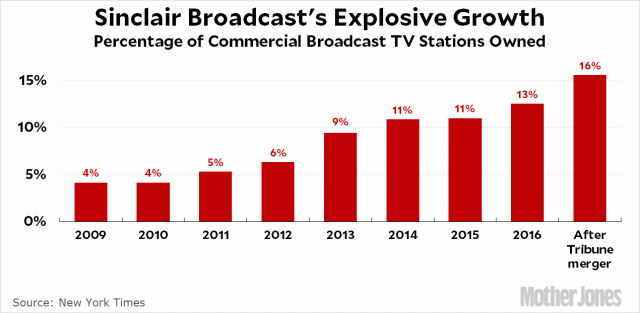
Sinclair’s deal with Tribune will make them by far the largest TV station ownership group in the country, owning 16% of the TV stations in the U.S. (Image: Mother Jones)
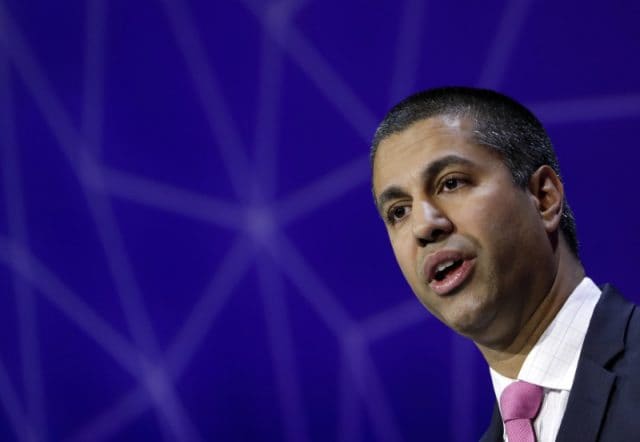
After a hard-hitting piece analyzing the close ties between President Donald J. Trump, FCC Chairman Ajit Pai, and Sinclair Broadcasting appeared in this morning’s New York Times, a group of leading House Democrats serving on the House Energy & Commerce Committee have written Mr. Pai asking for answers about his possible “favorable treatment” of Sinclair Broadcasting since becoming Chairman of the FCC.
These reports, according to the letter, raise two overarching questions:
- Whether actions taken by the FCC under your leadership show a pattern of preferential treatment for Sinclair, and
- Whether a series of interactions between your office, the Trump Campaign and Trump Administration, and Sinclair demonstrate inappropriate coordination.
The letter’s signers — all Democrats — are Rep. Frank Pallone, Jr. (ranking member of the full committee), Rep. Mike Doyle (ranking member of the Communications and Technology Subcommittee), and Rep. Diana DeGette (ranking member, Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations).
The 12-page letter presents Pai with multiple examples of potential collusion and favorable treatment of a television station group that airs mandatory pro-Trump Administration commentaries on all of its local newscasts, employs a former Trump campaign aide, has sought private meetings with administration officials , and has made substantial campaign contributions.
The Times article appears to be the source for most of the concern expressed in the letter, which lays out multiple issues and seeks Mr. Pai’s comments and explanations.
At the beginning of the Trump Administration, the Democrats claim, Mr. Pai has undertaken a number of actions in his role as Chairman of the FCC that fall squarely in line with the corporate expansion agenda at Sinclair Broadcast Group. Among the most important was Mr. Pai’s sudden decision to bring a party-line vote to reinstate an archaic UHF Discount rule, which allows a company to downgrade the reach of its UHF stations for the purposes of determining if it is within the FCC’s limit of one station owner reaching no more than 39% of the country. This “discount” was established at a time when analog television signals on the UHF band (Channels 14+) were at a distinct coverage disadvantage over stations occupying the VHF (Channels 2-13) band. The discount was retired after the U.S. switched to digital television broadcasting, which largely eliminated this coverage disparity.
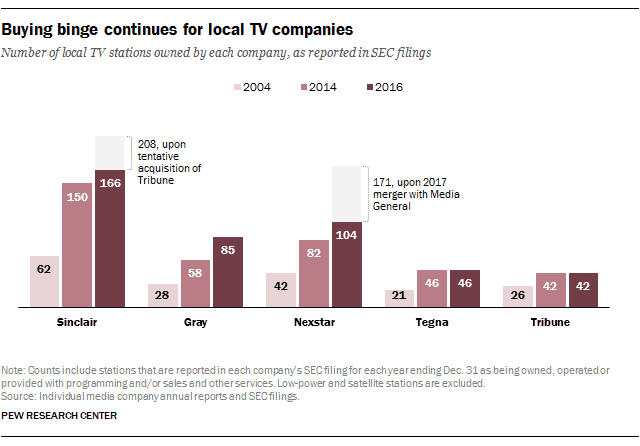
TV station owners saw a revival of the UHF Discount not as a way to deal with reception differences, but rather as a loophole to launch new acquisitions by discounting the coverage of their current stations. Only one company – Sinclair Broadcasting – stood to gain the most from the reinstatement of the UHF Discount. Almost on cue, two weeks after Pai brought this obscure rule up and reinstated it on a 2-1 vote, Sinclair announced a blockbuster merger with Tribune to acquire stations that will allow Sinclair to cover 70% of the United States, a number impossible to achieve without Pai’s support for the UHF Discount.
Democrats argue this was not what Congress intended, and it allows one station owner to own and control approximately double the number of stations the ownership cap would normally prohibit. They argue such a deal will reduce the diversity of media voices in communities across the country, especially in markets where Sinclair will own and operate more than one television station.
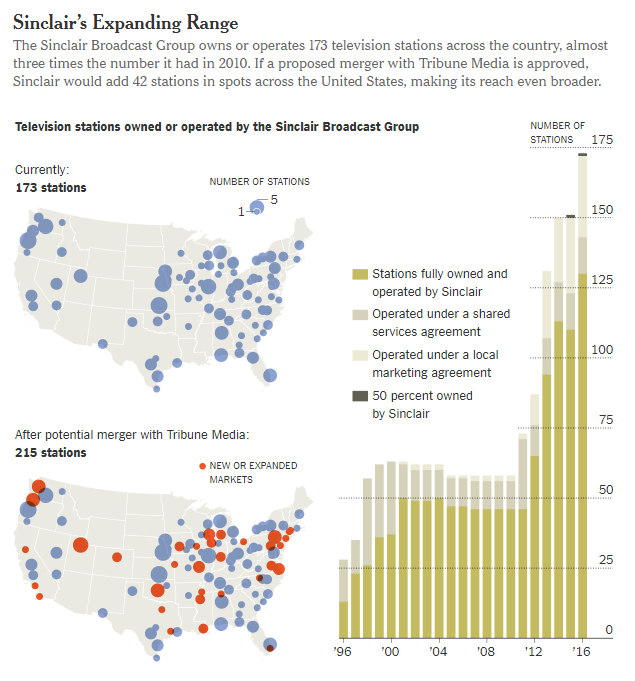
The New York Times provides this chart illustrating the vast expansion of stations if it wins control of Tribune Media.
The Democrats are also upset the FCC, under Pai’s leadership, appears to be in a hurry to get this deal reviewed and likely approved. It set a review window of just 30 days for public comment, considerably shorter than earlier, less controversial acquisition deals. Critics of the deal contend that the FCC is giving inadequate consideration of the deal’s lack of public interest benefits, and Sinclair’s application is vague and its claims are difficult to validate. Pai seems unconcerned, leading some to believe he intends to rubber stamp his approval with minimal conditions.
Under Pai’s watch, the Democrats charge, Sinclair has already benefited from a ‘rush to approval’ mentality at the FCC. Sinclair’s earlier deal to acquire stations owned by the Bonten Media Group was also convenient, coming shortly after the FCC under Mr. Pai revoked guidance that would have required the FCC to closely scrutinize the transaction. The FCC granted the deal, despite the fact several of Bonten’s stations are in areas where Sinclair now holds operating agreements to manage other local stations. Large station groups have used these agreements as loopholes to effectively gain day-to-day control of stations without actually transferring their ownership.
The Democrats also argue that Sinclair is well positioned to be in the lead of Next Gen TV, ATSC 3.0 technology that will replace the current digital TV standard in the United States in the next few years. Sinclair is the biggest cheerleader of the new technology, and Mr. Pai coincidentally has put a rush on getting ATSC 3.0 approved and into the marketplace. ONE Media 3.0, a wholly owned subsidiary of Sinclair, just happens to own six critical patents essential for using the Next Gen TV standard. That means every station in the country moving to the next broadcast platform will have to pay royalties to Sinclair estimated in the billions.
As the Times reports, whenever Sinclair sought something from Washington as part of its corporate agenda, the FCC’s Mr. Pai quickly aligned himself and the FCC’s Republican majority to fulfill Sinclair’s wishes.
The Democrats also question whether there is direct coordination between the Administration, Sinclair, and the FCC:
-
After the election, President Trump reportedly met with the Executive Chairman and former CEO of Sinclair and discussed changing FCC rules to help Sinclair. A news account stated that after the election, President Trump met with David Smith, Sinclair’s Executive Chairman and former CEO. According to this report, “potential FCC rule changes were discussed” after President Trump asked Mr. Smith, “What do you need to happen in your business?”
-
Before you became Chairman of the FCC, you reportedly met with then President-elect Trump in New York. Reports indicate that on January 16 of this year, you met with then-President-elect Trump in New York in a meeting that did not appear on your official calendar.
-
In March, shortly after you became Chairman of the FCC, you met with President Trump in the Oval Office. An FCC spokesperson confirmed that the meeting occurred, but did not indicate what was discussed during the meeting. When asked directly about your meetings with President Trump, you declined to disclose what you discussed, saying “I am not at liberty to say.”
-
The week after the election, you reportedly attended a company conference for Sinclair’s general managers, during which you met with Sinclair’s CEO. According to a Politico report, in January of this year, you met with Sinclair’s former CEO, David Smith, as well as the newly named Sinclair CEO, Chris Ripley.
-
The President’s campaign reportedly “struck a deal” with Sinclair to “secure better media coverage.” This arrangement came to light after the election, when Jared Kushner reportedly revealed that in exchange for access to then-candidate Trump and his campaign, “Sinclair would broadcast Trump interviews across the country without commentary.” Sinclair representatives have defended this arrangement by claiming that the Clinton campaign was offered the option for extended interviews with local anchors as well, but did not accept.
-
In April, Boris Epshteyn, who was “most recently Special Assistant to The President and Assistant Communications Director for Surrogate Operations for the Executive Office of President Trump,” and formerly a “senior advisor to the Trump campaign,” joined Sinclair to provide on-air political commentary. Epshteyn’s segments are “must-run” programming for Sinclair stations, with nine segments airing per week. One report has criticized the segments as “propaganda” and reporting on Sinclair’s selection of “must-run” programming has raised “suggestions that Sinclair pushed right-leaning views.”
The Democrats are requesting Mr. Pai answer their letter and provide additional information no later than Aug. 28.


 Subscribe
Subscribe