 All signs are pointing to a relative cake walk for Charter Communications’ executives this afternoon as they seek final approval from the California Public Utilities Commission to acquire Time Warner Cable systems in the state, with the help of an Administrative Law Judge that is recommending approval with a minimum of conditions.
All signs are pointing to a relative cake walk for Charter Communications’ executives this afternoon as they seek final approval from the California Public Utilities Commission to acquire Time Warner Cable systems in the state, with the help of an Administrative Law Judge that is recommending approval with a minimum of conditions.
In fact, the strongest condition Charter may have to accept in California came by accident. As part of Charter’s lobbying effort, it proposed a set of voluntary conditions it was prepared to accept, claiming to regulators these conditions would represent benefits of approving the transaction. One of those was a temporary three-year commitment to abide by the FCC’s Open Internet Order, which among other things bans paid prioritization (Internet fast lanes), intentionally blocking lawful Internet content, and speed throttling your Internet connection.
Somewhere along the way, someone forgot to include the language that sunsets (or ends) Charter’s voluntary commitment after three years.
Without it, Charter will have to abide by the terms of the FCC’s Open Internet Order forever.
 Soon after recognizing the change in language, Charter’s lawyers appealed to the CPUC to correct what it called a “drafting error.”
Soon after recognizing the change in language, Charter’s lawyers appealed to the CPUC to correct what it called a “drafting error.”
“[New Charter does] not seek modification of the second sentence, which matches their voluntary commitments, but believe[s] that the three-year limitation in the second sentence was intended to— and should—apply to the first sentence as well,” Charter’s lawyers argued two weeks ago.
In other words, the Administrative Law Judge’s apparent attempt to ‘cut and paste’ Charter’s own press release-like voluntary deal commitments into his personal recommendation went horribly wrong. Charter’s lawyers prefer to call it an “intent to track” the company’s voluntary commitments. Either way, Charter’s lawyers all call the new language unfair.
“Holding New Charter indefinitely to FCC rules even after the FCC’s rules are invalidated or modified, and irrespective of future market conditions or the practices or rules governing New Charter’s competitors, would be a highly unconventional requirement,” the lawyers complained.
That provides valuable insight into how “New Charter” is likely to feel about Net Neutrality three years from now. Charter’s lawyers argue it would be unfair to hold them to “invalidated” rules — the same ones the company itself has voluntarily embraced as a condition of approval, but only for now.
Remarkably, in the final revision of the Administrative Law Judge’s recommendations to the CPUC recommending approval, the language that is keeping Charter’s lawyers up at night is still there:
New Charter shall fully comply with all the terms and conditions of the Federal Communications Commission’s Open Internet Order, regardless of the outcome of any legal challenge to the Open Internet Order. In addition, for a period of not less than three years from the closing of the Transaction, New Charter (a) will not adopt fees for users to use specific third-party Internet applications; (b) will not engage in zero-rating; (c) will not engage in usage-based billing; (d) will not impose data caps; and (e) will submit any Internet interconnection disputes not resolvable by good faith negotiations on a case-by-case basis.
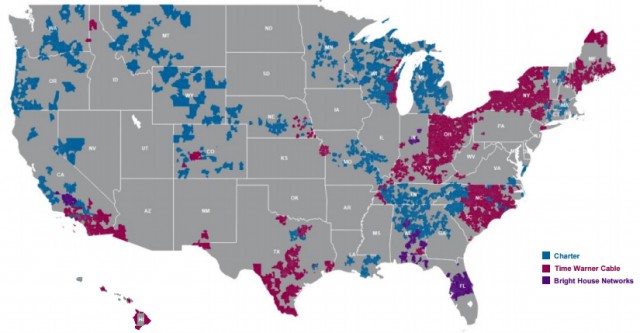
Charter’s new service area, including Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers.
If it remains intact through the vote expected this afternoon, New Charter will have to permanently abide by the FCC’s Open Internet Order, with no end date. That condition will apply in California, and because of most-favored state status, also in New York.
