 FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION
_______________________________________
Applications of Charter Communications, Inc., Time
Warner Cable Inc., and Advance/Newhouse
Partnership for Consent to the Transfer of MB Docket No. 15-149
Control of Cable Television Relay Service
Applications
_______________________________________
Statement of Opposition
(Click here to download a copy in PDF format.)
October 10, 2015
Stop the Cap! is a Rochester, N.Y.-based consumer group founded in 2008 to fight against the introduction of artificial limits on broadband usage (usage caps, consumption billing, speed throttling) and to promote better broadband speeds and service for consumers. Our group does not solicit or accept funding from lobbyists, companies, or others affiliated with the telecommunications industry. We are entirely supported by individual donors who share our views.
Introduction
It is our view that the application of Charter Communications to effectively acquire Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks offers no compelling public interest benefit and is therefore not in the public interest.
Our organization represents the interests of consumers and customers who face ever-growing broadband and television bills. Since its founding in 2008, we have witnessed a gap between the promised benefits of telecom mergers and what actually materializes for customers. Our conclusion is that consumers rarely benefit from these transactions. Prices continue to rise, customer service does not significantly improve, competition suffers, and conditions imposed by regulators to protect consumers or improve service are either not meaningfully met, expire too soon, or are too limited to be useful.
Charter’s claimed public interest benefits from its acquisitions are woefully inadequate and will, in fact, harm consumers if this merger is permitted.
The proposal asks the Commission to approve Charter’s acquisition of not one, but two established cable providers, one considerably larger than Charter itself:
- Time Warner Cable, the second largest U.S. cable operator with more than 11 million residential and business customers[1];
- Bright House Networks, the sixth largest U.S. cable operator with approximately 2.5 million customers.[2]
Charter Communications is about half the size of Time Warner Cable.[3]
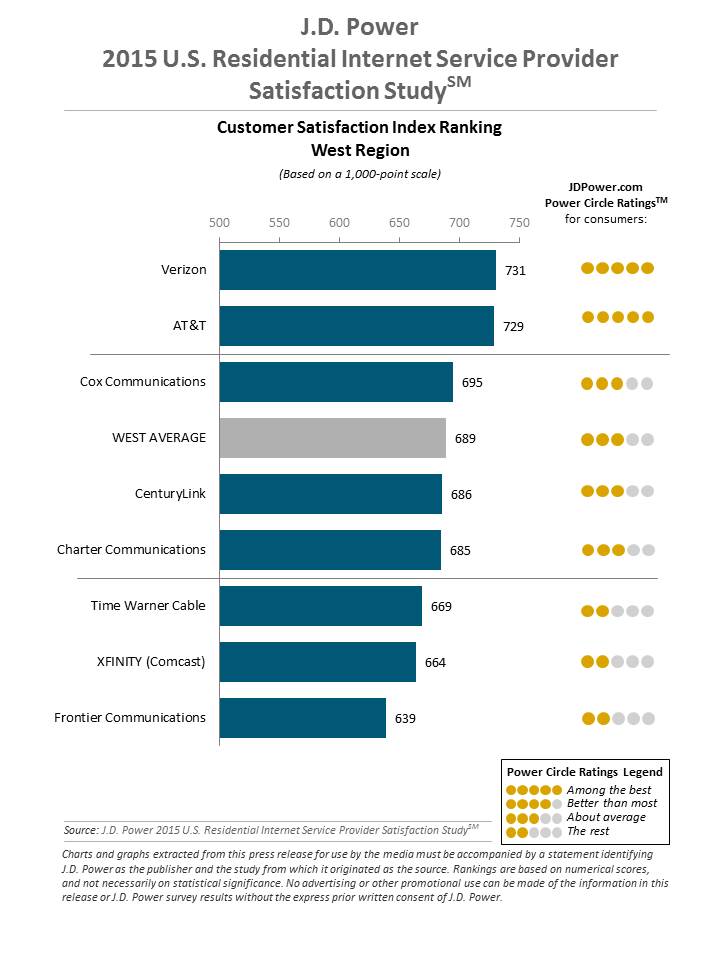
Charter’s broadband customer satisfaction scores are nothing to write home about. Time Warner is no prize either, especially in areas where Maxx upgrades are not yet available.
In the 2015 J.D. Power U.S. Residential Television Service Provider Satisfaction Study, Charter rated poor — second to last place behind five other providers in the North West region, fourth from last behind six others in the South region, and third from last behind five other providers in the West. In fact, at no time did Charter rank anything higher than “about average” for television, broadband, and telephone service and often scored worse.[4]
This is a critical measurement of how Charter is likely to perform in areas currently served by Time Warner Cable and Bright House, should the merger be approved.
“The ability to provide a high-quality experience with all wireline services is paramount, as performance and reliability is the most critical driver of overall satisfaction,” said Kirk Parsons, senior director and technology, media & telecom practice leader at J.D. Power. “The fact that households continue to choose to upgrade their wireline connection to digital service is a testament to its improved performance and benefits, such as higher quality video and faster Internet speeds.”
FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler has publicly stated his four preferences for telecommunications policies that promote competition and foster enhanced service.[5]
- “First, where competition exists, the Commission will protect it,” Wheeler said. “Our effort opposing shrinking the number of nationwide wireless providers from four to three is an example. As applied to fixed networks, the Commission’s Order on tech transition experiments similarly starts with the belief that changes in network technology should not be a license to limit competition.”
- “Communications policy has always agreed on one important concept: the exercise of uncontrolled last-mile power is not in the public interest,” Wheeler said. “This has not changed as a result of new technology. When network operators have unrestrained last-mile power, public policy can step in to protect consumers and innovators. When cable companies, for instance, were accused of using their control over the last-mile distribution of video programing to harm competition by keeping content from others, Congress stopped that practice in the 1992 Cable Act. There are two important lessons from this: First, last-mile power cannot be a lever for gaining an unfair advantage. Second, rules of the road can provide guidance to all players and, by restraining future actions that would harm the public interest, incent more investment and more innovation.”
