AT&T will spend $14 billion on its wireless and wired broadband networks in an effort to improve service for its urban and suburban customers, while preparing to argue its case for disbanding parts of the century-old landline network.
AT&T will spend $14 billion on its wireless and wired broadband networks in an effort to improve service for its urban and suburban customers, while preparing to argue its case for disbanding parts of the century-old landline network.
In a major 90-minute presentation with most of AT&T’s top executives on stage, the company announced its intention to move away from traditional landline service and towards a combination of an enhanced broadband platform and 4G LTE wireless access, especially in the 22 states where it currently delivers landline service.
The investment plan — Project Velocity — is a pivotal moment for AT&T, which has seen deteriorating revenue from its aging rural landline network and has focused most of its investments in recent years on its increasingly profitable wireless network.
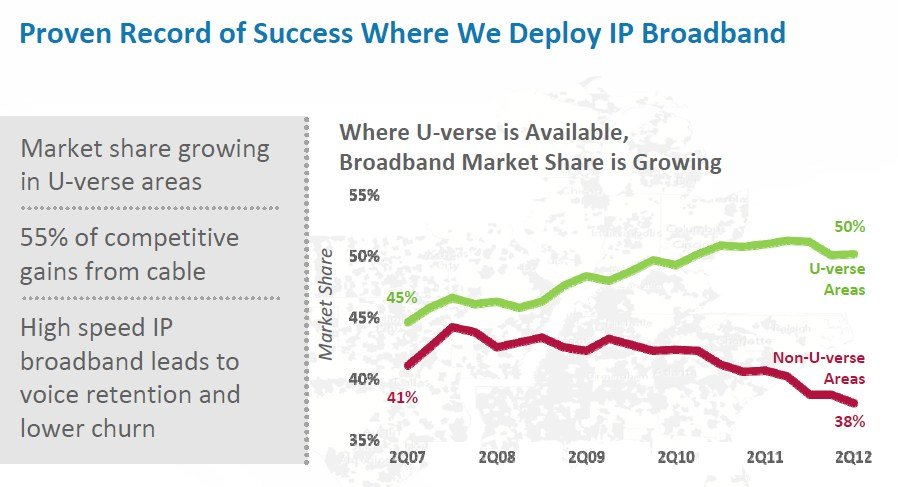
But AT&T also hoped to hang on to the enormous revenue it still earns providing traditional home phone service. Its early answer for landline cord cutting came in 2006 with U-verse, an IP-based network platform on which AT&T can sell video, voice, and broadband service with a minimum of regulatory oversight. U-verse succeeded attracting high-paying customers who either stayed with or returned to AT&T. But now company officials hope U-verse can help the company achieve victory in its next public policy fight: to abandon traditional landline service altogether.
That emerging battle is likely to pit urban and suburban customers enjoying enhanced U-verse service against rural AT&T customers deemed unsuitable for wired broadband. AT&T is seeking to decommission up to 25% of its rural landline network as part of the strategy announced today, shifting affected customers to its 4G LTE wireless voice and broadband service, which comes at a higher cost and includes draconian usage caps.
Critics contend such a move could leave AT&T largely unregulated with monopoly control over its networks, with few service requirements or access concessions for competitors. It would also leave rural customers relegated to a wireless Internet future, perhaps permanently.
Landline/Wired Broadband: Good News for Some, Scary News for Rural America
 AT&T plans to expand and enhance its broadband network to 57 million consumers and small businesses across its 22-state operating area, reaching 75 percent of customers by the end of 2015. AT&T will operate three broadband networks going forward, while gradually decommission its existing ADSL network.
AT&T plans to expand and enhance its broadband network to 57 million consumers and small businesses across its 22-state operating area, reaching 75 percent of customers by the end of 2015. AT&T will operate three broadband networks going forward, while gradually decommission its existing ADSL network.
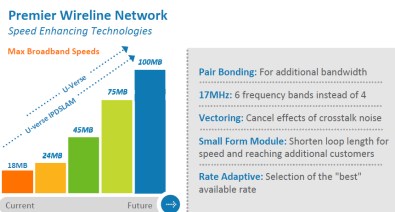
- U-verse: AT&T’s triple play package of TV, Internet, and Voice over IP phone will be expanded by more than a third to reach an additional 8.5 million customers by the end of 2015. This will make U-verse available to 33 million customers in AT&T home phone service areas. Most of the expansion will be in urban and suburban areas bypassed during the initial U-verse construction phase. To remain competitive, AT&T will also increase available broadband speeds for existing customers up to 75Mbps;
- U-verse IPDSLAM: An additional 24 million customers will be offered a combo voice-broadband package that could be called “U-verse Lite.” It will offer speeds up to 45Mbps and is primarily intended as a replacement for the company’s DSL service in exurban and semi-rural areas. Arrives by the end of 2013;
- Fiber to Multi-Tenant Business Buildings: AT&T plans to expand its fiber network to reach more commercial buildings, but also lay the foundation to use these facilities for future distributed antenna systems and small cell technology that will create mini-cell sites serving individual neighborhoods, cutting down the demand on existing cell towers.
Customers living in rural, open country in AT&T service areas in states like Texas, northern Mississippi, western Tennessee and Kentucky, central and northern California and Michigan, and the rural areas of the Carolinas may eventually find themselves using AT&T’s wireless network as the company seeks to decommission its landline infrastructure.
