Utility poles in Puerto Rico down in enormous numbers.
Many parts of the island of Puerto Rico remains in a total communications blackout after Hurricane Maria decimated the territory’s utility networks, with many mayors warning some communities won’t have restored service until “sometime in 2018.”
Stop the Cap! has collected information about the actual state of Puerto Rico’s telecommunications networks after the Federal Communications Commission admitted it has incomplete information as a result of the voluntary nature of its Disaster Information Reporting System. Some providers have no way to submit reports to the FCC and there have been questions about whether the submitted reports are “unrealistic and optimistic,” and don’t always indicate whether service has been restored to an equivalent level in place before the hurricane.
Javier (we are omitting his last name to protect his job) is a senior engineer at one of Puerto Rico’s larger telecom companies. He has communicated with us for over a year, primarily on events surrounding Puerto Rico’s cable industry on the island and media consolidation issues. Early this morning, we heard a candid assessment of the situation in Puerto Rico, where he lives and works.
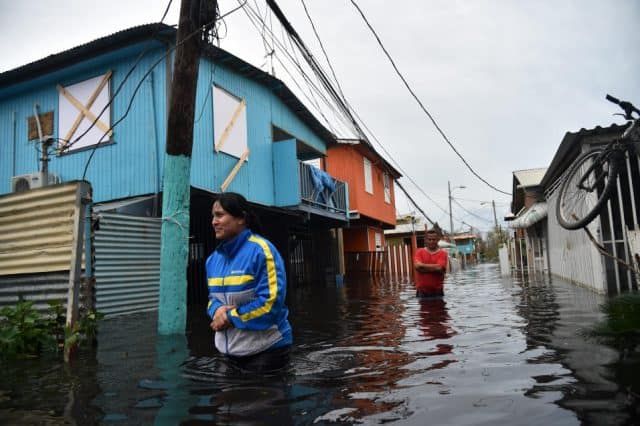
“It is completely catastrophic down here to the point where you feel paralyzed, unsure of where to begin cleaning up,” Javier shared with us. “It looks like the eastern and northern parts of Puerto Rico got the worst the storm, but there are lots of areas on the western half of the island nobody has heard from since the storm. There is absolutely no communications with some of what we think are the most vunerable communities. The news media has taken helicopters into some of these areas and stations like WAPA are reporting there is life, but water is in short supply and the destruction is unbelievable — nothing Puerto Ricans can recall during their lifetime.”
 Javier reports anyone moving between towns outside of the urban areas needs an all terrain vehicle with plenty of gas and a chainsaw to clear debris from the roads. Many are not passable because bridges have been washed out or collapsed. His job of late is utility infrastructure inspection and the news is not good.
Javier reports anyone moving between towns outside of the urban areas needs an all terrain vehicle with plenty of gas and a chainsaw to clear debris from the roads. Many are not passable because bridges have been washed out or collapsed. His job of late is utility infrastructure inspection and the news is not good.
“A lot of this island’s electrical transmission network is probably going to be rebuilt from the ground up,” he reports. “There are towers — many metal or concrete, that are completely bent over or fallen, and some of the higher voltage lines are going the take weeks just to reach because they are blocked by the huge number of trees down. Many are in such a compromised state, they are still toppling over. Some cell towers collapsed over the weekend, so it can be very dangerous to climb these.”
Javier says some parts of the island have gotten desperate for food and water, followed by safe housing and access to telecommunications to let distant family members know how they are doing.
“Many Puerto Ricans are not kidding themselves, and they expect they will not be treated the same as hurricane victims in Florida and Texas, in part because of the territory’s status in the United States and the fact its needs have usually been ignored or cut short by Washington. Local and state officials have tried to maintain a positive attitude about the relief effort and have repeatedly thanked first responders, FEMA, and the Trump Administration, but there are clear signs the goodwill is straining as days pass with inadequate relief. It threatens to become worse than Hurricane Katrina.”
“We know there is a transportation issue between Miami and Puerto Rico, but we also know other Caribbean countries like the Dominican Republic and Cuba are either providing credible aid that is getting through, or will be soon. The same is not consistently true with the United States,” Javier notes.

Cell tower collapse in Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico’s cell phone network remains almost completely offline, with some small exceptions in larger communities like San Juan, where one-third of the city’s cell towers are back up and running, often on generator power.
“Providers have claimed, without credibly knowing, that their towers are offline because of power interruptions, but once they visit those cell sites they will find a number of them have been badly damaged and will need to be replaced,” Javier said. “Some of the towers being reported restored are working because of temporary low-power portable cell sites that do not have the coverage of the original tower, but something is better than nothing.”
The FCC claims more than 90% of the island remains without cell service, and virtually 100% are without cable or landline service. Residents and officials on the ground confirm that, with some minor exceptions, and note the most reliable service they have are the satellite phones provided by FEMA and kept in government offices. Some private businesses like Home Depot also have them. Satellite internet access is available in some rural locations, and where it works, it has attracted large crowds of locals trying to connect to the outside world to get messages through.
“The Dominicans are supplying Puerto Rico with backup generators for cell towers which will help, but we will need an army of people to help clear damaged infrastructure before we can repair or replace it,” writes Javier.
Those satellite phones and very limited internet access have allowed some important reports to get through. Univision is collecting regular reports at least daily from various social networking communities and publishing regular updates. We have collected the latest telecom-related developments to share with readers.
ADJUNTAS
Mayor Jaime Barlucea Maldonado: “We have not lost lives and access to all neighborhoods is enabled,” explained Barlucea who also said he has re-established communications with San Juan via Ponce. Tertiary roads are impassable and residents in Utuado cannot cross through Adjuntas. Half the area has no drinking water, doctors fled the health center and medicines are almost gone.
Besides the government communications network, ordinary residents do not have reliable landline or wireless service at this time.
AGUADA
The government confirmed two deaths — both police officers who drowned in a river. Mayor Manuel Gabina, said the town is “devastated” and that there are eight thousand families that lost everything they owned, including their homes. The Guanabanos and Jaguey Chiquito bridges are “damaged or about to collapse.”
Gabina collected enough supplies to last the town a month, but “water and shelter for the displaced” are in short supply, as are supermarkets and gas stations. Phone service is somewhat working in Aguada and Moca, and locals are sharing phone lines to stay in touch.
AGUADILLA
Aguadilla was spared the worst of the storm and food and water has already reached this municipality and the airport is now prepared to receive military-supplied relief flights. Road cleanup is ahead of schedule and Wi-Fi access is returning in some areas like the Burger King on PR-2 highway. Families have flocked there to send messages out.
AGUAS BUENAS
Mayor Javier García Pérez reported that some 3,000 families lost their residences in Aguas Buenas. The worst affected areas are Santa Clara, Las Corujas sector, Parcelas Bayamoncito, and the neighborhood of Juan Asencio. There is a major water shortage and many of the transmission towers for electricity and wireless service have collapsed.
“We are more likely to have water than electricity first,” said the mayor. There is no working cell service, the hospital is closed, and roads have been gridlocked because of reports six gas stations are open in the community.

Alicea
AIBONITO
Mayor Willie Alicea reported this morning the entire area is still without cell phone or internet access. But relief did arrive in some forms:
- 40,000 gallons of gas arrived.
- Commercial businesses are open, operating and serving food.
- The supermarkets are open.
- About 2,500 volunteers are clearing the roads, helping with traffic and in operations.
- All roads are open to vehicular traffic with the exception of the Cuyón neighborhood.
AÑASCO
In Añasco, the roads are still blocked and communication is scarce, at best. No significant reports since Sunday.
ARECIBO
On its Facebook page, the municipal government indicated that damages in the city were “disastrous” and that “no area of Arecibo has the resources of water, electricity and communications.” Some areas of the municipality are still isolated. At least three bridges collapsed in the municipality: one in the neighborhood Jaguar, another in Bajadero and one between Calichoza and Esperanza.
Promised diesel fuel has not arrived.
ARROYO
There is very little updated information available about the municipality of Arroyo. A few that managed to enter the outskirts report it was unrecognizable because of the destruction. All cell towers have been destroyed. Temporary antennas are expected… eventually. The damaged utility infrastructure is, in some cases, hanging directly above or near the roads.
BARCELONETA
Town has water but no electricity. Gasoline is usually not available. Cellular service is possible if you go to the outskirts of town.