- “Where meaningful competition is not available, the Commission will work to create it. For instance, our efforts to expand the amount of unlicensed spectrum create alternative competitive pathways. And we understand the petitions from two communities asking us to pre-empt state laws against citizen-driven broadband expansion to be in the same category, which is why we are looking at that question so closely.”
- “Where competition cannot be expected to exist, we must shoulder the responsibility of promoting the deployment of broadband. One thing we already know is the fact that something works in New York City doesn’t mean it works in rural South Dakota. We cannot allow rural America to be behind the broadband curve. Our universal service efforts are focused on bringing better broadband to rural America by whomever steps up to the challenge—not the highest speeds all at once, but steadily to prevent the creation of a new digital divide.”
We will return to these four themes in our statement to see if Charter’s application helps or hinders these priorities. It is our contention Charter’s application does not meaningfully advance the stated goals of the Chairman or the Commission. In fact, Charter’s proposal impedes achievement of some of these goals significantly.
In our presentation, we will regularly refer to Charter’s existing product suite, usually referred to as “Charter Spectrum.” We will also refer to two different types of service from Time Warner Cable.

Wheeler
On January 30, 2014, Time Warner Cable announced its new TWC Maxx initiative that substantially improved broadband speeds for customers without a corresponding rate increase. The upgrade also introduced a new class of cable equipment for video customers offering an enhanced viewing experience, increased plant/service reliability, improved customer support – including more options for in-home service calls, and retained and improved existing budget-priced broadband tiers for fixed and low-income customers.[6]
We will therefore refer to both Time Warner Cable Maxx-upgraded service areas defined above and “legacy service areas” that are currently awaiting Maxx upgrades and now offer slower top Internet speeds ranging from 50-100Mbps.
It is our contention that Charter’s proposal to bring improved broadband speeds, better set-top boxes, faster upgrades, and a three-year commitment to voluntarily adhere to Net Neutrality/Open Internet policies and not impose usage caps on residential broadband service offers little because Time Warner Cable Maxx already offers consumers a more compelling offer on an upgrade timeline nearly equivalent to that proposed by Charter Communications.
Time Warner Cable has also never been credibly accused of violating Net Neutrality principles, is unlikely to do so in the future, and has repeatedly insisted it will not impose compulsory usage caps on its customers. We also argue Charter Communications’ heavy indebtedness as a result of this transaction will likely pose a challenge to complete the company’s promised upgrade plan and its ongoing operations.
In short, consumers are much better off remaining Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks customers as opposed to Charter Communications customers.
Should the FCC ultimately disagree with our contention, we urge you to impose our ideas for strong and meaningful conditions to protect consumers. Without this, we fear the executives of both companies and their shareholders will be the only ones to actually benefit from this transaction. Consumers will be left with little more than a higher bill.
Discussion
 Charter Communications’ proposition to the Commission and customers is to deliver a more compelling product suite offering faster Internet speeds, better set-top equipment, and a three-year commitment to adhere to the Commission’s Open Internet principles and not impose usage caps or modem rental fees on customers.
Charter Communications’ proposition to the Commission and customers is to deliver a more compelling product suite offering faster Internet speeds, better set-top equipment, and a three-year commitment to adhere to the Commission’s Open Internet principles and not impose usage caps or modem rental fees on customers.
While on the surface these commitments may seem laudable, when they are closely examined it quickly becomes apparent they offer little to Time Warner Cable customers, particularly the approximately 45% of which will have been upgraded to “Maxx” service by the end of 2015.[7]
Charter customers can generally choose from two tiers of Internet service, according to Charter’s website[8]:
We offer two different Charter Internet connection packages:
Plus – up to 30Mbps Download and 4Mbps upload
Ultra – up to 100Mbps Download and 5Mbps Upload
With Charter Internet Ultra, network speeds can reach up to 100 Megabits per second (Mbps). Your exact speed will depend on the service level to which you subscribe.
Charter charges new customers an introductory monthly price ranging from $29.99 (when Internet service is bundled with video/phone service) to $39.99 (Internet-only service) for its 60Mbps Standard broadband tier.[9] It is this promotional rate Charter is proposing to extend to Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks customers. But Charter does not commit to a specific time frame under which this promotional rate will apply to these customers. According to Charter’s disclaimer, the promotional rate expires after one year, after which the rate resets to a “standard rate,” currently $59.99 a month.[10]
 In contrast, Time Warner Cable offers a much larger variety of Internet tiers, starting at $14.99 a month and generally increasing in $10 increments, based on offered speed.[11] In legacy service areas, Time Warner Cable’s pricing can be more compelling, even with the slower Internet speeds, because income-challenged consumers may feel a need to buy service based on price, not performance. Charter all but eliminates these lower-cost options, except in limited circumstances where a customer manages to meet onerous requirements to qualify for a low-income broadband discount plan.
In contrast, Time Warner Cable offers a much larger variety of Internet tiers, starting at $14.99 a month and generally increasing in $10 increments, based on offered speed.[11] In legacy service areas, Time Warner Cable’s pricing can be more compelling, even with the slower Internet speeds, because income-challenged consumers may feel a need to buy service based on price, not performance. Charter all but eliminates these lower-cost options, except in limited circumstances where a customer manages to meet onerous requirements to qualify for a low-income broadband discount plan.
Achieving faster Internet speeds is another priority for Chairman Wheeler. At a speech last fall at 1776, the Chairman said, “a 25Mbps connection is fast becoming ‘table stakes’ in 21st century communications.”[12]
Both Time Warner Cable and Charter Communications will deliver twice or more that minimum speed as their Standard tier offering. Time Warner already achieves this goal in their Maxx service areas, where 50Mbps is the new Standard speed tier. Charter proposes to take more than two years to upgrade Time Warner Cable customers to an incrementally faster 60Mbps speed tier. Additionally, Time Warner Cable Maxx customers are assured they can further upgrade that speed in increments up to 300Mbps. Charter, in contrast, offers most customers a maximum of 100Mbps.[13]
The most important question before the Commission is which cable operator is better positioned to deliver the services customers want and/or need. We argue Time Warner Cable and Bright House, not Charter Communications, are both in a stronger position to deliver.
