President Barack Obama’s strong commitment to robust Net Neutrality protections for the Internet has created a nightmare scenario for Net Neutrality opponents who can no longer count on an ex-telecom industry lobbyist now in charge at the Federal Communications Commission to take care of their business interests with watered down, damage-controlled, net-protection-in-name-only.
The attacks on President Obama’s convictions began almost immediately after his video was published on whitehouse.gov with Sen. Ted Cruz’s declaration that Net Neutrality was Obamacare for the Internet, a statement that may have played well with his Texas tea party base, but was quickly parodied on social media:

Hal Singer from the ironically named Progressive Policy Institute opined that President Obama’s decision to declare real Net Neutrality would likely lead to the new majority of Republicans to completely defund the agency in retaliation. PPI is strongly opposed to Net Neutrality and many other consumer protection measures and represents the interests of the George W. Bush wing of the Democratic Party, which consists of about six people (and Harold Ford, Jr. probably wishes he was one of them.)
 “We are stunned,” Michael Powell, a former FCC chairman who is now president of the National Cable & Telecommunications Association, said in an e-mail to Bloomberg reporters. After six years of supine oversight of giant telecommunications companies from former FCC chairman Julius “Data caps are innovative” Genachowski and the installation of an ex cable and wireless industry lobbyist as chief regulator of the country’s telecommunications industry, AT&T, Verizon and Comcast have faced few challenges to their regulatory wish lists.
“We are stunned,” Michael Powell, a former FCC chairman who is now president of the National Cable & Telecommunications Association, said in an e-mail to Bloomberg reporters. After six years of supine oversight of giant telecommunications companies from former FCC chairman Julius “Data caps are innovative” Genachowski and the installation of an ex cable and wireless industry lobbyist as chief regulator of the country’s telecommunications industry, AT&T, Verizon and Comcast have faced few challenges to their regulatory wish lists.
The Washington Post “Innovations” editorial page proved once again the Post is now the leading publication neocons and pro-business conservatives keep hidden under their mattresses next to the Wall Street Journal for those private moments. WaPo devoted news space to a hack editorial from Larry Downes, who turned up in Congress earlier this summer to cheerlead the merger of AT&T and DirecTV and has vociferously opposed Net Neutrality since at least 2011.
In his generally fact-challenged piece, Downes proclaims the Obama Administration was seeking nothing less than to saddle the Internet with oppressive outdated regulations written in 1934, that the courts threw out earlier hybrid/compromise Net Neutrality regulations simply because they lacked the words “commercially unreasonable,” and that implementing Net Neutrality would destroy investment in the world’s leading cable, mobile, and fiber networks.
Downes does not get out much, because other countries as diverse as South Korea, Lithuania, Bulgaria, Japan and Singapore have long since passed the United States, with much of Europe poised to follow their lead. Some of them even enforce Net Neutrality and the sky failed to collapse as a result. Broadband life is good in Bucharest.
Nothing about the Obama Administration’s proposal for Net Neutrality would do anything beyond preserving the Internet as we know and love it and judges told the FCC’s attorneys they had no authority to impose Net Neutrality under the freak flawed framework established by Michael Powell, former FCC chairman-turned cable industry lobbyist.
Downes also laims he is shocked, shocked I tell you to discover the FCC isn’t immune to political pressure from the White House and other Beltway forces. Except he is one of those Beltway forces.
The Post was content disclosing that Downes was simply a co-author of “Big Bang Disruption: Strategy in the Age of Devastating Innovation” (Portfolio 2014) and the project director at the harmless-sounding Georgetown Center for Business and Public Policy.
If you suspected Downes was just a tad closer to the industry he often advocates for than the newspaper was letting on, you would be right.
 In fact, Downes is a “fellow” at the Bell Mason Group, a corporate advisory firm “passionate about partnering with forward-thinking corporate venturing and innovation executives, […] helping clients build risk-reduced, impactful programs and overcome corporate antibodies and obstacles [and deliver] measurable value.”