Barranquitas
BARRANQUITAS
Large sections of community unrecognizable because of lack of vegetation and number of homes destroyed. Electric and phone cables are on the ground “everywhere” and there is no road service between Barranquitas and Naranjito. Obviously, communications are sporadic.
BAYAMÓN
Cell service sporadic but functional in some areas. This area survived Maria with less damage than others.
CABO ROJO
Mayor Roberto Ramírez is going door to door with a satellite phone to every home in the community allowing relatives to communicate with family members. The main roads in and out of the area are walkable, but cannot be driven on. The mayor reports 50% of homes are total losses.
CAGUAS
Some areas of the municipality have communication via cell phone.
CAMUY
The northern half of the town’s utility services have been completely obliterated. At least 460 homes destroyed and 642 uninhabitable. There is a major water shortage and residents are being told to drink nearby river water.
CANÓVANAS
The Red Cross is in town passing out snack packs. Rural roads are collapsed and impassable. Telecom services are spotty.
CAROLINA
Doing better than some. All urban roads are open. Mayor Jose Carlos Aponte reports 95% of rural roads open and 30% of bridges have been cleaned of debris.
“Carolina suffered a great impact and is seen with the great amount of residences of wood and zinc that were destroyed by the strong winds. The areas of Barrazas, Cacao, Santa Cruz and Carruzo were the most affected,” he said.
Utility infrastructure has been seriously damaged and will have to be rebuilt.

Cataño
CATAÑO
Cataño has suffered some of the worst flooding caused by Hurricane Maria as it passed through the island. About 60% of the 28,000 people in the town are now homeless and in some areas, 80% of structures were damaged.
The mayor of Cataño, Felix Delgado Montalvo, said Tuesday that municipal officials are trying to visit every residence in the municipality to bring aid to the victims and asked people to be calm.
Nearly 1,000 utility poles fell in the community and will need to be replaced.
CAYEY
Cayey Mayor Rolando Ortiz Velázquez told WKAQ 580 AM on Monday that the municipality already has opened access to all communities, vehicular traffic or walking. The community was hit hard, but the city authorities are handing out bottled water and the town has enough food on hand.
In this municipality there are complete sectors of communities in Farallón, Guavate and El Polvorín that lost their wooden houses. Access to neighboring municipalities like Cidra, Aibonito, Guayama and Salinas is limited at the moment.
CEIBA
A “desolate environment” with lots of vegetation, blocked streets and families affected. Reporter Bárbara Figueroa reports that the governor’s house was “totally destroyed.”
The state of telecommunications in the area is unknown.

