Pai
As a result of the multibillion dollar cable merger between Charter Communications, Bright House Networks, and Time Warner Cable, the three companies involved freely admitted: your cable bill was unlikely to decrease, you won’t have any new competitive options, there was no guarantee your service would improve, or that you would get faster broadband service than what Time Warner Cable Maxx was already delivering to about half its customer base.
While shareholders and Wall Street bankers made substantial gains, top Time Warner Cable executives walked away with multimillion dollar golden parachute packages, and Charter took control of what is now the country’s supersized, second most powerful cable operator, regulators also required the dealmakers share at least a tiny portion of the spoils with customers.
Then President Donald Trump’s FCC chairman — Ajit Pai — took leadership of the telecom regulator. Now all bets are off.
Pai is reconsidering the settled deal conditions imposed by the FCC under the last administration, and wants to give Charter Communications a free pass to let them out of their commitment to compete. Last week, Pai circulated a petition among his fellow commissioners to roll back the commitment Charter acknowledged to expand its service area to at least one million new homes that already get broadband service from another cable or telephone company.
Former FCC chairman Thomas Wheeler sought the competition requirement to prove that cable operators can successfully run their businesses in direct competition with each other, potentially inspiring other cable companies to face off with incumbent operators outside of their own territories. A paradigm shift worked for Google, which inspired ISPs to boost speeds in light of its gigabit Google Fiber service, which reset customer expectations.
 The FCC order approving the merger deal was hardly onerous, requiring Charter to compete head-to-head for customers in places the company can choose itself. Lawmakers eliminated exclusive cable franchise agreements years ago, but established major cable operators like Charter have gone out of their way to avoid competing in areas that already receive cable service. While Wheeler may have hoped some of that competition would be directed against fellow cable companies, Charter CEO Thomas Rutledge quickly made clear to investors and the FCC Charter would continue to avoid direct cable competition, instead promising to expand service into non-cable areas that already get DSL service from the phone company or no broadband at all.
The FCC order approving the merger deal was hardly onerous, requiring Charter to compete head-to-head for customers in places the company can choose itself. Lawmakers eliminated exclusive cable franchise agreements years ago, but established major cable operators like Charter have gone out of their way to avoid competing in areas that already receive cable service. While Wheeler may have hoped some of that competition would be directed against fellow cable companies, Charter CEO Thomas Rutledge quickly made clear to investors and the FCC Charter would continue to avoid direct cable competition, instead promising to expand service into non-cable areas that already get DSL service from the phone company or no broadband at all.
“When I talked to the FCC, I said I can’t overbuild another cable company, because then I could never buy it, because you always block those,” Rutledge said. “It’s really about overbuilding telephone companies.”
Charter’s CEO believes most phone companies are not competing on the same level as cable operators and are unwilling to make the necessary investments to upgrade their aging wired infrastructure to offer faster internet speeds. That makes competing with telephone companies like Windstream, Frontier, and Verizon’s DSL-only service areas a much better proposition than trying to compete head-to-head with Comcast, Cox, or Cablevision.
 Rutledge’s clear views about Charter’s expansion plans apparently never made it to the American Cable Association, a cable industry lobbying group that defends the interests of independent and smaller cable operators. Despite Rutledge’s public statements, the ACA and its members are afraid Charter could expand on their turf anyway, potentially forcing small cable operators to compete with the same level of service Charter offers. The horror.
Rutledge’s clear views about Charter’s expansion plans apparently never made it to the American Cable Association, a cable industry lobbying group that defends the interests of independent and smaller cable operators. Despite Rutledge’s public statements, the ACA and its members are afraid Charter could expand on their turf anyway, potentially forcing small cable operators to compete with the same level of service Charter offers. The horror.
The ACA’s arguments found a sympathetic audience in Mr. Pai and now he wants to let Charter off the hook, at the expense of competition and better service for consumers.
Under the proposal circulated by Pai, Charter would still be required to expand its cable broadband service by at least one million new homes, but those homes would no longer have to be in areas outside of Charter’s existing service footprint. In practical terms, this would mean Charter would focus on wiring areas not far from where it provides service today — ‘DSL or nothing’-country. Charter would also be able to fritter away the number of expansions required by counting newly constructed neighborhood developments it would have likely wired anyway, as well as upgrading its remaining shoddy legacy cable systems — some still incapable of offering broadband or phone service.