Stop the Cap!’s recommendations to the CPUC are also in the same document, although our views were not shared by the judge:
Stop the Cap! objects to [New Charter’s] 3-year moratorium on data caps and usage based pricing for broadband services. It argues that such bans should be made permanent or, if not permanent, should last at least 7 years in parallel with the lifespan of the conditions imposed in the FCC’s approval of the parent company merger. In addition, Stop the Cap! objects to what it asserts will be a major price increase for existing Time Warner customers when Charter’s pricing plans replace Time Warner’s pricing plans.
More broadly, Stop the Cap! president Phillip Dampier called the revised recommendations to approve the deal underwhelming and disappointing.
“By window-dressing what is essentially Charter’s own voluntary offer to the CPUC, the commission is continuing to miss a golden opportunity to win deal conditions that will meaningfully benefit Californian consumers that will otherwise get little more than higher cable and broadband bills,” Dampier told Communications Daily. “Virtually everything Charter is promising customers is already available or soon will be from Time Warner Cable, often for less money. Time Warner Cable committed to offering its customers 300Mbps speeds, no usage caps or usage billing, and all-digital service through its Maxx upgrade program, expected to be complete by the end of 2017 or 2018. The CPUC is proposing to allow New Charter to wait until 2019 to provide 300Mbps service and potentially cap Internet service three years after that, four years less than what the FCC is demanding.”
Among the conditions Charter will be expected to fulfill in return for approval of its merger in California:
- Within a year of the closing of the merger deal, New Charter must boost broadband download speeds for customers on their all-digital platform to at least 60Mbps, an upgrade that is largely already complete.
- Within 30 months, New Charter must upgrade all households in its California service territory to an all-digital platform with download speeds of not less than 60Mbps, an upgrade that has already been underway for a few years.
- By Dec. 31, 2019, New Charter shall offer broadband Internet service with speeds of at least 300Mbps download to all households with current broadband availability from New Charter in its California network. Time Warner Cable essentially promised to do the same by early 2018, with many of its customers already getting up to 300Mbps in Southern California.
- While Charter talks about a bright future for the Time Warner customers joining its family, the company has not done a great job maintaining and upgrading its own cable systems in parts of California. Many smaller communities still only receive analog cable TV from Charter, with no broadband option at all. Therefore, the CPUC is giving New Charter three years to deploy 70,000 new broadband “passings” to current analog-only cable service areas in Kern, Kings, Modoc, Monterey, San Bernardino and Tulare counties. But the CPUC is giving New Charter a break, only requiring them to offer up to 100Mbps service in these communities.
- Time Warner Cable and Bright House customers in California will be able to keep their current broadband service plans for up to three years. Customers will also be allowed to buy their own cable modems and set-top boxes, but there is no requirement New Charter compensate customers who do with a service discount.
- Within six months of the deal closing, New Charter must offer Lifeline phone discounts within its service territory in California.
- New Charter must print and distribute brochures explaining the need for backup power to keep phone service working if electricity is interrupted. Those brochures must be available in multiple languages including, but not limited to, English, Spanish, Chinese and Vietnamese, as well as in accessible formats for visually impaired customers.
The CPUC is also expected to adopt Charter’s own voluntary commitments not to impose usage caps, usage billing, modem fees, and other customer-unfriendly practices for three years, a point that drew strong criticism from Stop the Cap! and the California Office of Ratepayer Advocates for being inadequate.
Both groups proposed that bans on data caps and usage billing should stay in place “until there is effective competition in Southern California, or no shorter than seven years after the decision is issued, whichever is later.”
ORA’s program supervisor Ana Maria Johnson believes the proposed changes don’t go far enough to “mitigate the harms that the merger will likely cause, especially in Southern California.”
Dampier was surprised how little the CPUC seemed to be asking of New Charter, especially in comparison to regulators in New York.