Since the termination of the Comcast-Time Warner Cable merger, Time Warner Cable has responsibly invested in their infrastructure without assuming an irresponsible amount of debt. Bright House Networks’ owners have taken the company private, but their ongoing investments in a robust Wi-Fi platform, their high consumer satisfaction scores, and their investments in ongoing upgrades to meet challenges of competitors like Verizon FiOS suggest the company is in healthy financial shape.
Time Warner Cable CEO Robert Marcus reported significant progress in their first quarter 2015 report to shareholders and customers, despite the distraction of the Comcast merger[14]:
Over the past 16 months, we’ve made significant investments to improve our customers’ experience:
- Investing more than $5.2 billion to, among other things, improve the reliability of our network and upgrade customer premise equipment – including set-top boxes and cable modems – with the latest technologies and expand its network to additional residences, commercial buildings and cell towers;
- Launching TWC Maxx, which features greater reliability, all-digital video, advanced TV services, standard tier of Internet speeds at 50 Mbps, and higher tiers of service up to 300 Mbps. New York, Los Angeles and Austin are complete; Dallas, San Antonio and Kansas City are underway; Charlotte, Raleigh and Hawaii are slated for later this year; and San Diego is expected to be done in early 2016;
- Introducing Enhanced DVR, a six-tuner set-top box that allows customers to record up to six shows simultaneously and store up to 150 hours of HD content;
- Increasing the number of Cable Wi-Fi hotspots available to our customers to 400,000;
- Rolling out our cloud-based video guide to 8 million set-top boxes to date. The guide also makes it easier to browse our On Demand library, which now sits at 30,000 free and paid titles and continues to grow;
- Expanding our industry-leading TWC TV app – which allows customers to watch live TV and On Demand content and control and program their DVR from inside and outside the home. TWC TV is now available on Xbox One, Xbox 360, Amazon Kindle Fire HD and HDX tablets, Android and IOS phones and tablets, Fan TV, PCs, Samsung TV and Roku;
Serving customers on their schedules rather than ours. We expanded one-hour appointment windows across the company and in Q1 met that window 97 percent of the time. We continue to add nighttime and weekend appointments.

Marcus
Since that report, Time Warner Cable has announced new Maxx service upgrade areas – Greensboro and Wilmington, N.C. Marcus has indicated additional cities will receive upgrades in 2016.[15]
On the January 29, 2015 quarterly results conference call with investors, Marcus indicated Maxx upgrades delivered tangible benefits to the company, including increased customer satisfaction, higher network reliability, and a stronger product line.[16] Based on those factors, it would be logical to assume Time Warner Cable would continue its upgrade project, and indeed Marcus confirmed this in his remarks:
“Our aim is to have 75% of our footprint enabled with Maxx […] by the end of [2016], and my guess is we’re continuing to roll it out beyond that,” said Marcus. “So the only question is prioritization, and obviously as we think about where to go first, competitive dynamics are a factor. So that includes Google, although it’s not explosively dictated by where Google decides to go. In fact I think we announced the Carolinas before Google did their announcement this week. So competitors are certainly relevant obviously.
At the rate Time Warner Cable has been rolling out Maxx upgrades, which were first announced on January 30, 2014[17], with 45% of its service area upgraded within 23 months, it is likely the company would complete its Maxx upgrade to all of its service areas within the next 24-30 months. Notably, the staff of the New York Department of Public Service found, while investigating this deal, “there is no indication that Petitioner’s plan for converting to all-digital in New York is any different from Time Warner’s existing plan.”[18]
Charter’s upgrade proposal is, in fact, generally inferior to what Time Warner Cable is accomplishing on its own. We strongly recommend the Commission carefully consider whether Charter’s proposal is as truly compelling as they claim.
 We are also very concerned about Charter’s plans to deliver affordable Internet access. Chairman Wheeler expressed his concerns about the digital divide in broadband. The cost of access is perhaps the most important factor for getting broadband service in income-challenged households. If Charter’s price is too high, many will go without service.
We are also very concerned about Charter’s plans to deliver affordable Internet access. Chairman Wheeler expressed his concerns about the digital divide in broadband. The cost of access is perhaps the most important factor for getting broadband service in income-challenged households. If Charter’s price is too high, many will go without service.
Charter has no plans to continue Time Warner Cable’s $14.99 Everyday Low Price Internet service – a very important offer for low income residents and senior citizens who are unable to afford the nearly $60 regular price both companies charge for their 50 or 60Mbps tiers. Time Warner Cable offers this $14.99 tier without preconditions, restricted qualifiers, contracts, or limits on what types of services can be bundled with it. Any consumer can buy the service and bundle it with Time Warner Cable telephone service for an additional $10 a month, which offers a nationwide local calling area, as well as free calls to the European Union, Mexico, Puerto Rico, and several Asian nations.
The loss of a $25 plan that includes basic Internet access and a bundled, 911-capable telephone line would be devastating to low-income households and senior citizens. During the Comcast-Time Warner Cable merger hearings in New York, no topic elicited as much interest as Internet affordability and the onerous restrictions cable operators place on their income-qualified budget Internet plans.[19] The same concerns exist today with Charter’s application. Time Warner Cable clearly offers a superior product line for these customers, including two other Internet service tiers offering stepped up Internet speeds in $10 increments. These options would be unavailable from Charter.
Charter’s proposed solution to serve low-income customers is adoption of Bright House Networks’ Connect2Compete program, which offers restricted access to $9.95/month Internet service for those who qualify.
 Stop the Cap! investigated Bright House Networks’ existing offer in a report to our readers in June 2015, and we urge the Commission to look much more closely at the specific conditions Bright House customers have had to endure to qualify to subscribe[20]:
Stop the Cap! investigated Bright House Networks’ existing offer in a report to our readers in June 2015, and we urge the Commission to look much more closely at the specific conditions Bright House customers have had to endure to qualify to subscribe[20]:
1) You must have at least one child qualified for the National School Lunch Program. They need not be enrolled now.
