Phillip “Follow the Money” Dampier
“In the 1990s, U.S. policymakers faced critical choices about who should build the Internet, how it should be governed, and to what extent it should be regulated and taxed. For the most part, they chose wisely to open a regulated telecommunications market to competition, stimulate private investment in broadband and digital technologies, and democratize access.” — Will Marshall, guest columnist
Is competition in Internet access robust enough for you? Has your provider been sufficiently stimulated to invest in the latest broadband technologies to keep America at the top of broadband speed and availability rankings? Is Net Neutrality the law of the land or the latest victim of a Verizon lawsuit to overturn the concept of democratizing access to online content?
I’m not certain what country Will Marshall lives in, but for most Americans, Internet access is provided by a duopoly of providers that must be dragged kicking and screaming to upgrade their networks without jacking up prices and limiting usage.
Marshall is president and founder of the Progressive Policy Institute, a so-called “third way” group inspired by centrist Democrats led by President Bill Clinton in the 1990s. Unlike traditional liberals suspicious of corporate agendas, these Democrats were friendly to big business and welcomed the largess of corporate cash to keep them competitive in election races. It was under this atmosphere that Clinton signed the bought-and-paid-for 1996 Telecom Act, ghostwritten by lobbyists for big broadcasters, phone and cable companies, and other big media interests. Long on rhetoric about self-governing, free market competition but short on specifics, the ’96 law transformed the media landscape in ways that still impact us today.
 Media ownership laws were relaxed, allowing massive buyouts of radio stations under a handful of giant corporations like Clear Channel, which promptly dispensed with large numbers of employees that provided locally produced programming. In their place, we now get cookie-cutter radio that sounds the same from Maine to Oregon. Television stations eagerly began lobbying for a similar framework for relaxing ownership limits in their business. Phone companies won their own freedoms from regulation, including largely toothless broadband regulations that allowed Internet providers to declare victory regardless of how good or bad broadband has gotten in the United States.
Media ownership laws were relaxed, allowing massive buyouts of radio stations under a handful of giant corporations like Clear Channel, which promptly dispensed with large numbers of employees that provided locally produced programming. In their place, we now get cookie-cutter radio that sounds the same from Maine to Oregon. Television stations eagerly began lobbying for a similar framework for relaxing ownership limits in their business. Phone companies won their own freedoms from regulation, including largely toothless broadband regulations that allowed Internet providers to declare victory regardless of how good or bad broadband has gotten in the United States.
Marshall’s views appeared in a guest column this week in The Orlando Sentinel, which is open to publishing opinion pieces from writers hailing from Washington, D.C., without bothering to offer readers with some full disclosure.

Marshall
While Marshall’s opinions may be his own, readers should be aware that PPI would likely not exist without its corporate sponsors — among them AT&T, hardly a disinterested player in the telecommunications policy debate.
Marshall’s column suggests competition is doing a great job at keeping prices low and allows you – the consumer – to decide which technologies and services thrive. There must be another reason my Time Warner Cable bill keeps increasing and my choice for broadband technology — fiber optics — is nowhere in sight. I don’t have a choice of Verizon FiOS, in part because phone and cable companies maintain fiefdoms where other phone and cable companies don’t dare to tread. That leaves me with one other option: Frontier Communications, which is still encouraging me to sign up for their 3.1Mbps DSL.
“The broadband Internet also is a powerful magnet for private investment,” Marshall writes. “In 2013, telecom and tech companies topped PPI’s ranking of the companies investing the most in the U.S. economy. And America is moving at warp speed toward the ‘Internet of Everything,’ which promises to spread the productivity-raising potential of digital technology across the entire economy.”
Nothing about AT&T or the cable companies is about “warp speed.” In reality, AT&T and Verizon plan to pour their enormous profits into corporate set-asides to repurchase their own stock, pay dividends to shareholders, and continue to richly compensate their executives. It’s good to know that PPI offers rankings that place telecom companies on top. Unfortunately, those without a financial connection to AT&T are less optimistic. The U.S. continues its long slide away from broadband leadership as even developing countries in the former Eastern Bloc race ahead of us. Verizon’s biggest single investment of 2013 wasn’t in the U.S. economy — it was to spend $130 billion to buyout U.K.-based Vodafone’s 45% ownership interest in Verizon Wireless. Verizon’s customers get stalled FiOS expansion, Cadillac-priced wireless service, and a plan to ditch rural landlines and push those customers to cell service instead.

AT&T financially supports the Progressive Policy Institute
“A recent federal court decision regarding the FCC’s Open Internet Order has prompted pro-regulatory advocates from the ’90s to demand a rewrite of the legal framework that allowed today’s Internet to flourish,” Marshall writes in a section that also includes insidious NSA wiretapping and Internet censorship in Russia and China.
Marshall’s AT&T public policy agenda is showing.
Net Neutrality proponents don’t advocate an open Internet for no reason. It was AT&T’s former CEO Ed Whitacre that threw down the gauntlet declaring Google and other content providers would not be allowed to use AT&T’s pipes for free. AT&T has since patented technology that will allow it to discriminate in favor of preferred web traffic while artificially slowing down content it doesn’t like on its network.
“Pro-regulatory advocates” are not the ones advocating change — it is AT&T, Verizon, and Comcast, among others, that want to monetize Internet usage and web traffic for even higher profits. Net Neutrality as law protects the Internet experience Marshall celebrates. He just can’t see past AT&T’s money to realize that.