In fact, Downes is a “fellow” at the Bell Mason Group, a corporate advisory firm “passionate about partnering with forward-thinking corporate venturing and innovation executives, […] helping clients build risk-reduced, impactful programs and overcome corporate antibodies and obstacles [and deliver] measurable value.”
Net Neutrality is an example of one of those “risky corporate obstacles” to total monopoly control that could deliver Big Telecom companies “measurable value.” Among Downes’ past clients is a tiny phone company named AT&T, but you wouldn’t know it from Bell Mason’s well-scrubbed website. Too bad for them archive.org took a snapshot of an earlier version of his bio, revealing his less-than-arm’s-length relationship with AT&T.
None of this is apparently pertinent to the editors of the Washington Post. Disclosing Downes’ co-authorship of a far-less germane book one critic called a “big bang disappointment” was more than enough.
Bloomberg News avoided the hopelessly unbelievable talking points about Internet takeovers and concluded President Obama threw his FCC chairman under the bus. But even that conclusion originated from the conservative, anti-Net Neutrality group the Heritage Foundation, quoted in the piece:
“He threw Tom Wheeler under the bus,” said James Gattuso, a senior research fellow at the Heritage Foundation, a Washington-based policy group. Obama’s strong stance makes it harder for Wheeler to reach a compromise among proponents of regulation, Gattuso said.
Except proponents of Net Neutrality are tired of compromises that favor ungrateful telecom companies that routinely sue even the most minor consumer protections out of existence. Wheeler was rumored to be proposing yet another compromise as late as last week, one that would protect deep-pocketed content companies but leave consumers open to further abuse from high cost fast lanes and speed throttles.
Various tea party groups ginned up with claims of an imminent Obama socialist takeover of the Internet, Maoist censorship and protectionist rate regulation took to the comment sections of various news pieces and wrote comments like this:
“I don’t want government control that would force private companies not to control what I can see on the Internet.”
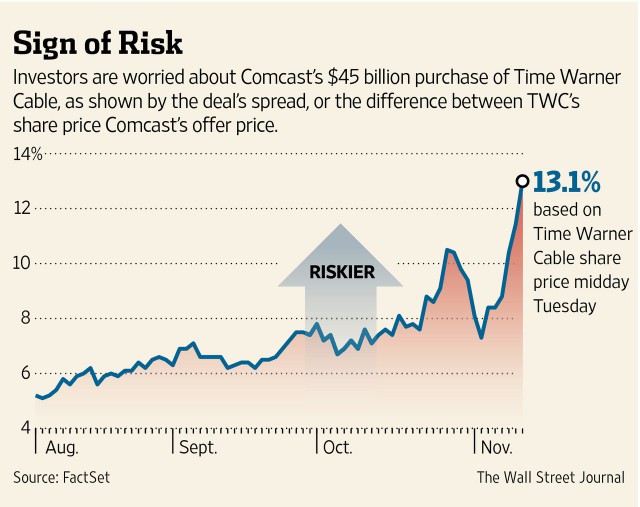 For public policy mavens that claim Net Neutrality is a solution in search of a problem, countering Wall Street’s decisive view that Net Neutrality is a disaster for plans of revenue boosting schemes are harder to counter.
For public policy mavens that claim Net Neutrality is a solution in search of a problem, countering Wall Street’s decisive view that Net Neutrality is a disaster for plans of revenue boosting schemes are harder to counter.
Obama’s intervention effectively kills Wheeler’s mixed plan, Paul de Sa, a senior analyst at Sanford C. Bernstein & Co. in New York, said in a note. It will be hard for the FCC, with a majority of Democrats appointed by Obama, to deviate significantly from his preference, and strong rules are likely, de Sa said.
Obama’s intervention “does not lead to price regulation of broadband,” in part because the FCC has no desire to do so, he said. Debate in Washington will intensify, with Congress holding “interminable hearings” and trying to prohibit the FCC from applying the strong rules, de Sa said.
The meaning to investors was clear: Internet profiteering plans are on indefinite hold. Comcast Corp. fell 63 cents or 1.2 percent, to $52.33 at 10:39 a.m. in New York trading, and are down as much as 5.1 percent this week. Time Warner Cable Inc. dropped $3.34, or 2.5 percent. AT&T Inc. fell 16 cents to $34.97 and Verizon Communications Inc. (VZ) fell 15 cents to $50.57.
A move to fully reclassify broadband, even if it includes “forbearance” from rate regulation, as President Obama suggested, would send investors scurrying, according to Kim Wallace, a policy analyst at Renaissance Macro Research. That is because it would cast doubt on cable and telecom companies’ abilities to generate a “sufficient return” on capital investments, which they expect to be sky high based on the limited amount of competition that exists today.
Craig Moffett, perennial cable stock booster, had the temerity to blame the latest developments on Comcast.
“The great irony is Comcast helped start this ball rolling by trying to buy Time Warner Cable in the first place,” said Moffett, an analyst at MoffettNathanson. “With the specter of possible price regulation hanging in the balance, [the question is] would Comcast still want to increase its exposure to distribution assets” in broadband.
The Wall Street press provides some salve for the chafed telecom industry high-flyer — the likely prospect of litigation tying up Net Neutrality long enough for Republicans to write new telecom laws that would lead to near-total regulatory capitulation and a free hand for providers. But investors sure hate uncertainty, so the Money Party will have to be postponed for now.
We have four illuminating news stories to share today on Net Neutrality:
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/PBS Why is Obama weighing in on net neutrality 11-10-14.mp4[/flv]
More than 3 million commenters crashed the Federal Communications Commission website in July to weigh in on the issue of net neutrality. Now President Obama has added his strong support, directing the FCC to protect equal access to all web content. Judy Woodruff speaks with U.S. chief technology officer Megan Smith about the president’s move. (7:33)
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Bloomberg Ex-FCCs Furchtgott-Roth Copps Debate Net Neutrality 11-10-14.flv[/flv]
Former Federal Communications Commission members Harold Furchtgott-Roth and Michael Copps talk about President Barack Obama’s call for the “strongest possible rules” to protect the open Internet and the value of so-called net-neutrality rules. They speak with Cory Johnson on Bloomberg Television’s “Bloomberg West.” (7:00)
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/CNN Here is why you should care about net neutrality 11-10-14.flv[/flv]
CNN explores why you should care about Net Neutrality and reminds us in a world of distorted punditry exactly what “Net Neutrality” is. (3:58)
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Fox Business Michael Powell Net Neutrality 11-10-14.flv[/flv]
Fox Business gives former FCC chairman Michael Powell an unchallenged platform to present his views on Net Neutrality. It becomes clear which side Fox is on when they call porn peddler Larry Flynt the quintessential Net Neutrality advocate. (5:08)
 AT&T is putting its gigabit fiber network upgrades on hold as long as President Barack Obama continues to insist on robust Net Neutrality for American broadband.
AT&T is putting its gigabit fiber network upgrades on hold as long as President Barack Obama continues to insist on robust Net Neutrality for American broadband.

 Subscribe
Subscribe
 “We are stunned,” Michael Powell, a former FCC chairman who is now president of the National Cable & Telecommunications Association, said in an e-mail to Bloomberg reporters. After six years of supine oversight of giant telecommunications companies from former FCC chairman Julius “Data caps are innovative” Genachowski and the installation of an ex cable and wireless industry lobbyist as chief regulator of the country’s telecommunications industry, AT&T, Verizon and Comcast have faced few challenges to their regulatory wish lists.
“We are stunned,” Michael Powell, a former FCC chairman who is now president of the National Cable & Telecommunications Association, said in an e-mail to Bloomberg reporters. After six years of supine oversight of giant telecommunications companies from former FCC chairman Julius “Data caps are innovative” Genachowski and the installation of an ex cable and wireless industry lobbyist as chief regulator of the country’s telecommunications industry, AT&T, Verizon and Comcast have faced few challenges to their regulatory wish lists. In fact, Downes is a “fellow” at the Bell Mason Group, a corporate advisory firm “passionate about partnering with forward-thinking corporate venturing and innovation executives, […] helping clients build risk-reduced, impactful programs and overcome corporate antibodies and obstacles [and deliver] measurable value.”
In fact, Downes is a “fellow” at the Bell Mason Group, a corporate advisory firm “passionate about partnering with forward-thinking corporate venturing and innovation executives, […] helping clients build risk-reduced, impactful programs and overcome corporate antibodies and obstacles [and deliver] measurable value.” For public policy mavens that claim Net Neutrality is a solution in search of a problem, countering
For public policy mavens that claim Net Neutrality is a solution in search of a problem, countering  In a major victory for net roots groups, President Barack Obama today announced his support for the strongest possible Net Neutrality protections, asking the Federal Communications Commission to quickly reclassify broadband as a “telecommunications service” subject to oversight and consumer protection regulatory policies that would prohibit paid fast lanes, the blocking or degrading of websites for financial reasons, and more transparency in how Internet Service Providers handle traffic.
In a major victory for net roots groups, President Barack Obama today announced his support for the strongest possible Net Neutrality protections, asking the Federal Communications Commission to quickly reclassify broadband as a “telecommunications service” subject to oversight and consumer protection regulatory policies that would prohibit paid fast lanes, the blocking or degrading of websites for financial reasons, and more transparency in how Internet Service Providers handle traffic. No blocking. If a consumer requests access to a website or service, and the content is legal, your ISP should not be permitted to block it. That way, every player — not just those commercially affiliated with an ISP — gets a fair shot at your business;
No blocking. If a consumer requests access to a website or service, and the content is legal, your ISP should not be permitted to block it. That way, every player — not just those commercially affiliated with an ISP — gets a fair shot at your business;


 “Those who advocated the Telecommunications Act of 1996 promised more competition and diversity, but the opposite happened,” said Common Cause president Chellie Pingree back in 1995. “Citizens, excluded from the process when the Act was negotiated in Congress, must have a seat at the table as Congress proposes to revisit this law.”
“Those who advocated the Telecommunications Act of 1996 promised more competition and diversity, but the opposite happened,” said Common Cause president Chellie Pingree back in 1995. “Citizens, excluded from the process when the Act was negotiated in Congress, must have a seat at the table as Congress proposes to revisit this law.” The majority of 3.7 million comments received by the FCC advocate strong and unambiguous Net Neutrality protections for the Internet, but that seems to have had little impact on FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler, who is laying the groundwork for a hybrid Net Neutrality Frankenplan that would marginally protect deep pocketed content producers while leaving few, if any, protections for consumers.
The majority of 3.7 million comments received by the FCC advocate strong and unambiguous Net Neutrality protections for the Internet, but that seems to have had little impact on FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler, who is laying the groundwork for a hybrid Net Neutrality Frankenplan that would marginally protect deep pocketed content producers while leaving few, if any, protections for consumers. Large telecommunications companies argue that deregulation promotes broadband investment and expansion to create world-class service. But years of statistics and comparisons with other countries suggest deregulation has not inspired sufficient competition to keep prices in check and force regular network upgrades. In fact, competition is much more robust at the wholesale level, while the majority of retail consumers have a choice of just one or two providers that receive almost no oversight. Those providers are now exercising their market power to further monetize broadband usage to boost profits and raise prices.
Large telecommunications companies argue that deregulation promotes broadband investment and expansion to create world-class service. But years of statistics and comparisons with other countries suggest deregulation has not inspired sufficient competition to keep prices in check and force regular network upgrades. In fact, competition is much more robust at the wholesale level, while the majority of retail consumers have a choice of just one or two providers that receive almost no oversight. Those providers are now exercising their market power to further monetize broadband usage to boost profits and raise prices.