Imagine if your electric utility billed you for service based on a meter that was developed by the company, had no third party verification, no oversight by a Bureau of Weights and Measures, and wrote provisions into the company’s terms and conditions that allowed the company to terminate your service if you complained too much about the resulting bills.
Imagine if your electric utility billed you for service based on a meter that was developed by the company, had no third party verification, no oversight by a Bureau of Weights and Measures, and wrote provisions into the company’s terms and conditions that allowed the company to terminate your service if you complained too much about the resulting bills.
Rethink possible. AT&T.
When America’s largest phone company implements its arbitrary and unjustified Internet Overcharging scheme this May, it will bring its controversial usage meter to bear on every one of its broadband customers — a meter implicated in wild over-measurements of customers’ broadband usage — usage that will put customers perilously close to, or over the limits AT&T wants to establish. The result? Fat additional profits in the form of $10 overlimit penalties for every 50GB AT&T says you consumed for broadband traffic that costs them pennies to deliver.
The broadband usage meter is no stranger to controversy and lawsuits over accuracy issues. Despite reflexive denials that a particular provider’s usage meter couldn’t be wrong, far too many have had to backpeddle and confess that the meter that should have measured $40 in usage and resulted in $4,000 bills instead “was in error.”
Whether providers are developing meters that are just flat inaccurate or are quietly putting a virtual finger on the scale to increase the opportunity of overlimit profits is unknown, but past history shows the meters typically overmeasure usage, not undercount it.
Without independent verification and ongoing oversight, some customers wonder if AT&T is sticking a virtual finger on AT&T's usage scale.
Some recent past history:
- Telstra is Australia was implicated in December for a wireless usage meter that occasionally reported more than three times the usage measured by wireless phone owners’ built-in usage measurement tools. Company representatives ended up crediting some customers as much as $3500AUD in inappropriate overlimit fees that should never have been charged. Complaints continue to arrive as late as February about overbilling;
- Telecom New Zealand’s usage meter overmeasured usage this month resulting in overcharges and throttled speeds under the ISP’s “fair use policy.” One customer was billed for 27GB of usage during one overnight period, despite the fact the computer was switched off;
- BT in the United Kingdom confirmed it overbilled some of their broadband customers in February when their usage meter measured usage for customers who had switched their computers off or took them away on holiday. As far as BT was concerned, those computers were still at home and still racking up web usage. Only last week, the company finally confessed their meter was inaccurate — overmeasuring usage that never happened;
- AT&T’s counterpart in Canada — Bell, cannot manage to measure customer usage correctly either, so it suspended its usage tracker tool temporarily. In February, one customer tired of overbilling proved a point when he took his computer to the United States just to guarantee it could not go near Bell’s network. The result? Bell said he used 500MB anyway;
- In February, a class action lawsuit was filed against AT&T for “overmeasuring” wireless usage in some instances by up to 300 percent;
- Last fall, Verizon was forced to refund $25 million dollars for phantom data usage charges for service many customers claimed they never used.
 In virtually all of the prior incidents, a common pattern emerges, usually ending when providers fall on their swords, admit error and issue refunds:
In virtually all of the prior incidents, a common pattern emerges, usually ending when providers fall on their swords, admit error and issue refunds:
- Phase 1: Initial denials from providers there is a problem with the meter, usually blaming the customer, the customer’s measurement tool, or the process used instead;
- Phase 2: Once proven to be an issue, an effort to downplay its significance and impact with claims that only a “tiny” percentage of customers were affected;
- Phase 3: Refusal to submit usage meters, wholesale costs, and other components of Internet Overcharging to third-party verification;
- Phase 4: Refusal to allow an independent audit of customer accounts to verify overbilled customers were properly refunded every penny of excess charges;
- Phase 5: Class action lawsuit or government investigation commences;
- Phase 6: Settlement reached with refunds or low value coupons to customers who take the time to request one;
- Phase 7: Report excess profits from unclaimed refunds on balance sheet.
In too many cases, multi-billion dollar telecom companies that rely on those meters to measure and bill customers for their usage were implicated not for undermeasuring usage, but overmeasuring it — often substantially.
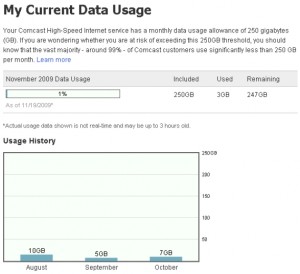
Some AT&T customers are already disturbed with what could be history repeating itself. A reader of Broadband Reports in Skokie, Ill., compiled his own detailed analysis and found AT&T’s measurement tool grossly overmeasured his usage, and even worse, couldn’t do simple math and overmeasured him again when adding up his daily usage totals:
AT&T said that I had used 361GB in a single month! Surely this couldn’t be right. I’m a heavy user, but every time I even so much as glanced at my usage stats they’ve always been in the 200GB range. Surely something was amiss, so I decided to dig deeper.