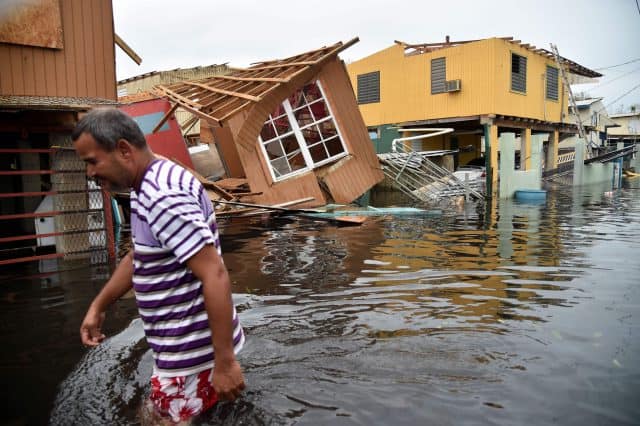
A Hurricane Maria victim.
CIALES
All the bridges of Ciales collapsed with the passage of Hurricane Maria, Angel Perez, director of the Emergency Management Center told local media.
There is extensive damage to homes, fallen ceilings, destroyed walls, lack of water and electricity.
CIDRA
On its roads there are fallen trees, branches, traffic lights, roofs and signs on the ground, as shown by a tour of El Nuevo Dia by the municipality.
Road 172, which leads from Caguas to Cidra, “is devastated, totally destroyed,” said Cidra Mayor Javier Carrasquillo in an interview with Primera Hora. Virtually all power lines and cement posts are on the ground, he added.
COAMO
A San Juan resident said that in the absence of communication with part of her family, she made a trip to Coamo to see how they were.
“Most of the damage was to wooden structures, zinc roofs, and glass,” said Isabella Scalley Fernandez. “There are many trees and power lines on the ground.”
COMERÍO
According to El Nuevo Día, the mayor of Comerío, Josian Santiago expressed concern about shrinking water and fuel supplies. Some parts of the area resemble a third world country and are still inaccessible.
Looters struck a warehouse of the Econo supermarket after the hurricane and stripped the warehouse clean of supplies.
“It was a scene worthy of a zombie series or movie,” the paper said.
Power and electricity may not be back until sometime in 2018.
 COROZAL
COROZAL
This mountainous, rural area took a severe beating and remains mostly inaccessible, but some expeditions found the local population did survive the storm. Utility infrastructure decimated.
CULEBRA
The island of Culebra, 85 miles east of Puerto Rico, is a major staging ground for hurricane relief for the main island. There remains a lack of electricity, but that is primarily because the island relies on a diesel generator to supply power. With deliveries spotty, electricity could go in and out of service. The island has communication problems and has not been able to communicate with the central government. To the east of Culebra and in high elevation areas, some cell service is available. That is where people are flocking to try and communicate with their friends and families on Puerto Rico.
DORADO
There is no water or communications, except at the airport.
FAJARDO
The ports of Vieques, Fajardo and Culebra have reopened, local Commissioner Jenniffer González Colón reported Monday afternoon at a press conference at the Convention Center. The official said that these ports are “open and operational for the transportation of passengers.” However, he clarified that the traffic will be “restricted” by the lack of electricity.
Thousands of utility poles were knocked down in the storm, taking the wiring with them. Cell service is spotty, but some Claro customers are getting limited service.
FLORIDA
Most of the homes in Florida were flooded and suffered some damage. The municipality is without electricity and without water. All utility cables are on the ground. Unless a residence was constructed of concrete, it no longer exists. There is no telecom service in Florida.
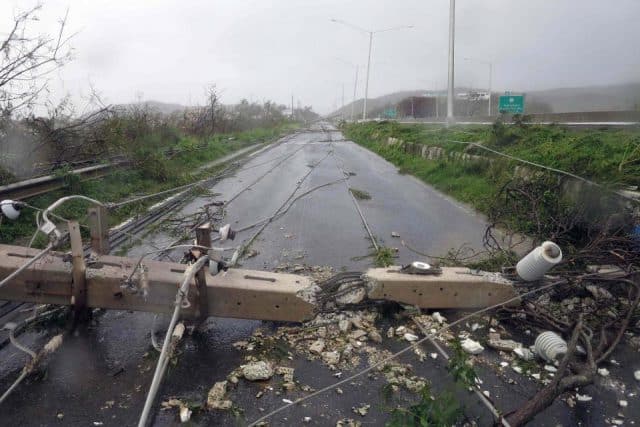

Even concrete poles no match for Maria.
GUÁNICA
Most of the community’s utility services no longer exist because of downed wires and fallen poles.
GUAYANILLA
Survived better than many. Its biggest problem seems to be establishing contact with San Juan.
GUAYNABO
Significant damage. Cell service did better in this area than most, with 20% of the cell towers working. Several banks and businesses are already resuming operations in several municipalities. Looting has grown to be a problem, however. So have curfew violations.
GURABO
Another area with decimated telecom infrastructure. Utility networks may have to be rebuilt from the ground up.
HATILLO
Hatillo Mayor Jose “Chely” Rodriguez said that “hundreds and hundreds” of homes in his municipality were destroyed. “It’s catastrophic.”
Facebook users indicate the only phone service for miles is at the Home Depot, which is lending out satellite phones residents are using to contact families and friends.
HORMIGUEROS
There is very little information about Hormigueros. The National Meteorological Service extended to this Tuesday at 8:30 pm the flood warning for Hormigueros, among other villages in the west, interior and central north of the island with warning of possible floods. The electric grid was essentially destroyed, but the town’s infrastructure fared better. The only news the town gets is from the radio.
HUMACAO
Fared reasonably well in comparison to some other areas. Its utility infrastructure was damaged, but is repairable and restorable.
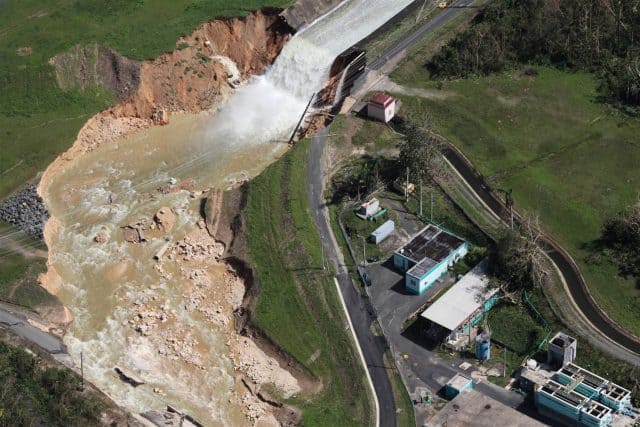

Damaged Guajataca Dam
ISABELA
The damaged Guajataca Dam continues to endanger Isabela. If it fails, it could seriously endanger Isabela. The National Weather Service extended the flood alert until Wednesday at 2:00 pm due to a possible total failure of the dam.
Mayor Carlos Altieri reports “terrible” damage to buildings and 80% of the electrical infrastructure is gone. Drinking water supplies have dwindled in Isabela and five other towns in the area. The local hospital is no longer air-conditioned and there is a medicine shortage. The mayor admitted he can no longer communicate with the authorities in San Juan due to growing telecommunications outages. Also, his satellite phone no longer works.
JAYUYA
Completely inaccessible except by helicopter. The town is completely cut off and incommunicado.
JUANA DÍAZ
Also effectively inaccessible due to fallen bridges. Significant damage and supplies dwindling.
JUNCOS
Claro reported it is working to reestablish the mobile network in the area and 20% in the municipality of Juncos had service again. There are two gas stations open in the area, with lines that stretched for more than half a mile. Supermarkets are rationing the sale of food.
LAJAS
Lajas has no electricity or telecom services working except some limited cell service from Claro in some areas. Most mobile phones have no lost their charge and with no way to recharge them, it may not make much difference. Most are traveling to Mayagüez or Ponce if they want to make or receive calls reliably.’
LARES
Although telecommunications service is out, the community fared acceptably well if you weren’t impacted by a landslide. But bodies in area graveyards were scattered all over the area, creating a potential health risk.

Villafañe
LAS MARÍAS
Although less is known about what is happening on the western half of Puerto Rico, the secretary of the governor, William Villafañe, managed to visit Las Marías, one of the municipalities where the least official information has gotten out due to difficulty to accessing then area and the lack of roads. There is significant damage to utility infrastructure, and this area is unlikely to get attention before larger communities have service restored.
LAS PIEDRAS
Mayor Miguel López reported the entire area was without power and facilities are severely damaged. At least 90% of utility poles and lines are damaged, likely beyond repair. Wind gusts reached 205mph, which also took out the enormous concrete pylons holding the regional high voltage power lines that act as the island’s electricity backbone. These will have to be rebuilt entirely.
LOÍZA
Flooding did the most damage to infrastructure in this area. Power is completely out, but some families acquired solar panels and are powering some bare essentials with them. This coastal area took significant storm surge damage.
LUQUILLO
The medical center no longer exists and looting of alcohol and the antisocial behavior that accompanies it is becoming a serious problem. The town has no functioning communication with the outside world.

Looking for the missing in Manatí.
MANATÍ
“My people do not have water, people are collecting water from a swimming pool,” said the mayor of Manatí José Sánchez in an interview with newspaper Nuevo Dia on Monday morning on the impossibility of solving problems with water supply. “I cannot make excuses that they have to do tests when we have a faucet. I can warn the inhabitants that it is not drinkable but we need to get water soon.”
“All the municipalities in my district are incommunicado,” said Rodríguez Aguiló. “There is not a single wooden house that has not been damaged. The damage to the electrical system was serious, as was the deforestation in Ciales, Manatí and Florida.”
MARICAO
This town has not been heard from since the hurricane. No information available.
MAUNABO
“Almost all of the structures are damaged. Many wooden houses suffered total loss,” the municipality explained.
El Nuevo Día reported looting at the Maunabo Diagnostic and Treatment Center, which began after the roof was blown during the hurricane and flooded. The members of the Office of Emergency Management, who went to the site to settle the robbery, moved the equipment to the municipal headquarters.
Manaubo is incommunicado. In Maunabo, 11 of the 12 telecommunication towers that allow cell phones to function are out of order, according to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in its latest report.

