the housing market is to blame for these subscriber defections. The problem is one of value perception.”
Value perception. That’s a measurement of whether or not one feels they are getting good value for the money they pay for a product or service. Value comes in several different forms, starting with emotional — do I feel good, safe, secure, or nostalgic using the service? Can I imagine life without it? What about my friends and family — will I stand out if I am not buying this product? It’s also practical — Can I afford this? Can I find a cheaper or better alternative? Do I really need this service anymore?
Tied into value perception is customer goodwill. If you have an excellent experience with a company, letting go of their products comes much harder. If you feel forced to deal with a company that has delivered poor and expensive service for years, pent up frustration will make it much easier (and satisfying) to cut them loose at the first opportunity.

Embarq used to be Sprint's pathway to prosperity in the local landline business, until cord cutting put landlines into a death spiral.
In the telecommunications industry, value perception is a proven fact of life. It began with phone companies. Formerly a monopoly, landline providers have been forced to try and reinvent themselves and become more customer-friendly. First long distance companies like Sprint and MCI moved in to deliver cheaper (and often better quality) long distance service. Sprint even got into the landline business themselves, forming EMBARQ, which at its peak was the largest independent phone company in the United States. When Voice Over IP providers like Vonage and the cable industry’s “digital phone” products arrived, they promised phone bills cut in half, and introduced the concept of unlimited long distance calling.
The value perception among consumers became clear as they began disconnecting their landlines. The alternative providers offered cheaper, unlimited calling services, often bundled with phone features the local phone company charged considerably more to receive. Even though VOIP is technically inferior in call quality in many instances, the value the services provided made the decision to cut the phone cord easier.
But local phone company landline losses would only accelerate with the ubiquity of the cell phone, but for different reasons. What began with high per-minute charges for wireless calls evolved into larger packages of calling allowances, with plenty of free minutes during nights and weekends, and often free calling to those called the most. Most Americans end the month with unused calling minutes. As smartphones gradually take a larger share of the cell phone market, the accompanying higher bills have forced a value perception of a different kind — ‘I can’t afford to keep my landline –and– my cell phone, so I’ll disconnect the landline.’
The cable industry has traditionally faced fewer competitive threats and regularly alienates a considerable number of customers, but still keep their business despite annual rate increases and unwanted channels shoveled into ever-growing packages few people want.
This pent up frustration with the cable company has led to perennial calls for additional competition. That originally came from satellite television, which involved hardware customers didn’t necessarily like, and no option for a triple play package of phone and broadband service. The cable industry offers both, and by effectively repricing their products to discourage defections from bundled packages, customers soon discovered the resulting savings from satellite TV were often less than toughing it out with the cable company.
 As a result, satellite television has never achieved a share of more than 1/3rd of the video market. Many satellite customers are in non-cable areas, signed up because of a deeply discounted price promotion, were annoyed with the cable company, or didn’t care about the availability of broadband or phone service. When the price promotion ends or technical issues arise, many customers switch back to cable.
As a result, satellite television has never achieved a share of more than 1/3rd of the video market. Many satellite customers are in non-cable areas, signed up because of a deeply discounted price promotion, were annoyed with the cable company, or didn’t care about the availability of broadband or phone service. When the price promotion ends or technical issues arise, many customers switch back to cable.
More recently, researchers like Strategy Analytics have discovered some potential game-changers in the paid video marketplace:
- The impact of broadband-delivered video content
- The Redbox phenomena
- Competition from Telco TV
- The digital television conversion
Strategy Analytics studied consumer perceptions and found customers braver than ever before about their plans to cut cable’s cord. According to the consumers surveyed, nobody scores lower in value perception than cable companies. Citing “low value for money,” over half of the cable subscribers surveyed told the research firm they intended to disconnect their cable TV package in the near future.
While other researchers dismiss those high numbers as bravado, there are clear warnings for the industry.
“Much ink has been spilled on the topic of cord cutting and even skeptics are now admitting that it can’t be ignored,” said Piper.
Indeed, Craig Moffett, an analyst with Sanford Bernstein who almost never says a discouraging word about his beloved cable industry, told Ad Age Mediaworks the issue of cord-cutting was real.
“It’s hard to pretend that cord cutting simply isn’t happening,” Moffett said.

Craig E. Moffett, perennial cable stock booster, even admits cord-cutting is real.
The most dramatic impact on the cable industry has been in the ongoing erosion of the number of premium channel subscribers, those willing to pay up to $14 a month for HBO, Cinemax, Showtime, or Starz!. The reason? Low value for money. As HBO loses subscribers, Netflix and Redbox gain many of them. Netflix still delivers a considerable number of movies by mail, but has an increasingly large library of instant viewing options over broadband connections. Strategically placed Redbox kiosks deliver a convenient, and budget-minded alternative.
The loss of real wage growth, the housing collapse, and the down-turned economy do put pricing pressures on the industry, but some cable executives hope the time-honored tradition of customers howling about rate increases without ever actually dropping cable service continues.
But as new platforms emerge, some delivering actual pricing competition to the cable TV package, increasing numbers of customers are willing to take their video business somewhere else. Some are stopped at the last minute with a heavily discounted customer retention pricing package, but that doesn’t keep them from sampling alternative online video options. Among those who actually do leave, some are satisfied with the increased number of channels they get for free over-the-air after America’s digital television conversion.
Many others are switching to new offerings from telephone companies. Both AT&T and Verizon deliver video packages to many of their customers, often at introductory prices dramatically lower than their current cable TV bill. When considering a bill for $160 for phone, video, and broadband from the cable company or $99 for the same services from the phone company, $60 a month in savings for the first year or two is quite a value perception, and the inevitable disconnect order is placed with the cable company.
Ad Age‘s own survey, more skeptical about cord-cutting, confirmed that many former cable TV customers left for budgetary reasons, but many also kept their triple play packages. They just bought them from someone else.
Also confirmed: a dramatic upswing in online viewing, sometimes paid but often ad-supported or free.
Strategy Analysts concludes in its report, available for $1,999, that the ongoing erosion of cable TV subscribers isn’t irreversible, but it requires urgency among providers to become more customer-friendly and increase the all-important value perception.
In other words: respecting the needs and wishes of your customers.
Thankfully, the cable industry is dealing with competitors like AT&T, who are willing to assassinate their current lead in value perception by slapping Internet Overcharging pricing schemes on their broadband service. That will certainly raise the ire of their DSL and U-verse customers, many who are treating the customer unfriendly usage limits as an invitation to leave. Their former cable companies are waiting to welcome them back. The real question remains, will cable customers now be treated better?


 Subscribe
Subscribe