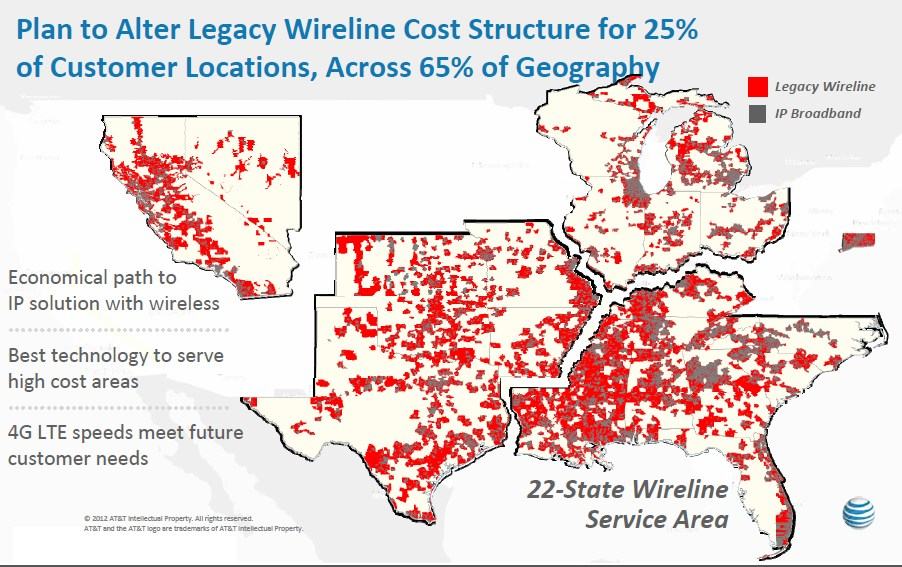
A number of AT&T customers living in areas shown in red may see red if and when AT&T begins trying to force rural Americans to its more profitable wireless networks.
But AT&T officials also admitted in a Wall Street Q & A session that the company planned nothing special for rural landline customers transitioned to wireless. Those customers will be sharing service with traditional mobile customers. If AT&T’s service plan resembles that of Verizon, customers will pay around $60 a month and limited to just 10GB of usage per month. If AT&T decommissions its existing landline infrastructure, no other wired provider is likely to take its place.
Most remaining regulations enforcing a level playing field for telecommunications networks remain with legacy copper-wire landline Plain Old Telephone Service. AT&T’s plan would effectively banish that network in its entirety through a series of regulatory and service-transition maneuvers:
- U-verse customers actually no longer have traditional landline service. U-verse offers barely regulated Voice over IP service, free from most state regulations and pricing oversight;
- U-verse IPDSLAM customers will also quietly forfeit their traditional landlines. This product works over an IP network, which means telephone service is Voice over IP;
- Wireless service is already barely regulated and not subject to price oversight or universal service requirements that landline providers must meet to deliver service to all Americans.
4G LTE Mobile Broadband: 99% Coverage Across 22 AT&T Landline States, Up to 300 Million Americans Served by the End of 2014
The majority of AT&T’s planned investment in its network will once again go to its highly profitable wireless division. At least $8 billion will be spent on bolstering AT&T’s 4G LTE wireless coverage area, especially in rural sections across its 22 state landline service area. That investment is necessary if AT&T hopes to win approval to decommission traditional landline service for rural customers.
- 4G LTE Expansion: AT&T plans to expand its 4G LTE network to cover 300 million people in the United States by year-end 2014, up from its current plans to deploy 4G LTE to about 250 million people by year-end 2013. In AT&T’s 22-state wireline service area, the company expects its 4G LTE network will cover 99 percent of all customer locations;
- Spectrum: AT&T continues its acquisition binge with more than 40 spectrum deals so far this year. AT&T’s biggest win of the year was approval for new WCS spectrum it will occupy alongside satellite radio. AT&T will have accumulated 118MHz of spectrum nationwide.
- Small Cell Networks: AT&T has already aggressively deployed a large number of Wi-Fi hotspots to encourage customers to shift traffic off its traditional wireless network. The next priority will be deployment of small cell technology, macro cells, and distributed antenna systems that can offer neighborhood-sized cell sites to serve urban and suburban customers and high density traffic areas like shopping malls and entertainment venues.
Using New Infrastructure to Drive New Business and Even Higher Revenue
AT&T would have had a hard time selling its planned investments to Wall Street without the promise of new revenue opportunities. AT&T’s new network enhancements will support a range of new services the company hopes to introduce to win greater revenue in the future:
- AT&T Digital Life: A nationwide all IP-based home security and automation service set to launch in 2013 that will let consumers manage their home from virtually any device — smartphone, tablet or PC.
- Mobile Premise Solutions: This new nationwide service, available today, is an alternative for wireline voice service and in the future will include high-speed IP Internet data services.
- Mobile Wallet: AT&T is participating in the ISIS mobile wallet joint venture. Market trials are underway in Austin, Tex. and Salt Lake City today.
- Connected Car: More than half of new vehicles are expected to be wirelessly connected by 2016. AT&T is positioned to expand from vehicle diagnostics and real time traffic updates to consumer applications that tie into retail wireless subscriber data plans. AT&T already has deals with leading manufacturers such as Ford, Nissan and BMW.
AT&T’s 2012 Investor Conference introduced major transformative changes for AT&T’s wired and wireless broadband networks. (2 hours, 9 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe