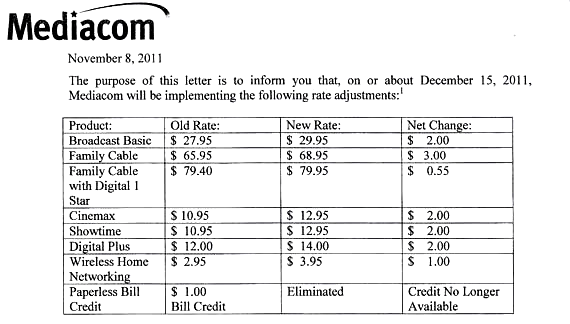
Mediacom is announcing broad price increases for many of its customers scheduled to take effect on Dec. 15. Most cable-TV subscribers will pay $2-3 more a month for basic cable, an additional $2 a month for Cinemax and Showtime, and $2 extra a month for “Digital Plus” cable service. To add insult, the paperless bill credit that used to knock $1 off your bill if you chose not to receive a mailed billing statement is also being eliminated.
 Lee Grassley, Mediacom’s chief lobbyist, delivered the company line about the rate increase in letters mailed to subscribers. In essence, he blamed everyone but Mediacom for the rate hikes, and in poetic language one normally doesn’t get from a cable company rate increase notification:
Lee Grassley, Mediacom’s chief lobbyist, delivered the company line about the rate increase in letters mailed to subscribers. In essence, he blamed everyone but Mediacom for the rate hikes, and in poetic language one normally doesn’t get from a cable company rate increase notification:
As our nation struggles to pull itself out of what has been called the Great Recession, we recognize that these are challenging times for the hardworking men and women living in the communities that we serve.
[…] Over the past few years, many broadcasters have used their monopoly powers to demand 100%, 200% and even 300% rate increases during contract negotiations. This has driven up cable and satellite rates and forced American consumers to pay billions of dollars for “free” over-the-air television.
The problems with sports programming are equally alarming. One look at the skyrocketing rights fees announced with recent deals and it is easy to see that the marketplace for live televised sports is out of control.
[…] Contrary to public perception, cable companies are reluctant to raise video prices because when we do, we lose subscribers. Mediacom does not make money when we raise video rates, since we remit virtually every penny of the increase on to programmers. In fact, over the last three years, our programming cost increases were more than double our video revenue increases.
Since the programming community has been unwilling to exercise even the slightest measure of self-restraint when it comes to reigning in their spending or increasing their price demands, Mediacom has taken the fight to Washington.
 Mediacom as new-found-friend fighting for lower cable rates comes across as ironic, at best, to Stop the Cap! reader Noel, who lives in Mediacom’s Iowa footprint.
Mediacom as new-found-friend fighting for lower cable rates comes across as ironic, at best, to Stop the Cap! reader Noel, who lives in Mediacom’s Iowa footprint.
“This is the same cable company who pocketed rate increases annually for as long as I’ve been a subscriber, and if they can’t raise the price of the television service, they’ll just make it up on the broadband side,” Noel writes. “They have their nerve complaining about monopolies.”
Noel points out the local station retransmission consent fees are a more recent phenomenon, and Mediacom rate increases in prior years were the same or higher.
“I think they are realizing there is an absolute maximum people in Iowa can afford for cable, and years of rate increases have allowed all of the players to assume they can slice a bigger piece from that pie for themselves, and we’re tapped out,” Noel adds.
Noel called Mediacom and threatened to cancel service and received a nice consolation price: customer retention pricing normally reserved for new customers.
“I have a year reprieve, but rest assured I will start dropping things after the deal expires at these prices.”
[flv width=”480″ height=”290″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/KCCI Des Moines Mediacom Rate Increases 11-28-11.flv[/flv]
KCCI in Des Moines covers Mediacom’s rate increases and the reaction from local residents who will have to pay more for cable service. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe