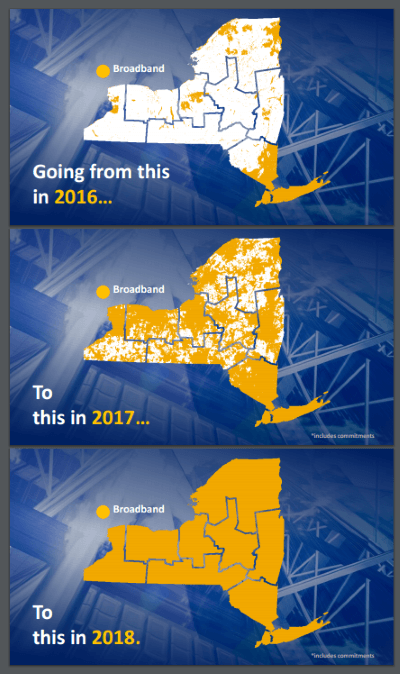
 Governor Andrew M. Cuomo yesterday announced that the “New NY Broadband Program” is well on its way to achieving “sweeping progress toward achieving its nation-leading goal of broadband for all” New Yorkers.
Governor Andrew M. Cuomo yesterday announced that the “New NY Broadband Program” is well on its way to achieving “sweeping progress toward achieving its nation-leading goal of broadband for all” New Yorkers.
The governor claimed that 97% of New York residents will have access to high-speed internet access by 2017, with a vague goal of serving 100% of New Yorkers by the end of 2018.
To do this, Gov. Cuomo relies heavily on the state’s new and overwhelmingly dominant cable operator – Charter Communications, which closed on its acquisition of Time Warner Cable earlier this summer. A press release promoting the governor’s efforts quotes Charter’s executive vice president of government affairs Catherine Bohigia as being excited to work with the governor and his administration to expand service to about 145,000 households currently not served by Time Warner Cable or Charter in New York.
Charter officials are working with the Public Service Commission to identify the households to be served, and highly redacted documents suggest Charter is identifying new housing developments and areas immediately next to existing Charter/Time Warner Cable service areas for this expansion.
A second separate plan to subsidize private cable and phone companies to help cover the costs of reaching another 34,000 homes that won’t be served by Charter is only expected to reach 50% of the remaining unserved homes and businesses in the state. A further round of funding will target the the remainder of unserved areas, including certain rural landline areas where Verizon has shown no interest in offering customers internet access of any kind.
Charter Communications
Charter Communications has effectively canceled the Time Warner Cable Maxx upgrades that were either underway, in progress, or in the planning stage in upstate New York. Instead, Charter plans to speed up the roll-out its own originally proposed upgrade, which includes two tiers: 60 and 100Mbps, for more than two million upstate homes and businesses by early 2017 in Buffalo, Rochester, Syracuse, Binghamton and Albany.
Customers in Central New York are likely to be left in limbo, some already getting Maxx upgraded 300Mbps internet access while others were scheduled to get the speed upgrade the same week Charter froze further Maxx upgrades. Those customers are now likely to receive a maximum of 100Mbps service sometime next year under Charter’s new plan.
Charter is also negotiating with state officials about where it will deploy broadband to 145,000 currently unserved homes in upstate New York over the next four years.
State-funded Rural Broadband Awards – Round I
New York State will help subsidize broadband rollouts to approximately 34,000 homes and businesses currently not served (or not served adequately) in rural areas. All but two of these projects will rely on fiber to the home service and each will offer service to a few thousand people:
| Applicant Name |
Technology | REDC Region | Census Blocks | Housing Units | Total Units | State Grant Total | Private Match | Total Project Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armstrong Telecommunications, Inc. | FTTH | Finger Lakes, Southern Tier, Western NY | 176 | 1,135 | 1,162 | $3,930,189 | $982,549 | $4,912,738 |
| Armstrong Telephone Company | FTTH | Southern Tier, Western NY | 74 | 466 | 504 | $1,778,256 | $444,564 | $2,222,820 |
| Citizens Telephone Company of Hammond, N.Y., Inc. | FTTH | North Country | 146 | 1,789 | 1,860 | $3,316,810 | $829,202 | $4,146,012 |
| Empire Access | FTTH | Southern Tier | 124 | 719 | 724 | $1,797,894 | $449,474 | $2,247,368 |
| Empire Access | FTTH | Southern Tier | 117 | 1,202 | 1,268 | $1,598,480 | $399,620 | $1,998,100 |
| Frontier Communications | FTTH | Southern Tier | 1 | 62 | 65 | $67,592 | $16,899 | $84,491 |
| Frontier Communications | FTTH | North Country | 3 | 188 | 216 | $129,634 | $32,409 | $162,043 |
| Frontier Communications | FTTH | Southern Tier | 12 | 129 | 142 | $197,104 | $49,276 | $246,380 |
| Frontier Communications | FTTH | Capital Region | 23 | 391 | 394 | $318,304 | $79,576 | $397,880 |
