Get out your tiny violins. Telephone and cable companies that have ignored your neighborhood for years are decrying attempts by the federal government to fund projects that would finally extend broadband service to rural America. Companies ranging from tiny Eagle Communications in Kansas, to major regional telephone companies like FairPoint Communications and Windstream, are upset that new providers are on the way to deliver broadband service to bypassed homes or communities stuck in their broadband slow lane.
The Associated Press reports coast-to-coast complaints from incumbents who have refused to deliver service or force customers to accept 1-3Mbps speeds indefinitely.
From the Blue Ridge Mountains to the Great Plains, some local phone and cable companies fear they will have to compete with government-subsidized broadband systems, paid for largely with stimulus dollars. If these taxpayer-funded networks siphon off customers with lower prices, private companies warn that they could be less likely to upgrade their own lines, endangering jobs and undermining the goals of the stimulus plan.
That’s rich coming from some providers who threaten to refuse to upgrade lines they’ve never upgraded, endanger employees they’ve long since cut, and threaten their quest for monopoly profits serving rural Americans larger carriers are rapidly abandoning.
Anemic Broadband Is Not in Kansas Anymore
Kansas-based Eagle Communications provides cable and wireless broadband service to more than a dozen small towns in the state. For more populated areas, it’s cable broadband service. For the rural parts of its service areas, Eagle relegates everyone to a slower speed, more expensive wireless network.
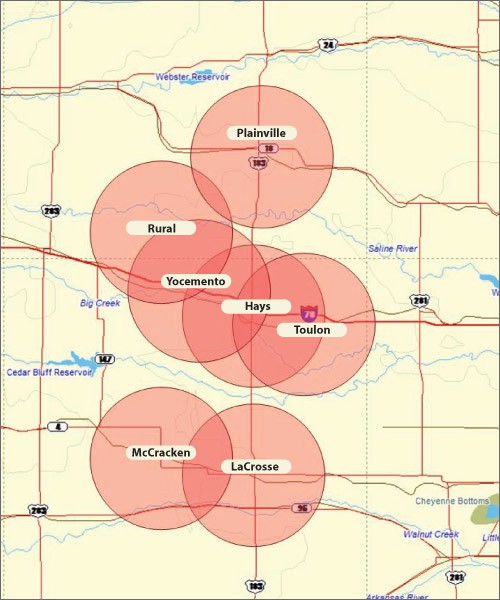
The company is upset to learn about additional expansion forthcoming from Rural Telephone Company, a cooperative which recently won a $101 million stimulus grant to construct a fiber optic system to expand service. With the grant, the co-op phone company will move beyond its currently constrained DSL broadband network into areas even Eagle’s rural wireless signal won’t reach.
Rural Telephone Company says their broadband grant will provide service “in an area 99.5 percent unserved/underserved and provide a rural infrastructure required for economic stability, education and health care.”
Eagle says it’s unfair competition.
“It is extremely unfair that the government comes in and uses big government money to harm existing private businesses,” Gary Shorman, president of Eagle Communications, told the AP. “This hurts our company.”
“It’s a little disappointing that companies that aren’t adequately serving these areas are trying to undercut those of us who are trying to step in and get the service where it’s needed,” says Lawrence Strickling, head of the National Telecommunications and Information Administration, the arm of the Commerce Department handing out much of the stimulus money.
The $101 million Kansas project, for instance, will bring connection speeds of up to 1 gigabit to businesses and up to 100 megabits to as many as 23,000 homes. While the network will cover the population center of Hays, where both Rural Telephone and Eagle Communications already offer broadband, that accounts for just eight of the 4,600 square miles to be reached. Much of the area has no broadband at all, says Larry Sevier, Rural Telephone’s chief executive.
The goal is to “close the digital divide between Hays and the outlying areas,” says Jonathan Adelstein, head of the Rural Utilities Service, which awarded the money.
For rural Kansans choosing between Eagle’s wireless service or Rural Telephone’s current maximum 1.5Mbps DSL service for those outside of the Hays city limits, the definition of “high speed service” maxes out at an anemic 3Mbps:
Eagle Communications Wireless Network Pricing – Hays, Kansas
- Eagle 256/256 $34.95 /per month
- Eagle 768/512 $37.95 /per month
- Eagle 1.0/384 $44.95 /per month
- Eagle 2/512 $54.95 /per month
- Eagle 3/512 $59.95 /per month
Rural Telephone Company Pricing for Outside the City Limits – Hays, Kansas
- Rural Telephone’s 1.5Mbps DSL — $29.95 per month
- Rural Telephone’s 512kbps DSL — $19.95 per month
Gone With the Windstream: Phone Company Says Broadband Stimulus Doesn’t Give a Damn About Their Georgia Business Model
Many of the projects seeking funding don’t actually want to get into the Internet Service Provider business, preferring to construct fiber-based networks available equally to all-comers at wholesale pricing. Sure they’ll wire government buildings, schools, and libraries as a public service, but their real goal is to make available super high speed networks that incumbent providers haven’t, under the theory a rising tide lifts all boats. They even invite existing ISP’s to hop on board, buying access to deliver improved service to their existing customers.