A common sight in Mayaguez.
MAYAGUEZ
Evelyn Vázquez, a senator in Puerto Rico, reported mayors in the western zone of Puerto Rico were supplied with satellite phones so they can stay in touch with San Juan authorities. But many and lending the phones out to residents to alert friends and families about their status. The cost – up to $10 a minute, is irrelevant to both island and federal government authorities. The mayor of Mayagüez says the first urgency is water and gas in western areas. Then electricity and telecommunications services can be restored once basic needs are met. In many western communities there is a lack of potable water, bread, coffee, and ice. Diesel is also in short supply, which worries public officials because of the impossibility of generator power without adequate fuel.
Utility infrastructure was reportedly in the poorest condition on the western side of Puerto Rico, some more than 50 years old and barely inspected. Almost all of that succumbed to the hurricane force winds, landslides, or flooding. Timely upgrades may have made a difference, but now the much greater expense of rebuilding the networks from scratch will begin.
MOCA
“The people who have relatives in Moca, do not worry. Everyone has been taken care of. Nobody has died in our town of Moca,” said Mayor Kiko Avilés late Friday. But Moca’s telecom networks are not operating at all and most communities around Moca cannot be reached except by amateur radio. Utility infrastructure was poor before the storm. Now a lot of it is destroyed.
MOROVIS
A lot of damage is still ongoing in the territory because of ongoing landslides after every rain storm. The mayor reports the town was “devastated” and there are continued headaches from major landslides across the region. The San Lorenzo Bridge collapsed leaving no access to Pasto, Vagas, and San Lorenzo. Many area roads are impassible because of downed trees, power lines, and landslides. Volunteers are now attempting to use machetes to cut their way through to incommunicado communities not heard from since the hurricane. There is no communications services working in the area.
 NAGUABO
NAGUABO
Electrical service, which had been suspended since before the hurricane hit, cannot be restored due to network damage. A public communications center has been established in the parking lot of the Benigno Ramos Coliseum so residents can use satellite phones to communicate with relatives. Access to the area is very difficult from the outside because of the large number of fallen trees. The electrical grid was severely damaged, taking with it the telephone network. As a result utility services have collapsed with no estimate when they can be resumed.
NARANJITO
There have been few updates from this town. The mayor reported “massive destruction” but no loss of life. The community’s most vulnerable areas were emptied before the hurricane with a mandatory evacuation. Pedestrian bridges are essentially unusable and PR-811, the main road into town, is completely blocked by masses of debris.
OROCOVIS
No reports since Sunday, when the town complained there was little recovery machinery and no diesel to power it. Local authorities were asking for water and supplies to clear the roads in and out of town. The town’s amateur radio operators successfully established a repeater transmitter that allows Orocovis, essentially in the dead center of the territory, to act as a relay point for messages to and from southern Puerto Rico. The radio service is about the only thing working. Satellite phones are not functioning due to power losses. Wireline and wireless networks are not functioning.
 PATILLAS
PATILLAS
The municipality of Patillas is located nine miles from Yabucoa, where the eye of the hurricane landed. The area resembles what an area looks like after a major tornado rampages through a town. Utility poles and trees are down, and what trees remain are completely without foliage. The village is without electricity, although some people have generators. There are fallen light poles, cables on the ground, many blocking roads.
PEÑUELAS
“Peñuelas is totally destroyed in terms of structures,” said Mayor Torres Maldonado. “State aid has not arrived.”
Utility networks did not fare well either. A lot of downed power poles and lines have left much of the area without any telecommunications services.
PONCE
Officials report the entire city is without electricity although there are sectors with water. There are trees, electric lines and traffic lights down on roads. One official stated that restoring the Ciudad Señorial will take more than a month. Other areas of Ponce should expect little electricity or telecom service for weeks, although wireless should be restored in urban areas if fiber backhaul infrastructure connecting the cell towers with providers has not been damaged.
QUEBRADILLAS
The mayor, Heriberto Velez, said that hundreds are homeless, there are businesses that lost everything and the number of utility poles broken and on the ground around the village is staggering.
“I never imagined something like this. I did not think this could happen,” Vélez said.
“I’ve worked for the Authority for 26 years, it’s the first time I’ve seen broken concrete posts,” Edwin Alicea said, referring to the “hurricane resistant” concrete utility poles.
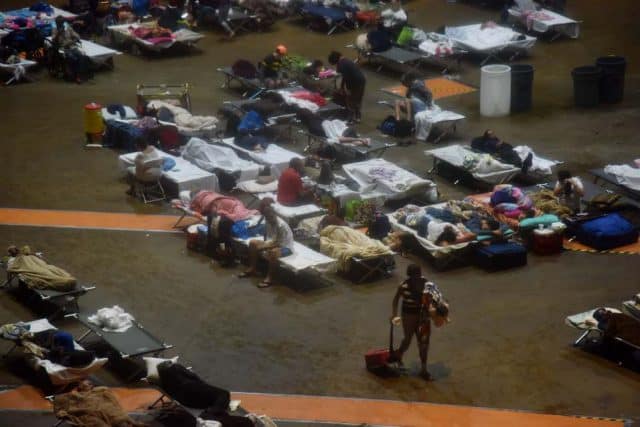