The ACA’s talking points prefer to emphasize the David vs. Goliath scenario of a big bully of a cable company like Charter being forced to compete (and likely obliterate) existing small cable operators:
“The overbuild condition imposed by the FCC on Charter is stunningly bad and inexplicable government policy,” said ACA president and CEO Matthew Polka, in a statement. “On the one hand, the FCC found that Charter will be too big and therefore it imposed a series of conditions to ensure it does not exercise any additional market power. At the same time, the FCC, out of the blue, is forcing Charter to get even bigger.”
 The real goal here is to minimize direct competition at all costs. The FCC’s deal conditions already included the need for more rural broadband expansion. Wheeler’s second goal was to introduce a new model — cable company competing against cable company — fighting for new customers by offering consumers better service and pricing. The existence of such competition would belie the industry’s claim that cable overbuilds and head-to-head competition is uneconomical. Wildly profitable, perhaps not, but certainly possible. Historically, the traditional way cable operators dealt with the few instances of direct cable competition was to buy them out to put them out of business. Rutledge was certainly thinking along those lines when he complained that the FCC’s order to compete did not include permission to eventually devour its competitor, effectively making competition go away.
The real goal here is to minimize direct competition at all costs. The FCC’s deal conditions already included the need for more rural broadband expansion. Wheeler’s second goal was to introduce a new model — cable company competing against cable company — fighting for new customers by offering consumers better service and pricing. The existence of such competition would belie the industry’s claim that cable overbuilds and head-to-head competition is uneconomical. Wildly profitable, perhaps not, but certainly possible. Historically, the traditional way cable operators dealt with the few instances of direct cable competition was to buy them out to put them out of business. Rutledge was certainly thinking along those lines when he complained that the FCC’s order to compete did not include permission to eventually devour its competitor, effectively making competition go away.
Had Charter chosen to compete with cable companies not afraid to spend money to upgrade service above and beyond the anemic broadband speeds Charter offers, it would likely find few takers for its maximum 300Mbps broadband service that comes with a $200 install fee.
“Why would we go where we could get killed?” Rutledge admitted.
Industry claims that the cable business is already fiercely competitive are also countered by Rutledge’s own statements making clear direct competition with brethren cable companies on the cusp of speed-boosting DOCSIS 3.1 upgrades was bad for business. Instead, he would focus on competing with inferior phone companies, which he characterized as mired in debt, still skeptical about the financial wisdom of fiber optic upgrades, and the only competitor where dismal 3-10Mbps DSL service presented a ripe opportunity to steal customers away.

Clyburn – A likely “no” vote.
Charter’s merger approval and its conditions are a sealed deal that was acceptable to Charter and its shareholders and at least offered small token treats to ordinary consumers. Mr. Pai’s willingness to reopen and undo those commitments is just one reason we’ve referred to his regulatory philosophy as irresponsible, nakedly anti-consumer, and anti-competitive. Mr. Pai’s willingness to embrace things as they are comes at the same time most consumers are paying the highest broadband bills ever while also facing an epidemic of usage caps, usage billing, and increasing service and equipment fees. Mr. Pai’s other actions, including ending an effort to introduce competition into the set-top box market, curtailing customer privacy, ending inquiries on usage caps/zero rating, threatening to eliminate Net Neutrality, and reducing the FCC’s already anemic focus on consumer protection makes it clear Mr. Pai is a company man, on a mission to defend the interests of Big Telecom companies and their lobbyists (that also have a history of hiring friendly regulators for high-paying positions once their government job ends.)
That conclusion seems apt considering what Mr. Pai said about Chairman Wheeler’s vision of improving broadband: “one more step down the path of micromanaging where, when, and how ISPs deploy infrastructure.” Missing from his statement are consumers who have spent the last 20 years watching ISPs govern themselves while waiting… waiting… waiting for broadband service that never comes.
Mr. Pai’s proposal needs just one additional vote to win passage. That extra vote is unlikely until President Trump appoints another Republican commissioner. Pai’s proposal isn’t likely to win support from the sole remaining Democrat commissioner still at the FCC — Mignon Clyburn.


 Subscribe
Subscribe As your AT&T wireless bill soars to new heights, the phone company is spent your money on an exclusive inside-the-beltway private soirée to help win approval of its merger deal with Time Warner, Inc.
As your AT&T wireless bill soars to new heights, the phone company is spent your money on an exclusive inside-the-beltway private soirée to help win approval of its merger deal with Time Warner, Inc.
