Charter's dumping ground for sneaky rate increases can be found in the Adjustments, Taxes and Fees portion of your monthly bill.
Charter Cable is literally passing the buck onto its cable TV subscribers.
Effective this October, Charter Cable customers will pay about a dollar more per month thanks to a new junk fee the company is adding to subscribers’ bills.
Federal law allows local U.S. broadcast television stations (i.e., affiliates of networks such as CBS, NBC, ABC, Fox, etc.) to negotiate with cable and satellite providers in order to obtain “consent” to carry their broadcast signals (Cable Television Consumer Protection and Competition Act of 1992).
As a direct result of local broadcast, or “network-affiliated,” TV stations increasing the rates to Charter to distribute their signals to our customers, we will be passing those charges on as a Broadcast TV Surcharge, in the Taxes and Fees section of the billing statement. These local TV signals were historically made available to Charter at no cost, or low cost. However, in recent years the prices demanded by local broadcast TV stations have necessitated that we pass these costs on to customers.
For most customers, the fee will average $0.94 per month, but in some areas it will be as high as $1.31 per month. Charter argues the fee is not arbitrary. claiming it represents the average price the company pays – per subscriber – for local broadcast stations in the communities it serves.
Stop the Cap! contacted Charter this morning and learned the company intends to impose this new fee even on customers with Charter’s Price Guarantee Package, which is supposed to guarantee customers no change in pricing for up to two years (see notes at the end of the article for an update). A Charter representative we contacted claimed the company will impose the fee on all customers, including those on contract, because of a clause in the terms and conditions which says, “The guaranteed price does not include the cost of installation and equipment, any applicable franchise fees, taxes or late fees, or costs for other ancillary services that you may order.”
Of course, the new fee is completely arbitrary and is neither a franchise fee or tax, nor is it for an “ancillary service.” We predict a closer review of Charter Cable’s thinking on this matter by state regulatory agencies and Attorneys General.
Charter’s FAQ seeks to pass the blame for the new fee to the federal government and local broadcasters:
Federal law treats [cable networks and over-the-air TV stations] differently. Unlike cable TV networks, local broadcast TV stations distribute their signals over the air, using free spectrum granted to them by the federal government. In effect, taxpayers are subsidizing the distribution of broadcast TV signals. These same broadcast TV stations are then allowed by the government to charge for their signals — and if we don’t agree to pay, broadcasters can force us to drop their channels, thereby adversely impacting our customers.
 “Given cable’s well-documented history of raising rates 4-6 times the annual rate of inflation, it seems rather disingenuous for them to now claim their rate hikes are coming as a result of broadcast TV stations, which provide the highest-rated entertainment and local news programming on the cable line-up,” National Association of Broadcasters Executive VP Dennis Wharton told Multichannel News in response to Charter’s move.
“Given cable’s well-documented history of raising rates 4-6 times the annual rate of inflation, it seems rather disingenuous for them to now claim their rate hikes are coming as a result of broadcast TV stations, which provide the highest-rated entertainment and local news programming on the cable line-up,” National Association of Broadcasters Executive VP Dennis Wharton told Multichannel News in response to Charter’s move.
The new Broadcast TV Surcharge will appear in the Taxes and Fees section of your bill, joined by other junk fees Charter has invented to pass along the ordinary costs of doing business to cable subscribers while claiming they are not increasing rates:
Charter’s “It’s Someone Else’s Fault We Charge These” Junk Fees
- TV and Internet Late Payment Fee — A late fee will be assessed for past due unpaid Charter TV and Internet charges.
- Phone Processing Fee — This fee is assessed when Charter does not receive payment for the full balance of your phone charges.
- Regulatory Cost Fee — The cost of doing paperwork and whatever else the company deems.
- State Telephone Relay Charge — Funds a Telecommunications Relay Service for hearing impaired/speech disabled residents.
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Fee — The FCC charges an annual regulatory fee for cable operators.
- Franchise Fee — Local communities collect a percentage of revenue from cable operators in return for doing business in the community.
- Public Education and Government Channels (PEG) Fee — Many cable franchise agreements ask cable operators to help fund the operations of these channels.
- Public Utilities Commission (PUC) Fee — Some states ask regulated providers to defray the costs of utility commissions that oversee providers on the state level.
- County 911 Charge (9-1-1 fee) — Some counties ask telephone providers to help pay to administer emergency 911 service.
- Telephone Right Of Way Fee (Municipal right-of-way fee) — A fee used to compensate municipalities for the use of their rights-of-way.
- E911 Equalization Surcharge (9-1-1 equalization fee) — A fee charged in wealthier, urban areas to help subsidize the costs of 911 service provision in rural and poor areas.
(Those fees in blue represent completely optional “junk fees” that hide revenue enhancements.)
(Those charges in red are fees mandated by government entities, but traditionally deemed “the cost of doing business.” Nobody requires these fees be billed directly to subscribers on a line-by-line basis, and most cable operators used to include them in the monthly price for service. But in a quest for increased revenue, cable companies began breaking them out of cable package pricing, charging for them independently. That effectively raises your total bill without changing the price of the programming package. It’s comparable to an airline charging for your airline ticket, but then padding the price with a Seat Rental Fee, a Boarding Fee to enter and exit the plane, an FAA Cost Recovery Fee to pay the Federal Aviation Administration for its services, a Flight Plan Filing Surcharge to cover the costs of filing a flight plan, and a Control Tower Charge to defray the expense of dealing with air traffic controllers. Snacks and soft drinks are extra.)
Charter Cable has been notifying subscribers about the new fee in mailings sent to subscribers. The company’s argument that broadcasters and the federal government conspired to make subscribers pay more may have some merit, but nobody forced Charter Cable’s hand to add a new junk fee to customer bills.
Local broadcasters are in an enviable position because federal government rules have given them all the cards to charge whatever they want for cable carriage. Government policy forbids most cable systems from taking their business elsewhere — perhaps to a station in a nearby city or network affiliate delivered via satellite that is willing to accept less than what local stations demand. Network-affiliated stations need not compete for cable carriage because they can demand cable systems not go outside of the area for an alternative.
Broadcasters do not enjoy “free spectrum granted by the federal government.” Television stations pay license fees and taxes just like other spectrum users and are mandated by the federal government to meet certain minimum programming standards and decency rules. Unlike other private license holders, broadcasters are supposed to serve the public interest, although what exactly defines that has evolved and eroded over the years. Cable programming is not regulated.
Charter Cable’s claim that “taxpayers are subsidizing the distribution of broadcast TV signals” is dubious at best. Broadcast radio and television preceded the paid television industry by decades, and was created to deliver unique “local service” to communities where stations were licensed in the public interest. Should Charter argue that broadcasters should bid for auctioned spectrum, they’d have much more to complain about when those costs are passed on in considerably higher broadcast carriage fees.
As usual, regardless of who wins the spat over local broadcast carriage fees, it’s Charter’s subscribers who will lose thanks to the higher bills that follow. But not our readers.
If you follow our advice, you can save far more than a dollar a month.

Score a new customer promotion and save far more than Charter hoped to collect from its new Broadcast TV Surcharge.
Stop the Cap! has been in touch with several Charter subscribers who successfully argued their way to considerably lower monthly bills, often by $20 or more a month. Here’s how you can let the bully boys argue over someone else’s money:
Gather Information
Get out a copy of your latest Charter Cable bill showing your packages, programming fees and the taxes and surcharges piled on at the end of the bill. Then, visit DISH Network or DirecTV’s website and gather pricing information for a comparable video package using their promotional pricing for new customers. Also visit your local phone company website for pricing for their phone and broadband services, taking note of any new customer promotional pricing and gifts.
On a sheet of paper, list the costs for Charter’s services on one side and the prices you would pay with their competitor(s) on the other and determine how much you would save with the competition.
Armed with this information, you’re now ready to sit down, call Charter, and talk business.
Sit Down And Make the Call
When you call Charter, select the option to cancel service or just say the word “cancel.” This will transfer you to Charter’s “customer retention” department. This group of customer service representatives have been specially trained to talk you out of dropping your service.
Explain that you are calling to cancel your Charter service after you received word of the latest fee increase. Tell them it was the last straw after years of rate increases and that you’ve been comparison shopping.
A Sample Conversation
You: “My husband/wife and I carefully considered an offer we received from [competitor] last night and decided it was time to make a change. It’s really all about the pricing. This economy has been killing us and we simply cannot handle a higher bill. When we looked at [competitor’s] offer, we discovered we could be saving $20 (insert amount applicable to you) or more a month over your own pricing. But I’ve been a Charter subscriber for a long time and I decided I should call and see if there was any way we could stay as a customer, if we could only negotiate a lower bill.”
Charter: “I see you have been a customer for a long time. Did you know that Charter delivers… (expect a comparison about the differences between satellite and phone company competition and Charter at this point. Your goal is to patiently wait until they finish and then stick to your guns that it’s really all about the monthly cost).
You: “I understand all that but you have to understand the only reason we are calling to cancel service is because of your prices. I am really giving you a last chance to see if we could stay and pay a lower price.”
Charter: “Let’s review your bill and see if we can drop any services you may not be using or perhaps sign you up for a different tier of broadband service.”
You: “The thing is, with [competitor’s] service, I don’t have to drop anything and I will still get a much lower price. Let me suggest an alternative idea. You could save our family as a customer if you could sign me up for the same kind of package pricing new customers pay.”
