 Requiring Frontier Communications to increase broadband speeds could make the service unaffordable for rural and poor Americans, the company is arguing before federal and state regulators.
Requiring Frontier Communications to increase broadband speeds could make the service unaffordable for rural and poor Americans, the company is arguing before federal and state regulators.
In separate filings with the New York Public Service Commission and the Federal Communications Commission, Frontier has asked both for further deregulation and less oversight to ease everything from minimum broadband speed definitions to video franchising regulations.
Frontier’s market focus is primarily on rural communities where it delivers traditional DSL broadband service, typically up to 6Mbps, although many customers complain they get lower speeds than advertised. The FCC is working to modernize the Lifeline program, which offers substantial discounts on basic telephone service to low-income Americans. The Commission is studying the possibility of requiring providers to offer Lifeline Internet access for the first time. What worries Frontier is the Commission’s proposed requirement that providers offer Lifeline Internet speeds starting at 10/1Mbps, something Frontier strongly opposes.
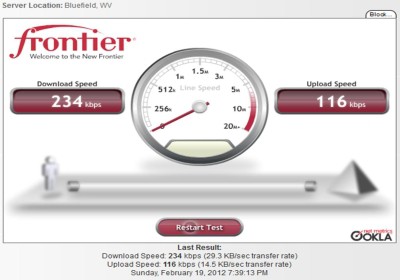 Frontier’s ability to deliver consistent 10Mbps service in rural areas is the issue.
Frontier’s ability to deliver consistent 10Mbps service in rural areas is the issue.
“Certain rural consumers […] may not currently have access to 10/1Mbps fixed Internet speeds and would thus be prevented from choosing to use Lifeline for a fixed Internet service,” Frontier wrote in its filing with the Commission. “Even if higher speeds are available, a minimum speed standard may prevent a customer from opting for a lower speed plan that may better meet their budget.”
Frontier told the Commission that most subscribers are happy buying 6Mbps service from Frontier, coincidentally the same speed it advertises as widely available across its service areas. Frontier argues if it was required to consistently provide 10Mbps service, the cost of the service may become unaffordable to many.
While Frontier argues against speed standards that are difficult for its aging copper-based network to consistently provide, it is using that same copper network as an argument against further regulation and oversight in New York.
“Traditional telephone service providers like Frontier continue to be legitimate and viable competitors in the marketplace—a testament to our tenacity and the quality of our services,” Frontier wrote in comments to the Public Service Commission. “To ensure that this continues to be the case, in the near-term, an immediate no-cost investment that the State can make in the existing copper-based network is to eliminate the regulatory requirements that apply to [traditional phone companies] but that do not apply to other telecommunications providers.
Frontier added, “consumers have a multitude of communications channels available to them including wireline and wireless voice services and wireline, wireless, cable and satellite broadband services.”

Frontier did West Virginia few favors when it took over Verizon’s landline business in the state.
Ironically, Frontier argued New York’s allegedly robust and fast broadband networks (offered by its competitors but usually not itself) are reason enough to support a “light regulatory touch.”
“Today, every municipality in New York has access to one or more wired or wireless networks that can provide voice, video and data services to residents and businesses,” Frontier claimed. “Over 95% of the state has access to the FCC benchmark speed of 25/3 Mbps and 98% of the State has 200kbps speed in at least one direction. New York’s broadband speeds are significantly faster than the national average and other countries.”
But Frontier failed to mention it is incapable of providing consistent access at or above the FCC benchmark speed because it still relies on a antiquated copper-based network throughout most of its New York service areas. Despite Frontier’s claims of offering quality service, the J.D. Power U.S. Residential Telephone Service Provider Satisfaction Study (2015) ranks Frontier dead last among all significant providers in the eastern U.S. It dropped Frontier this year from consideration for its Internet Provider Satisfaction Study, but a year earlier rated Frontier the worst ISP in the eastern U.S.
Although Frontier suggests it faces “robust competition” from “over 100 different broadband providers, especially at lower speeds,” in most of its service areas in New York it faces Time Warner Cable or no competitor at all.
Frontier’s latest defense over why it has failed to significantly upgrade its network infrastructure to remain competitive with cable is ‘customers don’t want or need faster speeds.’ While advertising lightning fast service on its acquired Verizon FiOS and AT&T U-verse networks, Frontier argues New York regulators “must keep in mind the consumer demands on broadband speeds.”
Frontier points to two rural broadband projects in New York, one in Hamilton County and the other in Warren County to make its speed argument (emphasis ours):
“These projects are examples of the importance of collaboration and innovation—rather than dogmatic adherence to performance requirements that are largely aspirational for many NYS citizen—in bringing high quality and transformative broadband access to unserved and underserved communities. Flexibility with regard to technology and broadband speed will enhance an already robust marketplace and result in greater affordability and access.”
Frontier has also told New York officials it wants to eliminate local oversight of video franchising and move New York to a “statewide video franchising” system to “promote competition and to streamline competitive entry into the video market in the state.”
“This will provide enhanced consumer choice as well as additional investment in broadband and video services,” Frontier argued. “In other states that have followed this model, such as Connecticut, consumers have a rich array of video providers and services from which to choose at competitive prices.”
That “rich array of video providers” in Connecticut is primarily Cablevision and Frontier. Frontier acquired a pre-existing U-verse network originally owned and operated by AT&T in the state.


 Subscribe
Subscribe
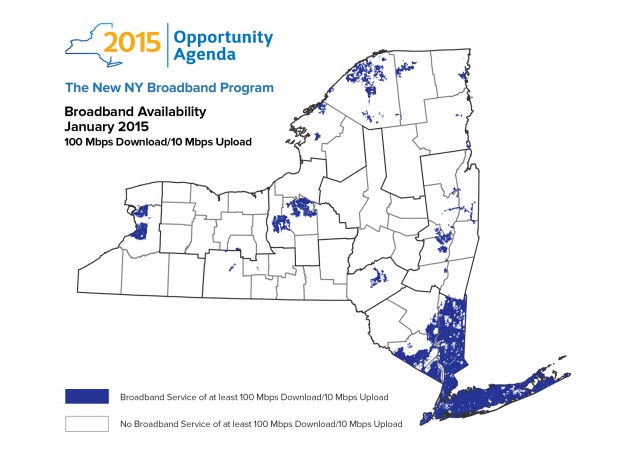 The attorney general’s investigation is particularly focused on so-called interconnection arrangements, or contractual deals that Internet service providers strike with other networks for the mutual exchange of data.
The attorney general’s investigation is particularly focused on so-called interconnection arrangements, or contractual deals that Internet service providers strike with other networks for the mutual exchange of data. The first provider in the country to offer community-wide gigabit fiber broadband to residential customers today announced it would far surpass the rest of the marketplace with a new 10 gigabit broadband package dubbed
The first provider in the country to offer community-wide gigabit fiber broadband to residential customers today announced it would far surpass the rest of the marketplace with a new 10 gigabit broadband package dubbed  An aversion of open, hilly landscapes and trees is apparently responsible for keeping residents of rural Connecticut from getting broadband service from the state’s two dominant providers — Comcast and Frontier Communications.
An aversion of open, hilly landscapes and trees is apparently responsible for keeping residents of rural Connecticut from getting broadband service from the state’s two dominant providers — Comcast and Frontier Communications.

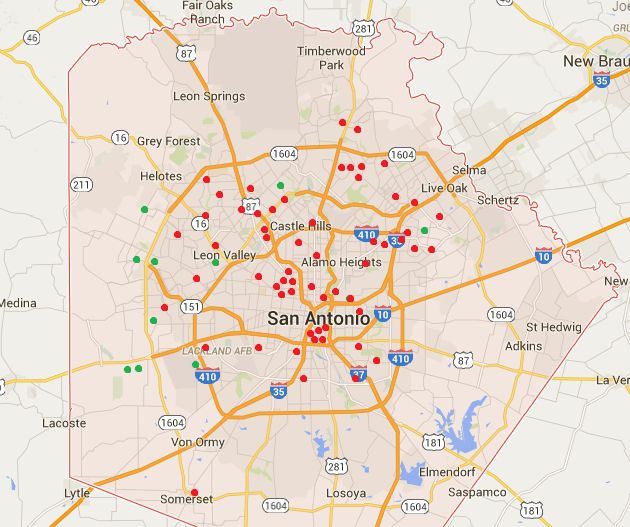
 The Consumerist writes AT&T is proving the importance of robust broadband competition. Communities that have it pay less and get quicker upgrades for faster Internet speeds. Those without pay AT&T a premium or are long way down on the upgrade list.
The Consumerist writes AT&T is proving the importance of robust broadband competition. Communities that have it pay less and get quicker upgrades for faster Internet speeds. Those without pay AT&T a premium or are long way down on the upgrade list.