 Comcast claims 93% of families participating in its affordable internet service for the income-challenged report an improvement in their children’s grades at school.
Comcast claims 93% of families participating in its affordable internet service for the income-challenged report an improvement in their children’s grades at school.
That result is not surprising, according to research cited by FCC Commissioner Jessica Rosenworcel, who told the New York Times last year that one-third of students from kindergarten through 12th grade who live in low-income or rural households either have no access, or cannot afford access to the internet at home.
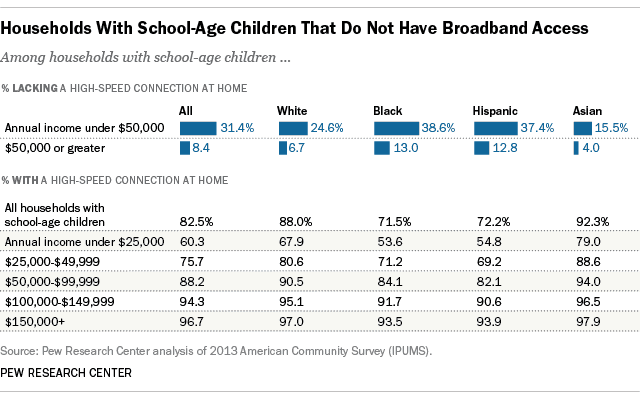
A 2015 Pew Research report found that with approximately 29 million households in America having children between the ages of 6 and 17, five million households with school-age children do not have high-speed internet service at home. Low-income households – and especially black and Hispanic ones – make up a disproportionate share of that number:
Pew Research analysis of the Census data finds that the lowest-income households have the lowest home broadband subscription rates. Roughly one-third (31.4%) of households whose incomes fall below $50,000 and with children ages 6 to 17 do not have a high-speed internet connection at home. This low-income group makes up about 40% of all families with school-age children in the United States, according to the bureau’s American Community Survey. (The survey asked questions on home internet use for the first time in 2013.)
There are fewer studies measuring how a lack of internet access impacts on academic performance. With ongoing budget constraints now forcing seven out of 10 teachers assigning homework that requires students to set aside outdated textbooks and do research online, a significant number of students from income-disadvantaged or rural homes are struggling to keep up with their richer peers.

Concerns about fraud in the Lifeline program are stalling aggressive efforts to get affordable internet into poor and rural family homes.
In Coachella, Calif., and Huntsville, Ala., school districts report the problem has become so bad, many students are now depending on buses equipped with Wi-Fi to function as mobile study halls, where students sometimes ride for hours frantically trying to complete homework they cannot do at home. Some school buses are now parked in neighborhoods overnight with Wi-Fi service left on continuously where few families can afford a home internet connection at the prices demanded by the local phone and cable companies.
“This is what I call the homework gap, and it is the cruelest part of the digital divide,” said Rosenworcel, a Democratic member of the FCC who has tried to adapt the Lifeline program to include home internet access.
Rosenworcel and others in favor of subsidizing internet access for the poor are up against two powerful groups in Washington — the providers themselves, which have launched a PR blitz designed to promote their own voluntary low-cost internet programs like Comcast’s Internet Essentials and Charter Communications’ Spectrum Internet Assist. The other obstacle comes from a number of Republicans in Congress who frequently demagogue Lifeline as a rat hole of waste, fraud, and abuse and are reticent about expanding it to cover broadband.
In a hearing held this morning by the Senate Commerce Committee, senators questioned a representative of the Government Accountability Office that released a report in May that found “extensive problems” with the Lifeline program. The report targeted 12 phone companies for approving Lifeline applications with fake eligibility information 63% of the time, potentially exposing taxpayers to millions of dollars in losses for non-qualified or deceased applicants.