2) You cannot have been a Bright House broadband customer during the last three months. If you are a current customer, you must first cancel and go without Internet service for 90 days (or call the phone company and hope to get a month-to-month DSL plan in the interim.)
3) If you have an overdue bill older than 12 months, you are not eligible until you pay that bill in full.
4) Bright House does not enroll customers in discounted Internet programs year-round. From a Bright House representative:
“We do participate in this particular program, however, it is only around September that we participate in it. This is a seasonal offer that we have which can only be requested from the middle of August to the middle of September, which is when most start up with school again for the year.”
5) Bright House does not take orders for the Low-Income Internet plan over the Internet. You have to enroll by phone: (205) 591-6880.
Families fall into poverty every day of the year, and poverty-stricken families move from one school district to another every day of the year. So it’s horribly unfair to tell them they’d qualify for this program if only they had fallen into poverty sometime between the middle of August and the middle of September.
It has been our experience covering service providers across all 50 states that most design these low-cost Internet access programs with revenue protection first in mind. Charter Communications is no different. As with Comcast, Connect2Compete is only available to families with school age children. Applicants face an intrusive, complicated, and time-restricted enrollment process that threatens to dampen and discourage participation.
Charter’s claimed interest to meet the needs of low-income customers might be more honorable if not for their insistence otherwise-qualified existing customers cannot downgrade their regular price broadband plan to Connect2Compete unless they voluntarily go without Internet access for three months.

Time Warner Cable goes out of its way to advertise “No Data Caps.”
We strongly recommend Charter Communications be compelled to continue Time Warner’s $14.99 Internet plan, but at speeds no less than 25Mbps, the minimum definition of entry-level broadband by the FCC. We also recommend Charter be required to further discount this plan to $9.95 a month for qualified customers who meet a simple income test the Commission can define and establish. These discount programs should not just be available to families with school-age children. Everyone needs affordable Internet access, whether you are single and looking for your first job or a fixed income senior citizen.
All restrictions for existing customers or those with an outstanding balance must be prohibited and sign-ups must be accepted 365 days a year with re-qualification occurring not more than once annually.
Charter’s broadband offer for lower-income Americans is inadequate, and so is their plan for customers who need enhanced service.
Time Warner Cable Maxx delivers a more compelling offer for consumers and small businesses that need much faster Internet access. Charter’s upgrade will offer customers two choices: 60 or 100Mbps service. Time Warner Cable Maxx offers considerably more[21]:
 Charter Communications’ commitment to not impose “usage caps” for three years is inadequate. As we have learned from Comcast, the industry definition of a “usage cap” differs widely from the definition understood by most consumers.
Charter Communications’ commitment to not impose “usage caps” for three years is inadequate. As we have learned from Comcast, the industry definition of a “usage cap” differs widely from the definition understood by most consumers.
Charter’s commitment must be expanded to prohibit all forms of usage pricing, such as those similar to what Comcast is market testing in several of its service areas.[22] In these markets, Comcast has established an arbitrary usage allowance and charges punitive overlimit fees to customers that exceed it. Comcast has repeatedly denied it has “usage caps” because its so-called ‘data plans’ allow customers to voluntarily exceed their usage allowance, at a cost. Without a commitment Charter will also not impose usage-based pricing, its commitment to regulators not to impose “usage caps” is largely meaningless.
More concerning, Charter Communications has a history of capping their customers’ usage. Less than three months before announcing it would acquire Time Warner Cable, Charter Communications quietly dropped usage caps in place on its broadband plans since 2009, without explanation.[23] The FCC itself is investigating this and other related issues as part of this proceeding.[24]
 Consumers have shown no interest in usage-based pricing or usage-capped wired Internet and strongly prefer unlimited access. One only need look at Time Warner Cable’s own results when offering an optional discounted Internet plan for customers volunteering to limit their usage.
Consumers have shown no interest in usage-based pricing or usage-capped wired Internet and strongly prefer unlimited access. One only need look at Time Warner Cable’s own results when offering an optional discounted Internet plan for customers volunteering to limit their usage.
Time Warner Cable CEO Rob Marcus noted customers strongly want to keep their unlimited use plans, even if they cost more. Speaking at the Deutsche Bank Media, Internet, and Telecom Conference, Marcus noted:
“If you take the 30GB a month and compare it to what median usage is, let’s say high 20s — 27GB a month, that would suggest a whole lot of customers would do well by taking the 30GB service,” Marcus said. “Notwithstanding that, very few customers — in the thousands — have taken the usage based tiers and I think that speaks to the value they place on unlimited — not bad because we plan to continue to offer unlimited for as far out as we can possibly see.”[25]
Marcus has repeatedly made it clear compulsory usage caps are off the table at Time Warner Cable – a lesson they learned after customers pushed back and forced them to shelve a usage cap experiment planned for Rochester, N.Y., Greensboro, N.C., and Austin, San Antonio, and Beaumont, Tex. in April 2009[26]. The company has never raised the possibility of compulsory usage limits or usage-based billing again.
“We have no intention of abandoning an unlimited product we think that something that customers value and are willing to pay for,” said Time Warner Cable CEO Robert Marcus. “The way we’ve approached usage-based pricing is to offer it as an option for customers who prefer to pay less because they tend to use less. And we’ve made those available at 5 gigabytes per month and 30 gigabytes per month levels.[27]”

A deal with Charter would mean Time Warner Cable’s bonds would be downgraded to junk status.
Time Warner Cable again offers a superior choice for Americans, and it is an important one. Chairman Wheeler said “last-mile power cannot be a lever for gaining an unfair advantage.” With many consumers having no practical choice for an alternative broadband provider, allowing Charter to impose usage limits or forcing customers into even higher-priced usage billing plans would deliver a major unfair advantage into the hands of the cable operator, always concerned with protecting its cable television package from emerging online video competition.
In fact, almost all of Charter’s so-called customer-friendly commitments and policies have a very unfriendly expiration date of just three years, which should be unacceptable to the Commission. There is no reason Charter cannot extend its commitments to not charge modem fees, adhere to the basic principles of Net Neutrality, and not impose usage caps or other forms of usage billing permanently. Without such a commitment, consumers could soon pay much higher prices for broadband service, and without robust competition unlikely to develop over the next three years, there will be every incentive for Charter to further boost earnings by imposing modem fees and usage pricing on its customers.