 Verizon Communications has opened preliminary talks with officials close to Charter Communications about a possible merger of the two companies, concerning regulators worried the massive combined telecommunications company would have a near-monopoly on residential broadband service in New York and western Massachusetts.
Verizon Communications has opened preliminary talks with officials close to Charter Communications about a possible merger of the two companies, concerning regulators worried the massive combined telecommunications company would have a near-monopoly on residential broadband service in New York and western Massachusetts.
 Verizon’s Heavy Dependence on Wireless Was a Mistake
Verizon’s Heavy Dependence on Wireless Was a Mistake Verizon executives have shown little interest in acquiring assets that rely primarily on linear/live television, which is why the company never moved to counter AT&T’s acquisition of DirecTV with an offer for its satellite competitor Dish Networks.
Verizon executives have shown little interest in acquiring assets that rely primarily on linear/live television, which is why the company never moved to counter AT&T’s acquisition of DirecTV with an offer for its satellite competitor Dish Networks. Higher bills, confusing and conflicting services and pricing, and badly trained customer service representatives are just a few of the problems afflicting customers transitioning from Bright House Networks and Time Warner Cable to service plans being gradually introduced around the country by Charter Communications/Spectrum. Stop the Cap! has collected more than 50 reports from customers experiencing problems, bill shock, lost access to Wi-Fi hotspots, and
Higher bills, confusing and conflicting services and pricing, and badly trained customer service representatives are just a few of the problems afflicting customers transitioning from Bright House Networks and Time Warner Cable to service plans being gradually introduced around the country by Charter Communications/Spectrum. Stop the Cap! has collected more than 50 reports from customers experiencing problems, bill shock, lost access to Wi-Fi hotspots, and 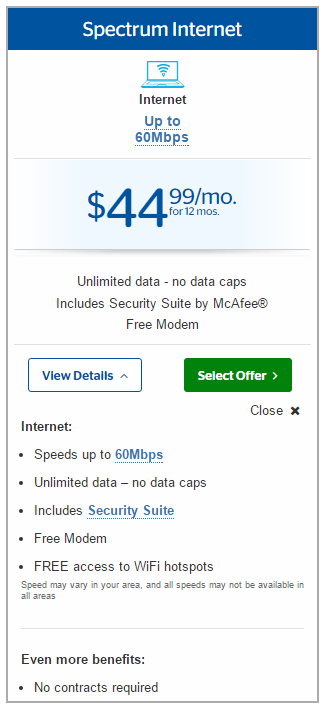
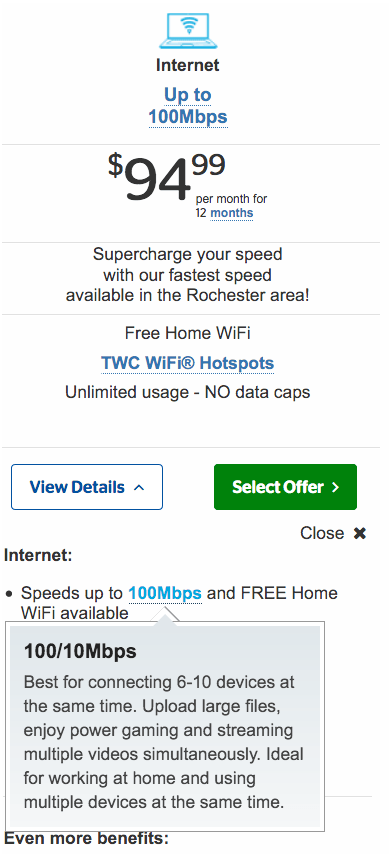
 Bright House Networks customers are also experiencing transition troubles. Residential customers reportedly lost any static IP addresses they signed up for when they converted to a Charter Spectrum residential plan. Static IP addresses are still available for Spectrum commercial plans. More troubling for many is the loss of access to Bright House Network’s secure Wi-Fi network.
Bright House Networks customers are also experiencing transition troubles. Residential customers reportedly lost any static IP addresses they signed up for when they converted to a Charter Spectrum residential plan. Static IP addresses are still available for Spectrum commercial plans. More troubling for many is the loss of access to Bright House Network’s secure Wi-Fi network. In Indianapolis, former Bright House Networks customers
In Indianapolis, former Bright House Networks customers 