| Frontier Communications | FTTH | Mohawk Valley | 30 | 402 | 405 | $924,663 | $231,166 | $1,155,829 |
| Frontier Communications | FTTH | North Country | 105 | 1,928 | 2,096 | $1,702,246 | $425,562 | $2,127,808 |
| Germantown Telephone Company | FTTH | Capital Region | 208 | 2,195 | 2,334 | $2,512,562 | $628,140 | $3,140,702 |
| Haefele TV Inc. | FTTH | Southern Tier | 413 | 3,029 | 3,238 | $271,568 | $67,892 | $339,460 |
| Hancock Telephone Company | FTTH | Southern Tier | 136 | 1,505 | 1,675 | $4,915,920 | $1,228,981 | $6,144,901 |
| Heart of the Catskills Communications | Hybrid-Fiber Coax | Southern Tier | 216 | 2,836 | 3,177 | $1,224,946 | $524,977 | $1,749,923 |
| Margaretville Telephone Company | FTTH | Mid-Hudson, Southern Tier | 209 | 1,882 | 2,002 | $4,791,505 | $2,053,503 | $6,845,008 |
| Mid-Hudson Data Corp | Fixed Wireless | Capital Region | 60 | 647 | 663 | $950,184 | $237,546 | $1,187,730 |
| Mid-Hudson Data Corp | FTTH | Capital Region | 6 | 354 | 362 | $59,155 | $14,789 | $73,944 |
| State Telephone Company, Inc. | FTTH | Capital Region | 231 | 3,801 | 4,134 | $5,805,600 | $1,451,400 | $7,257,000 |
| State Telephone Company, Inc. | FTTH | Capital Region | 101 | 516 | 595 | $2,914,960 | $728,740 | $3,643,700 |
| TDS Telecom | FTTH | Southern Tier | 156 | 2,369 | 2,423 | $1,895,390 | $1,895,390 | $3,790,780 |
| TDS Telecom | FTTH | North Country | 74 | 506 | 543 | $1,084,000 | $1,084,000 | $2,168,000 |
| TDS Telecom | FTTH | Central NY, Finger Lakes | 106 | 996 | 1,038 | $1,424,793 | $1,424,793 | $2,849,586 |
| TDS Telecom | FTTH | Southern Tier | 395 | 3,528 | 3,551 | $4,989,570 | $4,989,570 | $9,979,140 |
| The Middleburgh Telephone Company | FTTH | Capital Region, Mohawk Valley | 250 | 1,596 | 1,651 | $5,562,548 | $1,390,637 | $6,953,185 |
After Verizon abdicated any interest in participating in rural broadband expansion funding through the FCC’s Connect America Fund, New York’s Broadband Program Office (BPO) and the Public Service Commission urged the FCC to keep the original funding intended for rural New York intact and open to other applicants seeking to build rural broadband projects. The FCC has not fully committed to do this, but it is an agenda item. Assuming this funding becomes available, it will be used to help pay for independent broadband providers or rural cable operators to begin delivering broadband service into still unserved parts of New York not included in the Charter expansion or Round I projects noted above. Many Verizon territories are expected to be included.
Applicants will have to provide at least 100Mbps service in most places or a minimum of 25Mbps in the most remote corners of New York. The application form discourages applicants from delivering broadband over DSL or wireless and clearly favors fiber to the home or cable broadband technology. Price controls will be in place for the first few years to assure affordability and those winning funding are strictly prohibited from introducing usage caps or usage-billing.
A vaguely defined “third phase” is scheduled to launch early next year to offer internet access to all remaining unaddressed service areas. Nobody mentions where the money is coming from to cover the last 1-3% of unserved areas, which are likely to be notoriously expensive to reach.
Gov. Cuomo explains progress on his New York Broadband for All program. (26:31)


 Subscribe
Subscribe Verizon Communications is taking the New York Public Service Commission to court over the regulator’s ruling that $8 million in property tax refunds rebated to the phone company through a tax certiorari proceeding should be spent on improving Verizon’s service quality in the state.
Verizon Communications is taking the New York Public Service Commission to court over the regulator’s ruling that $8 million in property tax refunds rebated to the phone company through a tax certiorari proceeding should be spent on improving Verizon’s service quality in the state. Verizon calls the regulator’s demands arbitrary and unwarranted confiscation of its property.
Verizon calls the regulator’s demands arbitrary and unwarranted confiscation of its property.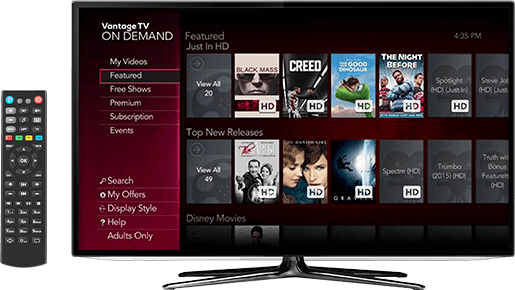 If you live in parts of the Hudson Valley (N.Y.) or Ohio where Frontier Communications provides phone service, Vantage TV may be coming to your neighborhood soon.