Hurricane shelter in Rincón, PR.
RINCÓN
The mayor of Rincón, Carlos López, continues to demand water for his town, as well as fuel and electric generators to maintain the shelter. He compared the impact of the hurricane to a nuclear bomb.
The mayor explained that the municipality, with 15,000 inhabitants, has no water supply and that the situation is very difficult but asked the citizens a little more calm and patience.
RÍO GRANDE
“We have no electricity, no water, no cellular service, and no gas, since the lines at each gas station are hundreds of cars long,” reported one resident. Mayor Angel Bori Gonzalez reported there is no cell service in the area.
SABANA GRANDE
Unconfirmed reports indicate there is limited phone and internet service, but no electricity. Scattered reports suggest there is running water and most of the flooding was in areas that routinely flood in storms. Unfortunately, there is no official confirmation of these reports.
SALINAS
Mayor Karylin Bonilla counted 3,000 wooden houses with zinc roofs damaged by Hurricane Maria. Some can be recovered. Bonilla reported that while there is a lot of damage to the infrastructure, there were no human losses. All residents have been advised that telephone services are expected to be offline for an undetermined amount of time and they should go to the mayor’s house or Carlos Colón Burgos High School to seek or share information.
SAN GERMÁN
There is limited mobile and landline service in this area. Claro had 20% of its network in the area up and running again. Most of the damage in this area was caused by fallen trees. Some callers reported they could get through to landlines, but multiple attempts were required.
 SAN JUAN
SAN JUAN
The mayor, Carmen Yulin Cruz, said that the priorities of San Juan are: drinking water, hospitals, bedding, and fuel.
Cruz said the capital of Puerto Rico was essentially “destroyed” in the storm, but recovery was now underway. The biggest problems are the number of downed utility poles and traffic signals. The city is without water or power. The city was expecting to receive additional generators that are targeted for cell phone network restoration, despite the fact most cell phone companies claim they already have generators at their cell sites. Most wireless carrier outages, providers claimed, come from inaccessibility to the cell site to refill generator fuel tanks. But now there may be questions about how well prepared providers were with backup equipment and whether it functioned well.
SAN LORENZO
The only cell tower in the area that has remained in service since the hurricane is accessible from the Chayanne Expresso, located adjacent to the tower. It appears to be operating at lower than usual power/signal strength, but calls can be made and received from the area. About 80% of wood residences were damaged in the storm and there is utility infrastructure damage, but not as severe as in other areas.
SAN SEBASTIÁN
No verifiable information available.
SANTA ISABEL
The Mayor of Santa Isabel, Enrique Questell, reported the economic base of the community – agriculture, was devastated.
“We are the capital of agriculture and we lost 100% of agriculture,” Questell said.
There is no power either. Utility poles were knocked down in large masses and will have to be replaced.
TOA ALTA
Received moderate storm damage but repairable. There is no wireline or wireless service functioning in the area and power remains out.
TOA BAJA
The mayor Bernardo ‘Betito’ Márquez informed El Nuevo Día that nine deaths were recorded in Toa Baja and that some of the people would have died drowned after the opening of gates of the Lake La Plata reservoir. The State Emergency Management Agency confirmed that Toa Baja is the most affected municipality in the islands due to flooding, but few evacuated because the area historically had not flooded before. There is no electricity or functioning telecommunications services in the area.
TRUJILLO ALTO
The municipality has no internet, gas stations in service are few and that community volunteers are now cleaning the roads because no help arrived.
Jose Luis Cruz Cruz, mayor of Trujillo Alto, said the municipality was “devastated” and was trying to break through on the main roads to reconnect with the rest of the island. The mayor reported that trees, electric lighting and street poles had fallen, so he asked citizens to be patient while they were cleaning. Outages remain widespread.