Attempts to strengthen verification procedures are ongoing, first initiated by former FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler, who approved a national verifier system for providers to ensure compliance. But for current FCC Chairman Ajit Pai, who voted against Wheeler’s compliance program, complaining that states did a better job of combating fraud, the results of the GAO study confirmed his own skepticism about the Lifeline program. Earlier this year, he blocked the approval of nine companies from joining the program to offer affordable internet access and shows no signs of relenting.
That leaves private telecom companies to continue expanding their own affordable internet programs. Comcast recently reported it had enrolled almost 20,000 families in its program in New Jersey alone. Its Internet Essentials program offers internet access to families qualified for the National School Lunch Program for $9.95 a month and offers a modest computer for $150. Comcast’s program now in its sixth year and recently increased its offered broadband speed to 15/2Mbps and offers 40 free hours a month to XFINITY Wi-Fi hotspots.
 Verizon does not want their customers to worry about their wireless and home internet bills during the COVID-19 crisis, so they are introducing some new affordable plans for low-income households, waiving late and overlimit fees, and giving wireless customers an extra 15 GB on their data allowance for the next month.
Verizon does not want their customers to worry about their wireless and home internet bills during the COVID-19 crisis, so they are introducing some new affordable plans for low-income households, waiving late and overlimit fees, and giving wireless customers an extra 15 GB on their data allowance for the next month.

 Subscribe
Subscribe A dispute is emerging in New York between Sprint and T-Mobile and the Communications Workers of America (CWA) and pro-consumer group the Public Utility Law Project (PULP) over the wireless companies’ attempt to argue for their merger deal in a partly secretive filing not open to review by the public.
A dispute is emerging in New York between Sprint and T-Mobile and the Communications Workers of America (CWA) and pro-consumer group the Public Utility Law Project (PULP) over the wireless companies’ attempt to argue for their merger deal in a partly secretive filing not open to review by the public.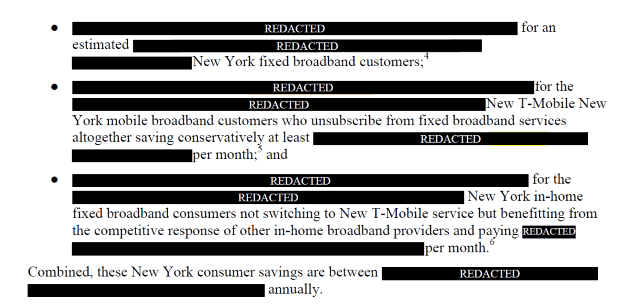
 The merger of the two wireless companies requires state and federal approval. Alaska, Colorado, Delaware, Georgia, Louisiana, Maryland, Minnesota, Nevada, Texas, Utah, West Virginia and the District of Columbia have already essentially “rubber-stamped” approval of the merger deal with little comment. Pennsylvania regulators submitted a series of questions that the two companies answered earlier this week.
The merger of the two wireless companies requires state and federal approval. Alaska, Colorado, Delaware, Georgia, Louisiana, Maryland, Minnesota, Nevada, Texas, Utah, West Virginia and the District of Columbia have already essentially “rubber-stamped” approval of the merger deal with little comment. Pennsylvania regulators submitted a series of questions that the two companies answered earlier this week.
 The wireless industry’s largest lobbying group, CTIA-The Wireless Association,
The wireless industry’s largest lobbying group, CTIA-The Wireless Association,  The CTIA doesn’t dwell on the real world impact of its member companies, with revenues well into the billions of dollars, simply absorbing the 36¢ a month charged to their Utah customers as a cost of doing business. Instead, the lawsuit argues Utah cannot apply USF surcharges in a way that is “inconsistent with the requirements related to the federal universal service Lifeline program.”
The CTIA doesn’t dwell on the real world impact of its member companies, with revenues well into the billions of dollars, simply absorbing the 36¢ a month charged to their Utah customers as a cost of doing business. Instead, the lawsuit argues Utah cannot apply USF surcharges in a way that is “inconsistent with the requirements related to the federal universal service Lifeline program.”