 Subscribe
Subscribe

 Where there is no disruptive new player in town to shake things up, there is little incentive to speed broadband service up. But there is plenty of room to keep increasing prices for a service that is becoming as important as a working telephone. Companies are using broadband profits to cover increasing losses from pay television service, investing in stock buybacks, paying dividends to shareholders, or just putting the money in a bank, often offshore.
Where there is no disruptive new player in town to shake things up, there is little incentive to speed broadband service up. But there is plenty of room to keep increasing prices for a service that is becoming as important as a working telephone. Companies are using broadband profits to cover increasing losses from pay television service, investing in stock buybacks, paying dividends to shareholders, or just putting the money in a bank, often offshore.
 That is why we still celebrate and honor Svetlana Radkevich from Belarus who competed in the speed skating competition at the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics. She made it to the finish line and ranked 33rd. Ironically, South Korea ranked fastest overall that year, taking home three gold and two silver medals. In Powell’s world, that’s a distinction without much difference. You don’t need South Korean speed and gold medals when Belarus is enough. That argument always plays well in the United States, where Americans can choose between Amtrak or an airline for a long distance trip. Who needs a non-stop flight when a leisurely train ride will get you there… eventually.
That is why we still celebrate and honor Svetlana Radkevich from Belarus who competed in the speed skating competition at the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics. She made it to the finish line and ranked 33rd. Ironically, South Korea ranked fastest overall that year, taking home three gold and two silver medals. In Powell’s world, that’s a distinction without much difference. You don’t need South Korean speed and gold medals when Belarus is enough. That argument always plays well in the United States, where Americans can choose between Amtrak or an airline for a long distance trip. Who needs a non-stop flight when a leisurely train ride will get you there… eventually.
 Deanna Cook of Rylie, Tex is just one victim who might still be alive today if 9-1-1 operators could have tracked her precise location. Last August, Cook called 9-1-1 from her home but was too badly injured in a domestic violence incident to provide her address. Operators relied on the current system to access her location. It took just a few seconds to find the cell tower Cook was accessing to place the call. Shortly after that, Cook’s street and general location became available in about a block-wide circumference, part of what the industry calls “Phase One” data. But the operator had to wait nine minutes for Cook’s wireless provider to finally pinpoint what they believed to be her exact address, the critical “Phase Two” data that can bring help to the right door.
Deanna Cook of Rylie, Tex is just one victim who might still be alive today if 9-1-1 operators could have tracked her precise location. Last August, Cook called 9-1-1 from her home but was too badly injured in a domestic violence incident to provide her address. Operators relied on the current system to access her location. It took just a few seconds to find the cell tower Cook was accessing to place the call. Shortly after that, Cook’s street and general location became available in about a block-wide circumference, part of what the industry calls “Phase One” data. But the operator had to wait nine minutes for Cook’s wireless provider to finally pinpoint what they believed to be her exact address, the critical “Phase Two” data that can bring help to the right door.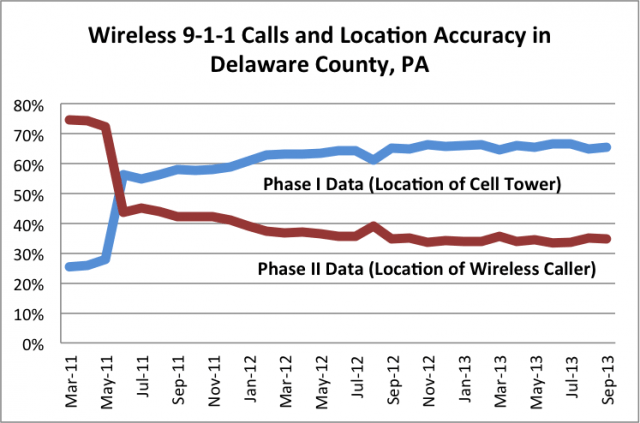
 The Coalition notes the FCC’s data shows an alarming drop in more accurate “Phase Two” data from 75 percent of all wireless calls placed during March 2011 to just 35% in September of this year.
The Coalition notes the FCC’s data shows an alarming drop in more accurate “Phase Two” data from 75 percent of all wireless calls placed during March 2011 to just 35% in September of this year. A portion of your cable bill pays for much more than programming, with millions diverted to Koch Brothers-backed astroturf groups, tea party candidates, fat paychecks for former public officials taking a trip through D.C.’s revolving door, and generous allowances for travel expenses racked up by high-flying industry lobbyists.
A portion of your cable bill pays for much more than programming, with millions diverted to Koch Brothers-backed astroturf groups, tea party candidates, fat paychecks for former public officials taking a trip through D.C.’s revolving door, and generous allowances for travel expenses racked up by high-flying industry lobbyists.