
Phillip Dampier: One customer calls FairPoint’s deregulation logic “moosepoop.”
In 2007, Verizon Communications announced it was selling its landline telephone network in Northern New England to FairPoint Communications, a North Carolina-based independent telephone company. Now, nearly a decade (and one bankruptcy) later, FairPoint wants to back out of its commitments.
In 2015, FairPoint stepped up its push for deregulation, writing its own draft legislative bills that would gradually end its obligation to serve as a “carrier of last resort,” which guarantees phone service to any customer that wants it.
The company’s lobbyists produced the self-written LD 1302, introduced last year in Maine with the ironic name: “An Act To Increase Competition and Ensure a Robust Information and Telecommunications Market.” The bill is a gift to FairPoint, allowing it to abdicate responsibilities telephone companies have adhered to for over 100 years:
- The bill removes the requirement that FairPoint maintain uninterrupted voice service during a power failure, either through battery backup or electric current;
- Guarantees FairPoint not be required to offer provider of last resort service without its express consent, eliminating Universal Service requirements;
- Eliminates a requirement FairPoint offer service in any area where another provider also claims coverage of at least 94% of households;
- Eventually forbids the Public Utilities Commission from requiring contributions to the state Universal Service Fund and forbids the PUC from spending that money to subsidize rural telephone rates.
 Such legislation strips consumers of any assumption they can get affordable, high quality landline service and would allow FairPoint to mothball significant segments of its network (and the customers that depend on it), telling the disconnected to use a cell phone provider instead.
Such legislation strips consumers of any assumption they can get affordable, high quality landline service and would allow FairPoint to mothball significant segments of its network (and the customers that depend on it), telling the disconnected to use a cell phone provider instead.
FairPoint claims this is necessary to establish a more level playing ground to compete with other telecom service providers that do not have legacy obligations to fulfill. But that attitude represents “race to the bottom” thinking from a company that fully understood the implications of buying Verizon’s landline networks in a region where some customers were already dropping basic service in favor of their cell phones.
FairPoint apparently still saw value spending $2.4 billion on a network it now seems ready to partly abandon or dismantle. We suspect the “value” FairPoint saw was a comfortable duopoly in urban areas, a monopoly in most rural ones. When it botched the conversion from Verizon to itself, customers fled to the competition, dimming its prospects. The company soon declared bankruptcy reorganization, emerged from it, and is now seeking a legislative/regulatory bailout too. Regulators should say no.
 Last week, even FairPoint’s CEO Paul Sunu appeared to undercut his company’s own arguments for the need of such legislation, just as the company renewed its efforts in Portland to get a new 2016 version of the deregulation bill through the Maine legislature.
Last week, even FairPoint’s CEO Paul Sunu appeared to undercut his company’s own arguments for the need of such legislation, just as the company renewed its efforts in Portland to get a new 2016 version of the deregulation bill through the Maine legislature.
“We’ve operated in and we have experience operating basically in duopolies for a long time,” Sunu told investors in last week’s quarterly results conference call. “Cable is a formidable competitor. Look, they offer a nice package and a bundle and they – in certain areas, they certainly have a speed advantage. So we recognize that and so our marketing team does a really good job of making sure that our packages are competitive and we can counter punch on a both aggregate and deconstructive pricing.”
“Our aim is not to be a low cost, per se,” Sununu added. “What we want to do is to make sure that people stay with us because we can provide a better service and a better experience and that’s really what we aim to do. And as a result, we think that we will be able to change the perception that people have of Fairpoint and our brand and be able to keep our customers with us longer.”

Paul H. Sunu
Of course customers may not have the option to stay if FairPoint gets its deregulation agenda through and are later left unilaterally disconnected. In fact, while Sunu argues FairPoint’s biggest marketing plus is that it can provide better service, its agenda seems to represent the opposite. AARP representatives argued seniors want and need reliable and affordable landline service. FairPoint’s proposal would eliminate assurances that such phone lines will still be there and work even when the power goes out.
At least this year, customers know if they are being targeted. FairPoint is proposing to immediately remove from “provider of last resort service” coverage in Maine from Bangor, Lewiston, Portland, South Portland, Auburn, Biddeford, Sanford, Brunswick, Scarborough, Saco, Augusta, Westbrook, Windham, Gorham, Waterville, Kennebunk, Standish, Kittery, Brewer, Cape Elizabeth, Old Orchard Beach, Yarmouth, Bath, Freeport and Belfast.
At least 10,000 customers could be affected almost immediately if the bill passes. Customers in those areas would not lose service under the plan, but prices would no longer be set by state regulators and the company could deny new connection requests.
FairPoint argues that customers disappointed by the effects of deregulation can simply switch providers.
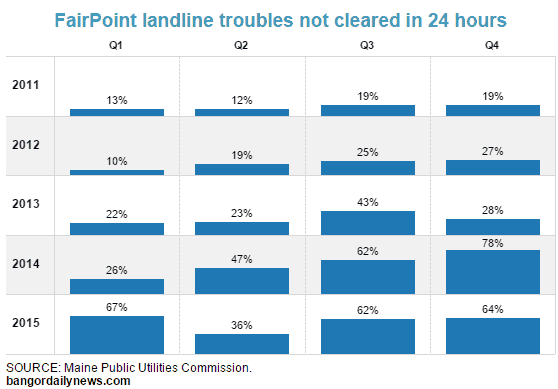 “The market determines the service quality criteria of importance to customers and the service quality levels they find acceptable,” Sarah Davis, the company’s senior director of government affairs, wrote. “To the extent service quality is deficient from the perspective of consumers, the competitive marketplace imposes its own serious penalties.”
“The market determines the service quality criteria of importance to customers and the service quality levels they find acceptable,” Sarah Davis, the company’s senior director of government affairs, wrote. “To the extent service quality is deficient from the perspective of consumers, the competitive marketplace imposes its own serious penalties.”
Except FairPoint’s own CEO recognizes that marketplace is usually a duopoly, limiting customer options and the penalties to FairPoint.
Those customers still allowed to stay customers may or may not get good service from FairPoint. Another company proposal would make it hard to measure reliability by limiting the authority of state regulators to track and oversee service complaints.
Company critic and customer Mike Kiernan calls FairPoint’s legislative push “moosepoop.”
“FairPoint has been, from the outset, well aware of the issues here in New England, since they had to demonstrate that they were capable of coping with the conditions – market and otherwise – in their takeover bid from Verizon,” Kiernan writes. “Yet now we see where they are crying poverty (a poverty that they brought on themselves) by taking on the state concession that they are trying desperately to get out from under, and as soon as possible.”
Vermont Public Radio reports FairPoint wants to get rid of service quality obligations it has consistently failed to meet as part of a broad push for deregulation. (2:23)
You must remain on this page to hear the clip, or you can download the clip and listen later.
Kiernan argues FairPoint should be replaced with a solution New Englanders have been familiar with for over 200 years – a public co-op. He points to Eastern Maine Electrical Co-Op as an example of a publicly owned utility that works for its customers, not as a “corporate cheerleader.”
Despite lobbying efforts that suggest FairPoint is unnecessarily burdened by the requirements it inherited when it bought Verizon’s operations, FairPoint reported a net profit of $90 million dollars in fiscal 2015.


 Subscribe
Subscribe AT&T has
AT&T has 


 The FCC under the leadership of Thomas Wheeler has targeted anti-municipal broadband laws in the states of North Carolina and Tennessee for federal pre-emption, effectively invalidating laws ghost-written by telecommunications industry lobbyists working for the states’ dominant telecom companies — Time Warner Cable in North Carolina and AT&T and Comcast in Tennessee. The laws are designed to restrict or discourage municipal broadband competition.
The FCC under the leadership of Thomas Wheeler has targeted anti-municipal broadband laws in the states of North Carolina and Tennessee for federal pre-emption, effectively invalidating laws ghost-written by telecommunications industry lobbyists working for the states’ dominant telecom companies — Time Warner Cable in North Carolina and AT&T and Comcast in Tennessee. The laws are designed to restrict or discourage municipal broadband competition. North Carolina residents bypassed by Google Fiber and impatient waiting for AT&T U-verse with GigaPower may still have a chance to get gigabit fiber Internet.
North Carolina residents bypassed by Google Fiber and impatient waiting for AT&T U-verse with GigaPower may still have a chance to get gigabit fiber Internet.
 Suddenlink’s Operating GigaSpeed has reached parts of Texas, Missouri and North Carolina — the first areas to get 1,000/50Mbps service from the cable company. But customers are not happy to learn it is accompanied by a 550GB usage cap.
Suddenlink’s Operating GigaSpeed has reached parts of Texas, Missouri and North Carolina — the first areas to get 1,000/50Mbps service from the cable company. But customers are not happy to learn it is accompanied by a 550GB usage cap. “Here in Greenville they are charging $110 a month for the service, $5 for a cable modem or $10 for a Wi-Fi router, and a $35 mandatory technician visit fee which sounded reasonable until they mentioned there was a 550GB data allowance on the service,” said Stop the Cap! reader J.J. Wallace. “That killed it for me. That is nothing short of outrageous to charge that kind of money and place a ridiculously low cap on it. It’s funny
“Here in Greenville they are charging $110 a month for the service, $5 for a cable modem or $10 for a Wi-Fi router, and a $35 mandatory technician visit fee which sounded reasonable until they mentioned there was a 550GB data allowance on the service,” said Stop the Cap! reader J.J. Wallace. “That killed it for me. That is nothing short of outrageous to charge that kind of money and place a ridiculously low cap on it. It’s funny  “If you impress on them they are charging too much, they will often find a promotion for you, but so far I’ve had no luck getting them to waive the caps unless you switch to business service,” said Wallace. “They always act like you are the first person to complain about usage caps, but if you read their social media pages, there are many others very upset to find they’ve lost unlimited use service after Suddenlink introduced speed upgrades. Most of my friends would rather have unlimited than faster service you can’t use.”
“If you impress on them they are charging too much, they will often find a promotion for you, but so far I’ve had no luck getting them to waive the caps unless you switch to business service,” said Wallace. “They always act like you are the first person to complain about usage caps, but if you read their social media pages, there are many others very upset to find they’ve lost unlimited use service after Suddenlink introduced speed upgrades. Most of my friends would rather have unlimited than faster service you can’t use.”