“The New York Public Service Commission did a more thorough job protecting consumers by insisting on faster and better upgrades, including readiness for gigabit service, and the same level of broadband service for all of New Charter’s customers in New York,” Dampier argued. “It also demanded and won meaningful expansion in rural broadband, low-cost Internet access, protection of New York jobs, and improved customer service. It is remarkable to us the CPUC did not insist on at least as much for California.”
The CPUC is expected to take a final vote on the merger deal this afternoon, starting at 12:30pm ET/9:30am PT and will be webcast. It is the 20th item on the agenda.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Stop the Cap! continues the fight for a better deal for Time Warner Cable customers that could soon end up as Charter Communications customers, if the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) approves the merger.
Stop the Cap! continues the fight for a better deal for Time Warner Cable customers that could soon end up as Charter Communications customers, if the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) approves the merger.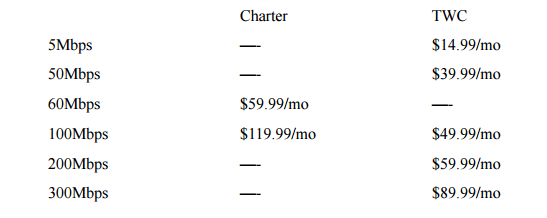

 “Clearly these TWC customers are materially much worse off under New Charter than TWC,” Friedman told the CPUC. “Equally clear is that Charter’s ‘Simplified Pricing’ (perhaps more accurately described as ‘Fewer Options and Higher Prices’) is far from a public benefit. This massive price increase will affect literally every stand-alone-broadband TWC customer other than the few who qualify for the School Lunch/Senior Assistance plan. While the low-cost School Lunch/Senior Assistance plan is great for the narrowly targeted group of consumers who manage to qualify, roughly doubling the cost of broadband for every other standalone customer more than offsets the combined value of every other ‘benefit’ that the applicants allege will come from this transfer.”
“Clearly these TWC customers are materially much worse off under New Charter than TWC,” Friedman told the CPUC. “Equally clear is that Charter’s ‘Simplified Pricing’ (perhaps more accurately described as ‘Fewer Options and Higher Prices’) is far from a public benefit. This massive price increase will affect literally every stand-alone-broadband TWC customer other than the few who qualify for the School Lunch/Senior Assistance plan. While the low-cost School Lunch/Senior Assistance plan is great for the narrowly targeted group of consumers who manage to qualify, roughly doubling the cost of broadband for every other standalone customer more than offsets the combined value of every other ‘benefit’ that the applicants allege will come from this transfer.” AT&T has indirectly announced it will enforce hard data caps on its U-verse broadband service for the first time, imposing overlimit fees for customers that exceed their allowance unless they agree to pay $30 extra a month for a new unlimited add-on plan.
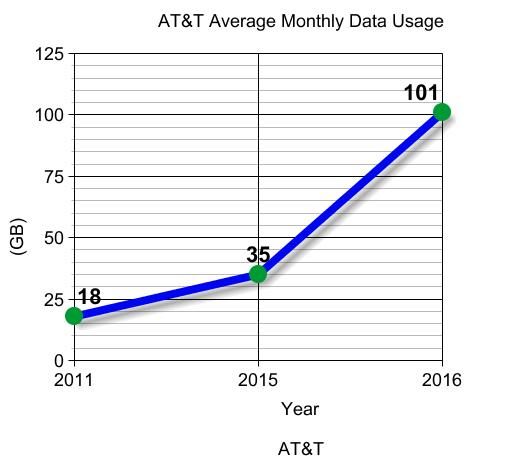
AT&T has indirectly announced it will enforce hard data caps on its U-verse broadband service for the first time, imposing overlimit fees for customers that exceed their allowance unless they agree to pay $30 extra a month for a new unlimited add-on plan.


 Time Warner Cable has a new friend from the “diversity” community.
Time Warner Cable has a new friend from the “diversity” community.