Flooding in Vega Baja
UTUADO
Electricity is out and most cell towers remain non-operational.
Univision journalist Carmen Graciela Díaz received information from her father about the precarious situation of this municipality.
“There is no water, there is no light, everything is a horror. It will be a very slow process to recover,” said Victor Diaz, owner of San Miguel Pharmacy in the center of town and life long resident.
But some landline phones are starting to work where infrastructure remains in place.
VEGA ALTA
The Mayor of Vega Alta, Oscar Santiago, reported 90% of the houses of wood and zinc in the municipality of Vega Alta were lost. Vega Alta village officials said they had not been able to reach the Fatima neighborhood and were particularly concerned about residents of a nursing home, according to the AP news agency. There is no way to reach the Fatima community because the bridge collapsed. Power remains out and telecommunications services are very spotty.
VEGA BAJA
In this area the floods reached more than 10 feet. Residents who were stranded shouted “Save me, save me,” using the lights on their cell phones to help rescue crews find them in the dark, said City Mayor Marco Cruz.
Reports indicate despite the flooding, services are being restored and wired and wireless phones are working in some areas intermittently.

Villalba
VIEQUES
There is no diesel or petrol on the island, which means that the machinery to remove debris cannot work. In addition, the last ferry with provisions arrived in Vieques five days ago, so supplies are running out.
The island’s mayor, Víctor Emeric, “if the Maritime Transport Authority does not return the system as soon as possible, there will be chaos with food, medicines, everything,” he said in a phone call to Primera Hora.
Telecommunications services are out.
VILLALBA
Completely isolated and without reliable communications, Villalba Mayor Luis Javier Hernandez told WKAQ 580 AM that they have been trying to open the main roads of the municipality for three days and that they managed to clear PR-149, PR-150 and open breaches in PR-151 towards Orocovis, but it is unsafe “and can collapse at any time.”
There are numerous communities in the mountainous municipality that “no longer exist” because of “complete destruction,” warned Hernandez. Many rural roads remain impassable even for pedestrians. Food was running out and the mayor was planning to break the locks on area schools and businesses to access food for the community.
YABUCOA
Rafael Surrillo, mayor of Yabucoa, reports 99% of structures in the municipal area collapsed.
Yabucoa is the town on the southeastern coast of Puerto Rico where the eye of Hurricane Maria entered and damages were most severe. Communications services are non-existent and there is no electricity.
YAUCO
“To all residents of Yauco, Yauco citizens outside of Puerto Rico and relatives outside of the city, the Honorable Mayor Luigui Torres wants to inform that Yauco has not reported any deaths. There is no communication anywhere in our city.”
 AT&T is staying committed to its wireline network in the face of two significant natural disasters by replacing beyond-repair copper wiring with fiber optics.
AT&T is staying committed to its wireline network in the face of two significant natural disasters by replacing beyond-repair copper wiring with fiber optics.

 Subscribe
Subscribe An undisclosed number of Frontier Communications customers in West Virginia were without phone service during the Christmas-New Year’s Day holidays because of copper thefts and slow repair crews that did not begin repairs for up to two weeks after the outages were reported.
An undisclosed number of Frontier Communications customers in West Virginia were without phone service during the Christmas-New Year’s Day holidays because of copper thefts and slow repair crews that did not begin repairs for up to two weeks after the outages were reported.

 Javier reports anyone moving between towns outside of the urban areas needs an all terrain vehicle with plenty of gas and a chainsaw to clear debris from the roads. Many are not passable because bridges have been washed out or collapsed. His job of late is utility infrastructure inspection and the news is not good.
Javier reports anyone moving between towns outside of the urban areas needs an all terrain vehicle with plenty of gas and a chainsaw to clear debris from the roads. Many are not passable because bridges have been washed out or collapsed. His job of late is utility infrastructure inspection and the news is not good.





 COROZAL
COROZAL




 NAGUABO
NAGUABO PATILLAS
PATILLAS
 SAN JUAN
SAN JUAN

 Frontier Communications spent $2 billion in 2014 to purchase AT&T’s Connecticut wireline business, believing it could make a fortune selling internet and cable television service to wealthy Nutmeg State residents over a network AT&T upgraded to fiber-to-the-neighborhood service several years earlier.
Frontier Communications spent $2 billion in 2014 to purchase AT&T’s Connecticut wireline business, believing it could make a fortune selling internet and cable television service to wealthy Nutmeg State residents over a network AT&T upgraded to fiber-to-the-neighborhood service several years earlier.