July 17, 2017
July 17, 2017
Marlene H. Dortch, Secretary
Federal Communications Commission
Office of the Secretary
445 12th Street, SW
Washington, DC 20554
Dear Ms. Dortch,
Stop the Cap! is writing to express our opposition to any modification now under consideration of the 2015 Open Internet Order.
Since 2008, our all-volunteer consumer organization has been fighting against data caps, usage-based billing and for Net Neutrality and better broadband service for consumers and businesses in urban and rural areas across the country.
Providing internet access has become a bigger success story for the providers that earn billions selling the service than it has been for many consumers enduring substandard service at skyrocketing prices.
It is unfortunate that while some have praised Clinton era deregulatory principles governing broadband, they may have forgotten those policies were also supposed to promote true broadband competition, something sorely lacking for many consumers.
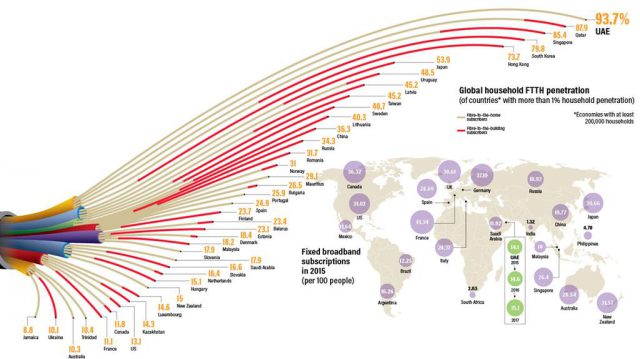
As a recent Deloitte study[1] revealed, “only 38 percent of homes have a choice of two providers offering speeds of at least 25Mbps. In rural communities, only 61 percent of people have access to 25Mbps wireline broadband, and when they do, they can pay as much as a 3x premium over suburban customers.”
 In upstate New York, most residents have just one significant provider capable of meeting the FCC’s 25Mbps broadband standard – Charter Communications. In the absence of competition, many customers are complaining their cable bills are rising.[2]
In upstate New York, most residents have just one significant provider capable of meeting the FCC’s 25Mbps broadband standard – Charter Communications. In the absence of competition, many customers are complaining their cable bills are rising.[2]
Now providers are lobbying to weaken, repeal, or effectively undermine the 2015 Open Internet Order, and we oppose that.
We have heard criticisms that the 2015 Order’s reliance on Title II means it is automatically outdated because it depends on enforcement powers developed in the 1930s for telephone service. Notwithstanding the fact many principles of modern law are based on an even older document – the Bill of Rights, the courts have already informed the FCC that the alternative mechanisms of enforcement authority that some seem motivated to return to are inadequate.
In a 2-1 decision in 2014, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. circuit ruled:
“Given that the Commission has chosen to classify broadband providers in a manner that exempts them from treatment as common carriers, the Communications Act expressly prohibits the Commission from nonetheless regulating them as such. Because the Commission has failed to establish that the anti-discrimination and anti-blocking rules do not impose per se common carrier obligations, we vacate those portions of the Open Internet Order.”[3]
In fact, the only important element of the pre-2015 Open Internet rules that survived that court challenge was a disclosure requirement that insisted providers tell subscribers when their internet service is being throttled or selected websites are intentionally discriminated against.
Unfortunately, mandatory disclosure alone does not incent providers to cease those practices in large sections of the country where consumers have no suitable alternative providers to choose from.
Reclassifying broadband companies as telecommunications services did not and has not required the FCC to engage in rate regulation or other heavy-handed oversight. It did send a clear message to companies about what boundaries were appropriate, and we’ve avoided paid prioritization and other anti-consumer practices that were clearly under consideration at some of the nation’s top internet service providers.
In fact, the evidence the 2015 Open Internet Order is working can be found where providers are attempting to circumvent its objectives. One way still permitted to prioritize or favor selected traffic is zero rating it so use of preferred partner websites does not count against your data allowance.[4] Other providers intentionally throttle some video traffic, offering not to include that traffic in your data allowance or cap.[5] Still others are placing general data caps or allowances on their internet services, while exempting their own content from those caps.[6]
Our organization is especially sensitive to these issues because our members are already paying high internet bills with no evidence of any rate reductions for usage-capped internet service. In fact, many customers pay essentially the same price whether their provider caps their connection or not. It seems unlikely consumers will be the winners in any change of Open Internet policies. Claims that usage caps or paid prioritization policies benefit consumers with lower prices or better service are illusory. One thing is real: the impact of throttled or degraded video content which can be a major deterrent for consumers contemplating disconnecting cable television and relying on cheaper internet-delivered video instead.
Arguments that broadband investment has somehow been harmed as a result of the 2015 Order are suspect, if only because much of this research is done at the behest of the telecom industry who helped underwrite the expense of that research. Remarkably, similar claims have not been made by executives of the companies involved in their reports to investors. Those companies, mostly publicly-traded, have a legal obligation to report materially adverse events to their shareholders, yet there is no evidence the 2015 Order has created a significant or harmful drag on investment.
In a barely regulated broadband duopoly, where no new significant competition is likely to emerge in the next five years (and beyond), FCC oversight and enforcement is often the only thing protecting consumers from the abuses inherent in that non-competitive market. Preserving the existing Open Internet rules without modification is entirely appropriate and warranted, and has not created any significant burdens on providers that continue to make substantial profits selling broadband service to consumers.
Transferring authority to an overburdened Federal Trade Commission, not well versed on telecom issues and with a proven record of taking a substantial amount of time before issuing rulings on its cases, would be completely inappropriate and anti-consumer.
Therefore, Stop the Cap!, on behalf of our members, urges the FCC to retain the 2015 Open Internet Order as-is, leaving intact the Title II enforcement foundation.
Respectfully yours,
Phillip M. Dampier
Founder and Director
Footnotes:
[1] https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/consulting/articles/communications-infrastructure-upgrade-deep-fiber-imperative.html#1
[2] “Thousands of Time Warner Cable Video Customers Flee Spectrum’s Higher Prices.” (http://bit.ly/2tjHJ8f); “Lexington’s Anger at Spectrum Cable Keeps Rising. What Can We Do?” (http://www.kentucky.com/news/local/news-columns-blogs/tom-eblen/article160754069.html)
[3] http://www.cadc.uscourts.gov/internet/opinions.nsf/3AF8B4D938CDEEA685257C6000532062/$file/11-1355-1474943.pdf
[4] https://cdn3.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/7575775/Letter_to_R._Quinn_12.1.16.0.pdf
[5] https://www.t-mobile.com/offer/binge-on-streaming-video.html
[6] http://www.chicagotribune.com/bluesky/technology/ct-data-cap-policies-20151214-story.html
 A DNS failure took out internet service for more than 15 hours for many Charter Communications broadband customers in Texas.
A DNS failure took out internet service for more than 15 hours for many Charter Communications broadband customers in Texas.

 Subscribe
Subscribe