One of the strongest incentives for rate increases is the level of debt Charter Communications will assume in this transaction. The Department of Public Service staff in New York concluded New Charter’s debt and lowered credit rating “represents the single most substantial risk of the proposed transaction.”[28]
Debt servicing costs and more expensive credit are both deterrents to investment and are likely to limit the scope of Charter’s ongoing system upgrades and maintenance. Charter is a much smaller cable operator than Time Warner Cable, and is itself still in the process of repairing and upgrading its own cable systems and those it acquired in earlier acquisition deals. Time Warner Cable, in contrast, is in a much stronger financial position to carry out its commitments associated with the Maxx upgrade program.
Charter’s general offer to consider expanding service into unserved areas is vague, or has been redacted. We remind the Commission the past history of winning expansion commitments from cable operators who rely on Return On Investment (ROI) formulas to determine which homes and businesses they will serve have met with limited success.
The pervasive problem of rural broadband availability is unlikely to be resolved substantially by this transaction without the strongest buildout requirements. But even that is unlikely to be of much help for large areas outside of existing video franchise areas.
Compelling Charter Communications to adopt universal service obligations within all existing Time Warner Cable and Bright House franchise areas may be a good start. Under such a requirement, any consumer or business that wants cable service and lives within the geographic boundaries of an existing franchise area would receive it upon request without construction fees, surcharges, or other passed-along fees to reach that customer, regardless of their distance from the existing cable plant or ROI formula. The largest impact of this would be to extend cable service into business parks and commercial buildings, which often lack cable service, but many suburban and exurban residential customers would also benefit. This also would achieve the Chairman’s goal to facilitate rural broadband where incumbents have generally failed to provide the service.
 The Commission must carefully consider Charter’s financial capacity to meet these obligations as well. No commitment is worth much if a company ultimately fails to deliver on it.
The Commission must carefully consider Charter’s financial capacity to meet these obligations as well. No commitment is worth much if a company ultimately fails to deliver on it.
An overburdened cable operator is also unlikely to make substantial investments in improving customer service, and that makes the risk of depending on Charter Communications to improve Time Warner Cable’s already poor customer service rating doubtful. It also risks the much higher scores Bright House customers have given to that company for its superior customer service.
Competition is the biggest incentive to improve customer service and responsiveness, and that is unlikely to deliver much pressure on cable companies like Charter over the next few years. In fact, we argue customer service is likely to deteriorate in the short term because of the disruptiveness of any ownership change and eventual billing system integration.
Consumer Reports already rates Time Warner and Charter’s Internet Service poorly[29]:
- Charter: 63 (Reader Score), Poor Value, Fair Reliability, Good Speed, Mediocre Phone/Online Support, Fair In-Home Support
- Time Warner Cable: 57 (Reader Score), Poor Value, Fair Reliability, Fair Speed, Mediocre Phone/Online Support, Fair In-Home Support
Charter Communications’ proposed benefits to Time Warner Cable and Bright House cable television customers are also weak and not compelling. Both Time Warner Cable and Charter proposed to move to all-digital cable television to free up bandwidth to offer improved broadband before the merger deal was announced. Bright House was also headed in the same direction.
 While consumers clamor for smaller, less-costly cable television packages, Charter Communications’ CEO Thomas Rutledge is credited for inventing the “triple play” concept of convincing customers to package more services – broadband, television and telephone — together in return for a discount. Reuters cited his preference for “simplified pricing,”[30] which is why Charter offers most customers only two options for broadband service and one giant television package dubbed Spectrum TV containing more than 200 channels.[31]
While consumers clamor for smaller, less-costly cable television packages, Charter Communications’ CEO Thomas Rutledge is credited for inventing the “triple play” concept of convincing customers to package more services – broadband, television and telephone — together in return for a discount. Reuters cited his preference for “simplified pricing,”[30] which is why Charter offers most customers only two options for broadband service and one giant television package dubbed Spectrum TV containing more than 200 channels.[31]
Unfortunately, any benefits from an all-digital television package are likely to be diluted when customers get the bill. Currently, many Time Warner Cable customers watch analog channels on television sets around the home without the need to rent a costly set top box. Any transition to digital television will require the rental of a set top box or purchase of a third-party device to view cable television programming. These can represent costly add-ons for an already high cable bill.
With approximately 99 percent of customers renting their set-top box directly from their pay-tv provider, the set-top box rental market may be worth more than $19.5 billion per year, with the average American household spending more than $231 per year on set-top box rental fees, according to findings from Senators Edward J. Markey (D-Mass.) and Richard Blumenthal’s (D-Conn.) query of the top-ten pay-tv multichannel video programming distributors (MVPDs).[32]
Passed by Congress in December, the STELA Reauthorization Act of 2014 repealed the set-top box integration ban, which enabled consumers to access technology that allowed use of a set-top box other than one leased from their cable company. Without the integration ban, by the end of this year, cable companies will no longer be required to make their services compatible with outside set-top boxes, like TiVo for example, bought directly by consumers in the retail marketplace.
American cable subscribers spend, on average, $89.16 a year renting a single set-top box. The average set-top box rental fee for each company was used to calculate an overall set-top box rental cost average across companies: $7.43 a month, or $89.16 per year. Considering many homes rent a DVR box to make and view recordings and maintain less-capable boxes on other televisions, the total cost adds up quickly. The average household spends $231.82 a year on set-top box rental fees, according to Sens. Markey and Blumenthal.
