 Susan Crawford’s new book, “Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age,” is on the receiving end of a lot of heat from industry lobbyists and those working for shadowy think tanks and “consumer groups.”
Susan Crawford’s new book, “Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age,” is on the receiving end of a lot of heat from industry lobbyists and those working for shadowy think tanks and “consumer groups.”
Most of the critics have not disclosed their industry connections. Stop the Cap! will.
Crawford’s premise that Americans are suffering the impact of an anti-competitive marketplace for broadband just doesn’t “add up,” according to Zack Christenson and Steve Pociask, both with the American Consumer Institute Center for Citizen Research.
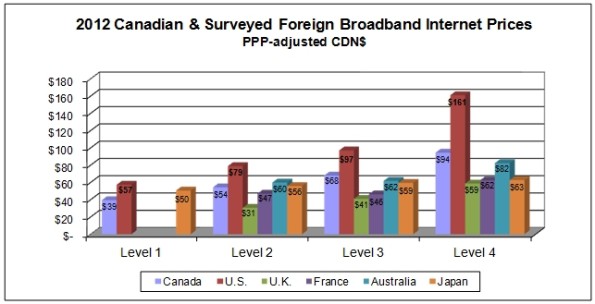
Christenson and Pociask’s rebuttal of Crawford’s conclusions about broadband penetration, price, and its monopoly/duopoly status relies on industry-supplied statistics and outdated government research. For instance, the source material on wireless pricing predates the introduction of bundled “Share Everything” plans from AT&T and Verizon Wireless that raised prices for many customers.
Their proposed solutions for the problems of broadband access, pricing, and competition come straight from AT&T’s lobbying priority checklist:
- Free up more wireless spectrum, which is likely to be acquired by existing providers, not new ones that enter the market to compete;
- Allow AT&T and other phone companies to abandon current copper-based networks, which would also allow them to escape legacy regulations that require them to provide service to consumers in rural areas.
One pertinent detail missing from the piece published in the Daily Caller is the disclosure Pociask is a a telecom consultant and former chief economist for Bell Atlantic (today Verizon). The “American Consumer Institute” itself is suspected of being backed by corporate interests from the telecommunications industry. ACI has closely mirrored the legislative agendas of AT&T and Verizon, opposing Net Neutrality, supporting cable franchise reform that allowed U-verse and FiOS to receive statewide video franchises in several states, and generally opposes government regulation of telecommunications.

Critics for hire.
The so-called consumer group’s website links primarily to corporate-backed astroturf and political interest groups that routinely defend corporate interests at the expense of consumers. Groups like the CATO Institute, the Competitive Enterprise Institute, the Koch Brother-backed Heartland Institute, and the highly free-market, deregulation-oriented James Madison Institute are all offered to readers.
The Wall Street Journal trotted out Nick Schulz to handle its book review. Schulz is a fellow at the American Enterprise Institute, which is funded by corporate contributions to advocate a pro-business agenda.
Schulz attempts to school Crawford on the definition of “monopoly,” eventually suggesting “oligopoly” might be a more precise way to state it.
“Washington’s fights over telecommunications—and just about every other industrial sector—could use a lot less militancy and self-righteousness and a lot more sound economics,” concludes Schulz, while ignoring the fact interpretation of what constitutes “sound economics” is in the eye of the beholder. All too often those making that determination are backed by self-interested corporate entities with a stake in the outcome.
Hance Haney from the Discovery Institute claims Crawford’s conclusions are “misplaced nostalgia for utility regulation.” Haney cites AT&T’s breakup as the spark for competition in the telecommunications sector and proof that monopolies cannot stand when voice, video, and data service from traditional providers can be bypassed. That assumes you can obtain those services without the broadband service sold by the phone or cable company (that also likely owns your wireless service provider and controls access to cable television programming).
Haney also ignores the divorce of Ma Bell has been amicably resolved. AT&T and Verizon have managed to pick up most of their former constituent pieces (the Baby Bells) and today only “compete” with one another in the wireless sector, where each charges identically-high prices for service.

Crawford’s critics often share a connection with the industry she criticizes in her new book.
Haney places the blame for these problems on the government. He argues exclusive cable franchise agreements instigated the lack of cable competition and allowed “hidden cross-subsidies” to flourish, causing the marketplace to stagnate. Haney’s argument ignores history. In the 1970s, before the days of USA, TNT and ESPN, the two largest cable operators TelePrompTer and TCI nearly went bankrupt due to excessive debt leverage. With a very low initial return on investment, exclusive cable franchise agreements were adopted by cities to attract cable providers to wire their communities. Wall Street argues to this day that there is no room for a high level of competition for cable because of infrastructure costs and the unprofitable chase for subscribers that will be asked to cover those expenses. Government was also not responsible for the industry drumbeat for consolidation, not competition, to protect turfs and profits.
The cable industry repeated that argument with cable broadband service, claiming oversight and regulations would stifle innovation and investment. The industry even won the right to exclude competitors from guaranteed access to those networks, claiming it would make broadband less attractive for future investment and expansion.
Haney never discloses the Discovery Institute was founded, in part, to support the elimination of government regulation of telecommunications networks. Broadband Reports also notes the Discovery Institute is subsidized by telecom carriers to make the case for deregulation at all costs.
The Discovery Institute is essentially a PR firm that will present farmed science and manipulated statistics for any donating constituents looking to make a political point.
Broadband for America, perhaps the largest industry-backed astroturf telecom group in the country and itself cited as a source by the American Consumer Institute, seized on the criticism of Crawford’s book for its own attack piece. But every book critic mentioned has a connection to the telecom industry or has ties to groups that receive substantial telecom industry contributions.
NetCompetition chairman Scott Cleland, who accused Crawford of cherry picking information, does not bother to mention NetCompetition is directly funded by the same telecom industry Crawford’s book criticizes. Cleland in fact works to represent the interests of his clients: large phone and cable operators.
Randolph May’s criticism of Crawford’s book is unsurprising when one considers he is president of the Free State Foundation, a special interest group friendly to large telecom companies. FSF also supports the work of the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC), a group with strong ties to AT&T.
Richard Bennett, who once denied to Stop the Cap! he worked for a K Street lobbyist (he does), attacked the book on behalf of his benefactors at the Information Technology and Innovation Foundation, a group Reuters notes receives financial support from telecommunications companies. He also received a $20,000 stipend from Time Warner Cable.
In fact, Broadband for America could not cite a single source criticizing Crawford’s book that does not have ties to the industry Crawford criticizes.


 Subscribe
Subscribe Susan Crawford’s new book, “Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age,” is on the receiving end of a lot of heat from industry lobbyists and those working for shadowy think tanks and “consumer groups.”
Susan Crawford’s new book, “Captive Audience: The Telecom Industry and Monopoly Power in the New Gilded Age,” is on the receiving end of a lot of heat from industry lobbyists and those working for shadowy think tanks and “consumer groups.”

 Russian state-controlled telecom operator Rostelecom has announced it is refocusing most of its capital investment on broadband expansion, after the Russian government called on providers to build out Russia’s broadband infrastructure.
Russian state-controlled telecom operator Rostelecom has announced it is refocusing most of its capital investment on broadband expansion, after the Russian government called on providers to build out Russia’s broadband infrastructure.