If you live in parts of the Hudson Valley (N.Y.) or Ohio where Frontier Communications provides phone service, Vantage TV may be coming to your neighborhood soon. Vantage TV offers up to 300 channels typically bundled with phone and internet service. Customers are provided a “total-home DVR” with 1TB of storage that can record up to six shows at the same time and played back on up to four wireless cable boxes attached to different televisions. An upgraded version 3.0 of Ericsson’s Mediaroom platform offers advanced set-top box features like improved visual search and the ability to watch up to four channels at once in a mosaic. Another feature lets customers bring up a small video screen showing another channel, useful if you are channel surfing during an ad break.
Vantage TV offers up to 300 channels typically bundled with phone and internet service. Customers are provided a “total-home DVR” with 1TB of storage that can record up to six shows at the same time and played back on up to four wireless cable boxes attached to different televisions. An upgraded version 3.0 of Ericsson’s Mediaroom platform offers advanced set-top box features like improved visual search and the ability to watch up to four channels at once in a mosaic. Another feature lets customers bring up a small video screen showing another channel, useful if you are channel surfing during an ad break. Connecticut, in contrast, is served with a mix of fiber and old copper wiring that has been in place for decades, since the days the state was served by the independent Southern New England Telephone Company. Learning how to deliver reasonable video quality over copper wires in Connecticut gave Frontier experience to go ahead with targeted upgrades that can boost broadband speeds and deliver HD video over an internet connection as low as 2.6Mbps in other states.
Connecticut, in contrast, is served with a mix of fiber and old copper wiring that has been in place for decades, since the days the state was served by the independent Southern New England Telephone Company. Learning how to deliver reasonable video quality over copper wires in Connecticut gave Frontier experience to go ahead with targeted upgrades that can boost broadband speeds and deliver HD video over an internet connection as low as 2.6Mbps in other states. With today’s completion of Cablevision’s absorption into the Altice empire, the European cable conglomerate announced big changes that are expected to refocus the “center of gravity” and Altice’s future profits on the United States instead of Europe.
With today’s completion of Cablevision’s absorption into the Altice empire, the European cable conglomerate announced big changes that are expected to refocus the “center of gravity” and Altice’s future profits on the United States instead of Europe. “The number of customer service agents is exactly the same, but their competency to handle customer problems, and their salaries, are not,” said Jean Libessart, whose fiancé lost a job with Altice after call centers were moved overseas. “They stayed within the competition authority’s rules by exploiting the loopholes.”
“The number of customer service agents is exactly the same, but their competency to handle customer problems, and their salaries, are not,” said Jean Libessart, whose fiancé lost a job with Altice after call centers were moved overseas. “They stayed within the competition authority’s rules by exploiting the loopholes.” “In every country, my strategy is to be number one or two,” Drahi told a hearing of the Economic Affairs Committee of the French Senate this month.
“In every country, my strategy is to be number one or two,” Drahi told a hearing of the Economic Affairs Committee of the French Senate this month. Some of America’s largest telecommunications companies continue to pay almost nothing in federal taxes even as state taxing authorities hungry for revenue are getting more aggressive about denying access to tax loopholes and suing some for failing to pay their fair share.
Some of America’s largest telecommunications companies continue to pay almost nothing in federal taxes even as state taxing authorities hungry for revenue are getting more aggressive about denying access to tax loopholes and suing some for failing to pay their fair share. Yesterday, the U.S. Supreme Court turned away
Yesterday, the U.S. Supreme Court turned away  While $300 million sounds like a lot, it pales in comparison to the money Verizon manages to dodge paying the Internal Revenue Service. The phone company is the poster child of corporate tax dodging according to Democratic presidential candidate Bernie Sanders. Sanders targeted Verizon because between 2008-2013, Verizon not only did not pay a nickel in federal taxes, it actually received a refund from the federal government after achieving a federal tax rate of -2.5%, despite booking $42.5 billion in profits. American taxpayers effectively subsidized Verizon when it got its refund check.
While $300 million sounds like a lot, it pales in comparison to the money Verizon manages to dodge paying the Internal Revenue Service. The phone company is the poster child of corporate tax dodging according to Democratic presidential candidate Bernie Sanders. Sanders targeted Verizon because between 2008-2013, Verizon not only did not pay a nickel in federal taxes, it actually received a refund from the federal government after achieving a federal tax rate of -2.5%, despite booking $42.5 billion in profits. American taxpayers effectively subsidized Verizon when it got its refund check. Bruce Kushnick, executive director of the New Networks Institute, claims
Bruce Kushnick, executive director of the New Networks Institute, claims