 The National Cable & Telecommunications Association (NCTA), the nation’s largest cable lobbying group, has outdone itself with a brand new fact-challenged video truth-seekers will quickly discover is little more than industry propaganda.
The National Cable & Telecommunications Association (NCTA), the nation’s largest cable lobbying group, has outdone itself with a brand new fact-challenged video truth-seekers will quickly discover is little more than industry propaganda.
“For nearly 20 years, cable has been building Internet networks that are empowering everyone from innovators and entrepreneurs to kids in the garage,” says the NCTA in its introduction of its new video “The Infinite Internet.” “The Internet propels business, education, entertainment – whatever we want. It’s a platform of possibilities and the fast growing technology in history. Cable is proud of the part we’ve played in advancing America’s future and we’ll continue to make it faster and more accessible.”
Except many NCTA member companies want to introduce usage caps and consumption billing that limit those possibilities on an already absurdly profitable service. The same broadband duopoly of cable and phone companies also holds America’s broadband rankings back, and has demonstrated its real priority is to charge more money for less service.
We’ve reviewed the video and found credibility problems with almost every claim:
Claim: “America’s ISPs have invested trillions of dollars and laid 400,000 miles of fiber optics.”
Our finding: FIB Even industry mouthpieces like the Progressive Policy Institute and NCTA members themselves have a problem with “trillions.” The chief executives of AT&T, Bright House Networks, Cablevision, CenturyLink, Charter, Comcast, Cox, Frontier, Suddenlink, Time Warner Cable, 15 other companies, and industry groups such as the National Cable & Telecommunications Association itself, the Telecommunications Industry Association, and the CTIA Wireless Association claimed in the spring of 2014 that the entire telecommunications industry (not cable alone) spent a combined $1.2 trillion on communications infrastructure. A considerable percentage of that investment was to build out cellular networks, first for mobile phone calls and only later for wireless data. The cable industry spent far less than $1 trillion on its own infrastructure and at the time of its most rapid growth, it was intended primarily to deliver cable television, not broadband.
Stop the Cap! also found the NCTA cheating in its claims of increasing investment in broadband. The trade group was citing cumulative spending, not actual year-to-year spending. A careful review shows broadband investments are generally flat or in decline and are nowhere near comparable to the investments the industry made in the late 1990s.
Although it may be true the cable industry has deployed 400,000 miles of fiber optics, the overwhelming majority of cable customers cannot directly access any of it. Virtually all the cable industry’s fiber is deployed between the company’s headquarters and individual communities where it is connected to the same coaxial cable platform that has been around since the 1960s. Most of the rest is laid for commercial purposes, notably providing backhaul connectivity for cell towers. Time Warner Cable alone deployed fiber to its 10,000th cell tower back in 2013. It’s a lucrative business, earning that cable company more than $61 million a quarter.
BroadbandNow found no cable company appearing on the list of top fiber broadband providers. In fact, as of 2012 only 23% of Americans have access to fiber broadband ranking the United States 14th among western countries in fiber optic penetration according to the OECD.
Claim: “High speed connections reach nearly every home with blazing fast speeds that power our lives.”
Our finding: HIGHLY MISLEADING The NCTA fails to define its terms here. What exactly constitutes a “high-speed connection.” The FCC currently defines broadband as providing speeds of 4Mbps or better. Is that “blazing fast?” The FCC is currently considering redefining broadband to mean speeds of at least 25Mbps, well below many cable company entry-level broadband tiers. The NCTA also likes to claim that 99% of households have access to high-speed Internet, but they include wireless technology at any speed in those figures. If you can get one bar from AT&T’s 3G wireless Internet network, you’ve got high-speed broadband in their eyes.
In fact, when it comes to stingy coverage areas, cable is notoriously not available outside of the biggest cities and suburbs, as the government’s own National Broadband Map depicts:
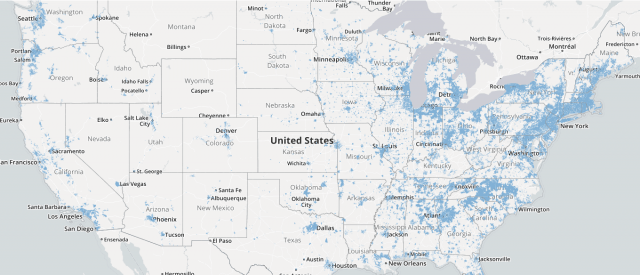
Map showing cable companies offering at least DOCSIS 3.0 cable broadband service.
Claim: “ISP’s want access for everyone.”
Our finding: TRUE, WITH MISSING FINE PRINT What company would not want to offer its products and services to everyone. The real question is whether they plan on doing that or simply wishing they had. The cable industry has no intention of implementing sweeping changes to the Return On Investment (ROI) formula that determines whether your home gets access to cable or not. Some companies like Time Warner Cable and Frontier Communications are expanding their cable and DSL networks, but only when the government steps in with broadband deployment grant funding.
Assuming service is available, the next hurdle is cost. BBC News reported in 2013 home broadband in the U.S. costs far more than elsewhere. At high speeds, it costs nearly three times as much as in the UK and France, and more than five times as much as in South Korea. Today it costs even more when you count the growing number of providers charging modem rental fees as high as $10 a month and often cap usage or force customers into usage-based billing schemes.
Claim: “With over 300,000 public Wi-Fi hotspots, the Internet of Things is emerging.”

Cox Cable sells their customers on accessing over 300,000 Wi-Fi hotspots, with a prominent asterisk. Access is only available for free if you are a current cable broadband customer.
Our finding: MISLEADING The NCTA is referring to collaboration between Bright House Networks, Cox Communications, Optimum, Time Warner Cable and XFINITY that allow each other’s high-speed Internet customers to use to each company’s Wi-Fi hotspots. They key word is “customers.” The hotspots may be technically reachable by the public, but unless you are a current cable broadband subscriber, using them typically requires the purchase of a daily use pass.
Claim: “Cable will continue to invest, building this platform of possibilities, if we preserve the freedom that created the Internet.”
Our finding: EMPTY CLAIMS The NCTA’s commitment that the cable industry will continue to invest is fulfilled if one cable operator spends just $1 on their network infrastructure. Notice the NCTA does not commit its members to stopping the ongoing decline in broadband investment, much less move to increase it. It also has no explanation for the annual rate increases and new fees and surcharges customers are paying, as the gap between broadband pricing abroad and at home grows even larger.
“Preserve the freedom” is code language for maintaining the deregulation that the industry has used to its advantage to raise prices in a broadband market most Americans will find is either a monopoly or duopoly. Although the NCTA implies it, the cable industry did not create the Internet. It was a government project (gasp!) initially developed through contracts with the Department of Defense and soon broadened to include educational institutions. The first significant commercial ISPs emerged only in the late 1980s. Cable industry broadband finally showed up around a decade after that. The industry’s claims are akin to boasting Lewis and Clark discovered Kansas City… in 1966.
If the cable industry gets some oversight of its broadband service and enforced protection of Net Neutrality, does that mean investment will flee? First, providers are already spending a lower percentage of capital on broadband expansion in the current deregulatory environment. Second, as broadband becomes the cable industry’s top earner, it provides an endless supply of revenue without the headaches of negotiating programming contracts, dealing with cable television network rate increases, and the growing phenomenon of cord-cutting. In other words, without significant new competition, it remains a license to print money.
[flv]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/NCTA The Infinite Internet 1-20-15.mp4[/flv]
The NCTA is trying to make hay with its new video, “The Infinite Internet” which purports to share how Big Cable’s vision of the Internet is making new things possible. They don’t mention many of their member companies want to place a usage cap on that innovation, even as they continue to raise prices way out of proportion of the cost of delivering the service. It’s classic cable industry propaganda. (1:08)




 Subscribe
Subscribe The National Cable & Telecommunications Association (NCTA), the nation’s largest cable lobbying group, has outdone itself with a brand new fact-challenged video truth-seekers will quickly discover is little more than industry propaganda.
The National Cable & Telecommunications Association (NCTA), the nation’s largest cable lobbying group, has outdone itself with a brand new fact-challenged video truth-seekers will quickly discover is little more than industry propaganda.


 “EPB’s efforts have encouraged other telecom firms to improve their own service,” states the report. “In 2008, for example, Comcast responded to the threat of EPB’s entrance into the market by investing $15 million in the area to launch the Xfinity service – offering the service in Chattanooga before it was available in Atlanta. More recently, Comcast has started offering low-cost introductory offers and gift cards to consumers to incentivize service switching. Despite these improvements, on an equivalent service basis, EPB’s costs remain significantly lower.”
“EPB’s efforts have encouraged other telecom firms to improve their own service,” states the report. “In 2008, for example, Comcast responded to the threat of EPB’s entrance into the market by investing $15 million in the area to launch the Xfinity service – offering the service in Chattanooga before it was available in Atlanta. More recently, Comcast has started offering low-cost introductory offers and gift cards to consumers to incentivize service switching. Despite these improvements, on an equivalent service basis, EPB’s costs remain significantly lower.”
 Looking for civil rights groups to support your multi-billion dollar telecom merger and keep minority groups off your back?
Looking for civil rights groups to support your multi-billion dollar telecom merger and keep minority groups off your back? While the money keeps rolling in, Sharpton has
While the money keeps rolling in, Sharpton has 

 “The telecommunications language will force the governor to veto this bill, as he has personally said and has also been repeated several times by other members of the administration,” Jim Zehringer, director of the Ohio Department of Natural Resources told the Ohio Senate’s Agriculture Committee during an informal hearing on the legislation. “We would be sacrificing all the great work done so far on this bill if these provisions are not removed.”
“The telecommunications language will force the governor to veto this bill, as he has personally said and has also been repeated several times by other members of the administration,” Jim Zehringer, director of the Ohio Department of Natural Resources told the Ohio Senate’s Agriculture Committee during an informal hearing on the legislation. “We would be sacrificing all the great work done so far on this bill if these provisions are not removed.”