Charter proposes to introduce a new generation of set top boxes but as far as we know, has not disclosed the monthly cost of these IP-capable boxes to subscribers. We do note the current generation of digital set-top boxes leased by Charter cost customers $6.99 a month each, slightly less than the national average.[33] We anticipate this fee may rise after the introduction of more advanced equipment. We note Charter also charges its television customers in a city like St. Louis an extra $6.05 a month for the “Broadcast TV Service Charge” and $4.99 a month for “Whole House Wire Maintenance.”[34]
Other points the Commission should consider in reviewing this transaction:
- While it is true Charter and Time Warner don’t compete for the same customers, it is inaccurate to suggest the transaction will not alter competition. Cable industry consolidation is underway, in part, to help larger combined operators secure better volume discounts for increasingly expensive video programming.AT&T’s primary motivation to acquire satellite provider DirecTV was to secure better prices for video programming, both for DirecTV customers but more importantly for its own, much smaller, U-verse TV operation.[35]The cost barrier for new, directly competing entrants into the cable television business is well-recognized, especially by smaller independent cable television providers that lack the ability to secure similar volume discounts for themselves. The American Cable Association, representing small operators, warned the FCC “existing providers of both broadband and MVPD services and new entrants will be deterred from expanding their broadband networks or otherwise undertaking new builds” as a result of increasing programming costs.[36]As a result, it is unlikely a new provider will be able to develop a sustainable business model that includes cable television while paying wholesale programming costs that are dramatically higher than what combined companies like New Charter will pay.
- The Commission must insist that Time Warner Cable customers in legacy service areas be treated the same as those already upgraded to Maxx service. If the deal is approved, Charter must be compelled to commit to continue Time Warner Cable’s Maxx upgrade initiative across the entire footprint of Time Warner Cable’s former service areas, to be completed within 30 months. We also agree with the staff recommendation of the N.Y. Department of Public Service that Charter also be compelled to upgrade its facilities to support gigabit broadband, but this should be extended to include all of its service areas, not just the largest cities.This does not pose a significant challenge to cable operators. With the upcoming introduction of DOCSIS 3.1 technology, operators even smaller than Charter will support 1Gbps broadband speeds as they drop analog television signals. Suddenlink[37], MidContinent[38], Cox[39], and Mediacom[40] already have gigabit deployment plans underway.
- The Commission must establish and enforce meaningful enforcement mechanisms should Charter fail to achieve its commitments as part of this transaction. Cable consolidation has never significantly benefited consumers. Charter is not guaranteeing Time Warner Cable or Bright House customers will receive a lower bill as a result of this merger. Nor is it committing to pass along the lower prices it will achieve through negotiations for wholesale video programming volume discounts. Cable rates, especially for broadband, will continue to increase. Without meaningful competition, there is no incentive to give consumers a better deal or better service.That is why if the Commission feels it must approve this transaction, the conditions that accompany it to achieve a true public interest benefit must be meaningful, directly relevant to the majority of customers, and ongoing.
Cable operators know once they secure a franchise or become the incumbent provider, no other cable company will negotiate with city officials to take over that franchise if the current provider’s application is denied during renewal. Once Charter (or any other cable company) establishes a presence, there is little or no chance a community will be able to get rid of that provider if it fails to perform. That is why any franchise transfer that comes from an acquisition or merger must be treated with the upmost seriousness. Customers will likely live with the decision the Commission makes for the next 10-20 years or more.
 As the Commission must realize, this transaction does not just involve entertainment. Recently, the Obama Administration declared broadband Internet access a “core utility.”[41]
As the Commission must realize, this transaction does not just involve entertainment. Recently, the Obama Administration declared broadband Internet access a “core utility.”[41]
“Broadband has steadily shifted from an optional amenity to a core utility for households, businesses and community institutions,” according to a report from the administration’s Broadband Opportunity Council. “Today, broadband is taking its place alongside water, sewer and electricity as essential infrastructure for communities.”
Our group strongly believes regulators should not take a risk on Charter’s less-then-compelling offer when Time Warner Cable and Bright House have both demonstrated a better financial position. Time Warner has a proven track record of delivering on its commitments to improve service with its Maxx upgrade project. Time Warner Cable has superior options for low-income consumers, offers more broadband options and faster speeds for entrepreneurs in the digital/information economy, and has committed to providing unlimited Internet access – a critical prerequisite for consumers choosing to drop cable television’s one-size-fits-all bloated video package and watch only the shows they want to see and pay for online.
At the start of our presentation, we referred to the Chairman’s four stated goals for improving broadband and competition. At this point, it should be obvious that shrinking the number of companies providing service has not delivered significant service improvements. In fact, for many customers, Charter’s offer is worse.
Allowing further marketplace consolidation widens the gap for cable television programming costs, which could deter new competitors from entering the market. Small providers pay dramatically higher programming costs while the largest receive substantial volume discounts. That is contrary to the Chairman’s goal of protecting last-mile competition.
Online video has created the “cord-cutting” effect, allowing consumers to shop for better video values beyond the local cable company. Without a permanent ban on usage caps and usage pricing, providers like Charter (that maintained usage caps until a few months before this application was filed) have a strong incentive to resume them after the deal’s token three-year commitment expires. Without also closing the obvious loophole of “usage pricing,” nothing precludes Charter from imposing usage-based pricing on consumers immediately after the deal is approved.
Promoting expanded rural broadband, another priority of the Commission, does little if the incumbent providers refuse to offer it. We see nothing in Charter’s public application that commits them to extending service to specific areas Time Warner Cable or Bright House do not service today. In fact, before this application was filed, Charter’s willingness to provide service to unserved areas in their own existing franchise areas was not always evident.[42] It is hard to believe Charter will voluntarily disregard their own Return On Investment formula to provide the service many rural customers eagerly hope might be forthcoming if the provider was somebody other than Time Warner Cable or Bright House.
We urge the FCC to deny Charter’s application. If it sees fit to make a different choice, we strongly recommend you demand Charter meet, at the minimum, the same level of service Time Warner Cable Maxx provides across the entire existing Time Warner franchise area, achieve the same customer service standard well-regarded Bright House manages for its customers, and a better deal for consumers that continue to face spiraling cable bills, few competitive choices, and no new alternatives on the horizon.