Charter: “I’m sorry, but those prices are only for new customers. But perhaps if we credited your account for a year’s worth of the fee you are upset about, that would help?”
You: “No, not really. Not after I saw what we could be paying by switching. Again, we’ve really already decided on making this change, but I decided it would be fair to give Charter a last chance to come closer to the prices I would be paying with your competitor. Isn’t there anything you could do to sign me up to a new customer promotion?”
Charter: “Well, let me put you on hold and talk to my supervisor.”
At this point, you may or may not get your request granted. Sometimes the representative will try and negotiate dollar amounts, try to sell you a bundled package of services to deliver “more savings,” or offer you a lower discount. Stick to your guns, but always remain polite. Sometimes their counteroffer may not deliver new customer pricing, but will still leave you saving far more than when you started, and keeps you off a term contract. If you are uncomfortable with the progress of the negotiations, or find an unsatisfactory outcome, politely end the call telling the representative you would like some time to think about it. It’s your chance to call back and speak with someone else.
In general, the more seriously they sense you are ready to commit to the competition, the better the offers will get to stay. Feel free to let them know you’ve already scheduled an installation with the “other guy” or would like information about where to drop off your cable equipment. If you are queasy about playing hardball, blame it on your spouse, letting Charter know “he/she will never go for that.” Stay friendly with the representative at all times — try to make them your advocate by encouraging them to find an even better deal for you and that you appreciate the time they are spending working with you. It’s a lot easier to get a better offer when you are not screaming at the representative that can’t wait to get off the phone with you.

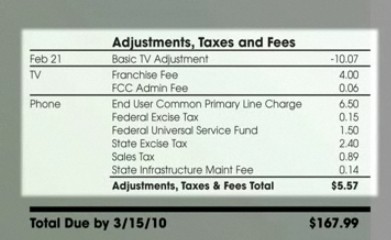
A Charter customer e-mailed this segment of their bill to clarify whether or not customers under a Price Guarantee contract would also pay the dollar fee.
If you find stubborn resistance to discounting your bill, consider showing up at the local cable office with your equipment and try negotiating one last time.
Charter Cable allows customers to cancel service and, after 30 days, sign up under a new customer promotion, so asking them to waive the 30 day requirement when it will save them money to reinstall service may be something they’ll consider. You could also re-establish “new service” under a spouse’s name for an even faster turnaround.
As Charter has taught their subscribers, it’s all about business with them. Turnabout is fair play, so give them the business about their pricing and demand savings.
[Updated 9:42pm ET — A Charter subscriber e-mailed Broadband Reports a copy of their latest Charter Cable bill saying the fee would -not- be applied to customers under a current Price Guarantee contract, in direct contradiction to what a Charter representative told us this morning. This is not much of a surprise, considering it took eight calls to Time Warner Cable last week to get the straight story about their DVR price hike in upstate New York.
Perhaps we should start calling cable companies not less than five times for answers to basic questions and then average the responses we get. As we said last week, we’ll believe the bill over what company representatives say any day.
Thanks to our reader Gabe and Broadband Reports for for alerting us to this development and helping clarify matters.]
[Update #2: 10:52am ET 9/16 — A Charter customer on Broadband Reports shared an online chat he had with Charter that shows I’m not the only one getting inaccurate information about this fee:
Scott: I heard that charter decided to add a new fee to user bills for “broadcast tv surcharge” even for customers that have locked in rates.
TTD Straissan : Yes. That is correct. The locked rates are for the services that are included on the locked promotion. Taxes and fees are not part of the locked promotion we have.
TTD Straissan : Broadcast TV Surcharge
Federal law allows local U.S. broadcast television stations (i.e., affiliates of networks such as CBS, NBC, ABC, Fox, etc.) to negotiate with cable and satellite providers in order to obtain “consent” to carry their broadcast signals (Cable Television Consumer Protection and Competition Act of 1992).
As a direct result of local broadcast, or “network-affiliated,” TV stations increasing the rates to Charter to distribute their signals to our customers, we will be passing those charges on as a Broadcast TV Surcharge, in the Taxes and Fees section of the billing statement. These local TV signals were historically made available to Charter at no cost, or low cost. However, in recent years the prices demanded by local broadcast TV stations have necessitated that we pass these costs on to customers.
This surcharge displays in the Taxes and Fees section of the bill statement.
Scott: when will this be on my bill?
TTD Straissan : Expected increase will be around October 1, 2010 on some areas.]
 Frontier Communications faced unhappy investors Thursday after announcing it was slashing its dividend nearly in half in an effort to raise money to sustain the company’s cash flow and reduce its debt.
Frontier Communications faced unhappy investors Thursday after announcing it was slashing its dividend nearly in half in an effort to raise money to sustain the company’s cash flow and reduce its debt.

 Subscribe
Subscribe