It’s an old habit, but the first thing I do when I suspect something is wrong with any bill is enter all the line items into a spreadsheet and add them up myself. It sounds like busywork, but sometimes you’ll catch unlisted charges that have been phantomly added to your bill, or occasionally an outright math error. I couldn’t believe what I found. AT&T’s usage meter results insist I had used 341.39GB down, and 20.18GB up. But when I added all the daily detail entries (the DSL equivalent of a call log), only 332.8GB down and 0.72GB up are accounted for.
AT&T is claiming that I used 361.57GB of data, but according to their own daily data I only used 333.52GB, an 8.5% overcharge.
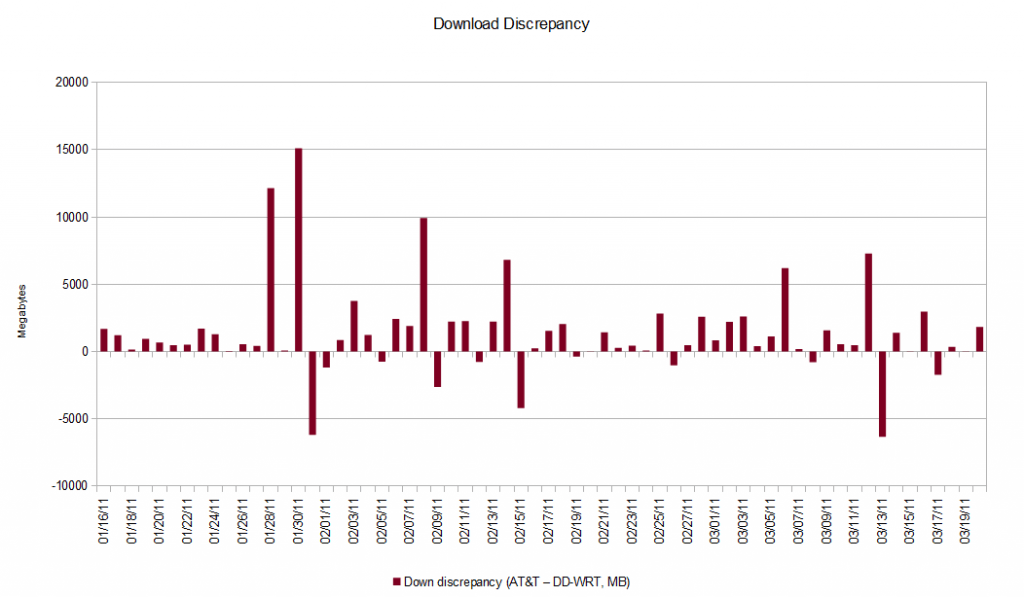
This AT&T customer discovered AT&T overmeasured his usage far more than it undercounted it. (Lines above the baseline show downstream traffic AT&T overmeasurement; lines below show undercounted usage. Click to enlarge.)
In total, this particular customer reports his usage was overmeasured by a whopping 33 percent. He is not alone. A robust thread of similar results is active on Broadband Reports.
AT&T’s response to the early criticism follows the same path taken by other providers, starting with denials.
“We’re addressing ways we can make the labels and information on the online metering tool more clear for customers between now and May (when the new policy goes into effect),” said AT&T spokesperson Seth Bloom. “I can also assure you our team is performing checks everyday to ensure accuracy. That said, we believe we have an accurate tool.”
“Other tools may measure at different 24-hour periods than we do, and most likely do not take into account the standard network protocols (e.g. Ethernet, IP) that are used to provide applications and content to our customers via the Internet. As you know, this is fairly standard to incorporate when measuring broadband traffic and is applied by other ISPs who measure usage.”

Customers and columnists alike are worried about AT&T's new data limits. This Milwaukee Journal-Sentinel columnist is not thrilled, and neither are customers who overwhelmingly want unlimited broadband access.
“In the end, AT&T expects the caps to impact only the aforementioned 2% [that comprise its heaviest users].”
With the right level of over-measurement, virtually anyone can be a member of the “2% Club.” One customer told Connected Planet AT&T was already overmeasuring her DSL account by as much as 4,700%.
How can you measure your usage to compare against AT&T?
“It’s not hard to maintain independent usage statistics to double-check AT&T’s numbers,” says the Broadband Reports reader in Skokie. “If you have a DD-WRT compatible router, it will keep your upload and download history automatically. If you don’t have a compatible router, you can still run WallWatcher or MRTG to get the total bandwidth used by your router. Finally, if your computer is connected directly to your DSL modem without a router, you can run software like Net Meter to track your internet usage.”
Customers inconvenienced by unnecessary usage meters which threaten to expose them to unjustified overlimit fees is just one more reason why we call out these Internet Overcharging schemes. Call AT&T and let customer service know you intend to switch providers if AT&T implements their usage cap scheme in early May. Tell them regardless of what kind of usage you incur each month, you cannot afford the chance AT&T’s apparently inaccurate usage meter could expose you to a higher bill. Tell them you don’t want the hassle, and the only way you will remain as a customer is if they do away with the entire scheme.


 Subscribe
Subscribe