- [1] https://dealbook.nytimes.com/2014/02/13/the-comcast-time-warner-deal-by-the-numbers/?_r=0
- [2] https://newsroom.charter.com
- [3] https://www.spectrum.com/about
- [4] http://www.jdpower.com/press-releases/2015-us-residential-television-internet-telephone-service-provider-satisfaction
- [5] https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/09/most-of-the-us-has-no-broadband-competition-at-25mbps-fcc-chair-says/
- [6] https://www.theverge.com/2014/1/31/5365816/time-warner-cable-maxx-plans-broadband-cable-improvements-in-nyc-la
- [7] https://www.fiercecable.com/cable/twc-promises-maxx-to-reach-45-customers-by-end-year-tivo-to-support-apple-s-airplay
- [8]
- [9] https://www.spectrum.com/packages
- [10] http://stopthecap.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/psc-staff-recommend-charter-twc-15-m-0388.pdf
- [11] https://www.spectrum.com/internet?cmp=TWC&iid=internet-lob:1:1:compareplans
- [12] https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/09/most-of-the-us-has-no-broadband-competition-at-25mbps-fcc-chair-says/
- [13]
- [14] http://www.twcableuntangled.com/2015/04/twc-gains-momentum-with-best-ever-subscriber-growth-customer-enhancements/
- [15] https://newsroom.charter.com/
- [16] https://seekingalpha.com/article/2864536-time-warner-cables-twc-ceo-rob-marcus-on-q4-2014-results-earnings-call-transcript
- [17] http://www.twcableuntangled.com/2014/01/get-the-details-on-twcs-plan-to-transform-ctv-internet-experience/
- [18] http://stopthecap.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/psc-staff-recommend-charter-twc-15-m-0388.pdf
- [19] See e.g., Case 14-M-0183, Joint Petition of Comcast Corporation and Time Warner Cable, Inc. for Approval of a Transfer of Control of Subsidiaries and Franchises, Information Forum/Public Statement Hearing (dated June 19, 2014) Tr. 29-33.
- [20] http://stopthecap.com/2015/06/25/bright-houses-mysterious-internet-discount-program-charter-wants-to-adopt-nationwide/
- [21] http://www.timewarnercable.com/en/enjoy/better-twc/internet.html
- [22] https://www.xfinity.com/support/articles/data-usage-plan
- [23] http://stopthecap.com/2015/09/23/fcc-demands-details-about-charters-suddenly-retired-usage-caps/
- [24] https://www.fcc.gov/document/request-information-sent-charter-communications-inc-0
- [25] http://stopthecap.com/2014/03/13/time-warner-cable-admits-usage-based-pricing-is-a-big-failure-only-thousands-enrolled/
- [26] http://abcnews.go.com/Technology/story?id=7368388
- [27] http://stopthecap.com/2014/10/30/time-warner-cable-recommits-mandatory-usage-caps-long-company-remains-independent/
- [28] http://documents.dps.ny.gov/public/Common/ViewDoc.aspx?DocRefId={C60985CC-BEE8-43A7-84E8-5A4B4D8E0F54} (p.39)
- [29] http://www.consumerreports.org/cro/electronics-computers/computers-internet/telecom-services/internet-service-ratings/ratings-overview.htm
- [30] http://www.reuters.com/article/2014/01/30/us-charter-timewarnercable-rutledge-anal-idUSBREA0T01D20140130
- [31] https://www.spectrum.com/cable-tv#/channel-lineup
- [32] http://www.markey.senate.gov/news/press-releases/markey-blumenthal-decry-lack-of-choice-competition-in-pay-tv-video-box-marketplace
- [33] https://www.charter.com/browse/content/rate-card-info (city of St. Louis, Mo.)
- [34] https://www.charter.com/browse/content/rate-card-info (city of St. Louis, Mo.)
- [35] http://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2015/07/24/fcc-approves-ts-acquisition-directv/30626421/
- [36] http://www.americancable.org/node/5229
- [37] http://www.multichannel.com/news/technology/suddenlink-boots-1-gig-broadband/392087
- [38] https://www.midco.com/PressRoom/2014/midcontinent-bringing-gigabit-internet-access-to-the-northern-plains/
- [39] http://www.multichannel.com/news/distribution/cox-plots-docsis-31-plans/393996
- [40] http://www.multichannel.com/news/cable-operators/mediacom-sets-residential-1-gig-rollout/393585
- [41] http://thehill.com/policy/technology/254431-obama-administration-declares-broadband-core-utility-in-report
- [42] http://www.dslreports.com/forum/r28864058-Why-won-t-Charter-come-another-1-2-mile-for-more-customers


 Subscribe
Subscribe
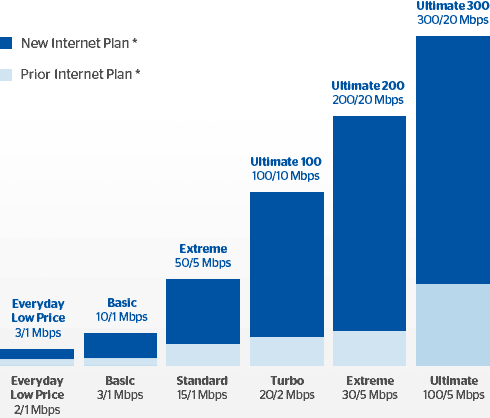
 Almost all of Charter’s so-called customer-friendly commitments and policies have a very unfriendly expiration date of three years, which should be unacceptable to the Commission. There is no reason Charter cannot extend its commitments to not charge modem fees, adhere to the basic principles of Net Neutrality, and not impose usage caps or other forms of usage billing permanently. Without such a commitment, consumers could soon pay much higher prices for broadband service, and without robust competition unlikely to develop in most of New York over the next three years, there will be every incentive for Charter to further boost earnings by imposing modem fees and usage pricing on its customers.
Almost all of Charter’s so-called customer-friendly commitments and policies have a very unfriendly expiration date of three years, which should be unacceptable to the Commission. There is no reason Charter cannot extend its commitments to not charge modem fees, adhere to the basic principles of Net Neutrality, and not impose usage caps or other forms of usage billing permanently. Without such a commitment, consumers could soon pay much higher prices for broadband service, and without robust competition unlikely to develop in most of New York over the next three years, there will be every incentive for Charter to further boost earnings by imposing modem fees and usage pricing on its customers.
 As Time Warner Cable customers loudly reminded the Commission in the Comcast merger proceeding, there is such a thing as a cable operator even worse than Time Warner Cable, already one of the lowest rated companies in the country. Comcast’s reputation preceded its intended entry into New York on a massive scale and the application was eventually withdrawn.
As Time Warner Cable customers loudly reminded the Commission in the Comcast merger proceeding, there is such a thing as a cable operator even worse than Time Warner Cable, already one of the lowest rated companies in the country. Comcast’s reputation preceded its intended entry into New York on a massive scale and the application was eventually withdrawn.


 Fans of the “hands-off” approach to broadband oversight finally have a country where they can see a deregulated free marketplace in action, where consumers theoretically pick the winners and losers and where demand governs the kinds of services consumers and businesses can get from their providers.
Fans of the “hands-off” approach to broadband oversight finally have a country where they can see a deregulated free marketplace in action, where consumers theoretically pick the winners and losers and where demand governs the kinds of services consumers and businesses can get from their providers. To attract investment and competition, the government declared all value-added services like Internet access deregulated and guaranteed the complete privatization of all government telecom facilities no later than 1998. It also initially limited the number of companies that could compete against PLDT in each region to two new entrants. The government felt that would be necessary to attract competitors that knew they would have to quickly invest millions, if not billions, to build telecom infrastructure in the Philippines. It would be hard to make a case for investment in a region where a half-dozen companies all engaged in a price war fighting for customers while stringing new telephone lines and building cell towers.
To attract investment and competition, the government declared all value-added services like Internet access deregulated and guaranteed the complete privatization of all government telecom facilities no later than 1998. It also initially limited the number of companies that could compete against PLDT in each region to two new entrants. The government felt that would be necessary to attract competitors that knew they would have to quickly invest millions, if not billions, to build telecom infrastructure in the Philippines. It would be hard to make a case for investment in a region where a half-dozen companies all engaged in a price war fighting for customers while stringing new telephone lines and building cell towers. The NTC remained more “hands-off” than the FCC, avoiding significant involvement in critical interconnection issues — how competing telephone companies handle calls from subscribers of a competing provider. That was last an issue in the United States in the early 1900s, where rare independent competitors to the rapidly consolidating Bell System faced a telecom giant that initially refused to handle calls from customers of other companies. American regulators eventually demanded interconnection policies that guaranteed customers could reach any other telephone customer, regardless of what company handled their service. In the Philippines, the NTC eventually mandated less-demanding access, allowing companies to charge long distance rates to reach customers of other companies. In the 1990s, it was not uncommon to find businesses maintaining at least two telephone lines with different companies to escape long distance expenses and stay accessible to all of their potential customers.
The NTC remained more “hands-off” than the FCC, avoiding significant involvement in critical interconnection issues — how competing telephone companies handle calls from subscribers of a competing provider. That was last an issue in the United States in the early 1900s, where rare independent competitors to the rapidly consolidating Bell System faced a telecom giant that initially refused to handle calls from customers of other companies. American regulators eventually demanded interconnection policies that guaranteed customers could reach any other telephone customer, regardless of what company handled their service. In the Philippines, the NTC eventually mandated less-demanding access, allowing companies to charge long distance rates to reach customers of other companies. In the 1990s, it was not uncommon to find businesses maintaining at least two telephone lines with different companies to escape long distance expenses and stay accessible to all of their potential customers.
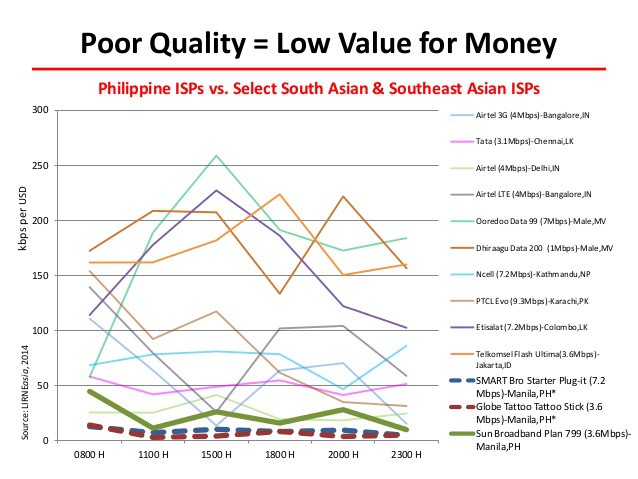

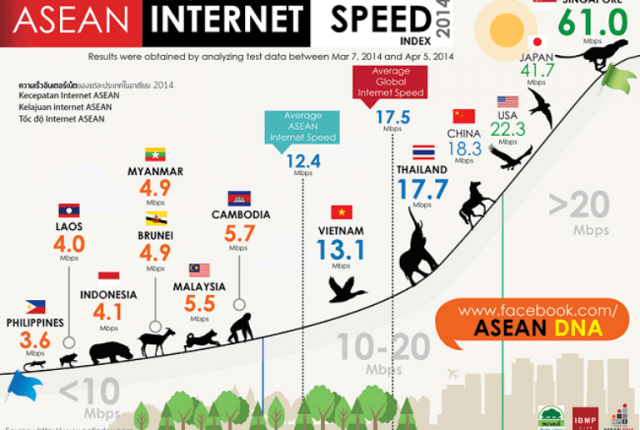

 While segmenting out popular mobile apps for special treatment, Philippine mobile providers have also taken Verizon and AT&T’s lead, pushing plans like
While segmenting out popular mobile apps for special treatment, Philippine mobile providers have also taken Verizon and AT&T’s lead, pushing plans like  Providers in the Philippines have learned a lot from America’s telecommunications lobbyists. Their advocacy campaigns revolve around the theme that the United States has the best wireless networks in the world, developed under a largely hands-off regulatory philosophy that the Philippine government should follow.
Providers in the Philippines have learned a lot from America’s telecommunications lobbyists. Their advocacy campaigns revolve around the theme that the United States has the best wireless networks in the world, developed under a largely hands-off regulatory philosophy that the Philippine government should follow. The NTC is
The NTC is 