But because some providers don’t own or control the infrastructure outright, they’re not interested.
One such project is the North Georgia Network Cooperative, created from a consortium of private business advocates, a state university, and two power company co-ops.
North Georgia sees broadband as a major economic stimulant… if they actually had it. Large parts of the region don’t, so the Cooperative applied for and won a $33.5 million NTIA grant to construct a 260-mile fiber ring running through 12 counties in the state. The network will easily deliver connections upwards of 10Gbps for institutions and broadband speeds far faster than incumbent DSL provider Windstream currently provides across the region.
Windstream’s DSL packages look better than many other independent phone companies, at least based on their website. Windstream offers 3, 6, and 12 Mbps DSL packages across northwestern Georgia, but that doesn’t mean you can actually obtain service at those speeds. Stop the Cap! reader Frederick, who tipped us off to this story, notes that he can’t obtain more than 1.5Mbps DSL service from his home in Dalton, Georgia because the phone lines in his area won’t support faster speeds.
“I’m actually less than a mile from my area’s central office, but because the phone lines in my area are deteriorated, they had to lock my speed in at 1.5Mbps — anything faster causes the modem to reset,” Frederick writes. “Windstream does the same thing to my cousin in Lafayette, who was offered 6Mbps service but can only get 3Mbps in reality.”
Frederick says most people in the community don’t really care where the faster broadband comes from — just that it comes.
“If Windstream, who incidentally also applied for government money, could do it there would have never been a need to go around them in the first place,” he says. “Hell, the ironic part is the Cooperative will sell wholesale access to Windstream to use as it sees fit, but because Windstream doesn’t own it they’re pouting, refusing to participate.”
Windstream says it has already invested $5 million in network upgrades covering northern Georgia over the last three years and the Cooperative’s stimulus grant undermines the economics of that investment. Michael Rhoda, Windstream’s vice president of government affairs told AP Windstream now has to share rural customers with a government-funded competitor. Windstream wants that funding limited strictly to those areas where broadband service is uneconomic to provide. To underline that point, the company has applied for $238 million in stimulus funding to reach the “last 11 percent” who don’t have broadband in Windstream’s service areas.
Maine’s Three Ring Binder Project Snaps Shut on FairPoint’s Monopoly Fingers

Maine's Three Ring Binder Project plans to serve most of Maine (click image for additional information)
More often than not, independent efforts to launch improved broadband service in a region come after years of dealing with an intransigent provider comfortable moving at a snail’s pace to improve service. Financially-troubled FairPoint Communications has been struggling to meet Maine’s broadband needs since the company took over service from Verizon two years ago. The state government, university, and smaller telecommunications companies decided they could do better — applying for, and winning a $25.4 million dollar grant to construct three fiber rings across the state.
FairPoint insists the project duplicates the company’s own efforts to improve connectivity in Maine and has appealed to lawmakers to stop the project. But FairPoint recently called a truce when it reached a deal to charge users of the new network a usage fee, with FairPoint getting a large share of the proceeds to expand its own broadband efforts.
[FairPoint’s financial problems have left the company] unable to bring broadband to wide swaths of rural Maine, says Dwight Allison, chief executive of Maine Fiber Co., which was created to build and operate the stimulus-funded network. The project, he says, represents a serious competitive threat to a company that “feels its monopoly is being attacked.”
Of course nothing precludes FairPoint from getting access to the new fiber network at the same wholesale pricing other providers will pay, but the company so far doesn’t seem interested.
Various talking points designed to derail the project are debunked by the Maine Fiber Company:
- Fiction: It’s government-run broadband.
- Fact: Three Ring Binder will be owned and operated by Maine Fiber Company, a private company based in Maine. MRC is unaffiliated with any telecom carrier to ensure fair and equal access to the system for all competitors.
- Fiction: This project will create unfair competition for private providers.
- Fact: MFC will be a wholesale provider of dark fiber, and its customers will be Internet Service providers, wireless carriers, and telephone companies. MFC will not provide “lit” service in competition with private broadband carriers. MFC is required to provide service on an open access and non-discriminatory basis. All carriers in Maine will be able to use the network to serve their customers in Maine, resulting in robust competition for the benefit of Maine consumers.
- Fiction: This project duplicates service FairPoint already provides.
- Fact: Prior to receiving a federal stimulus grant, the project was carefully reviewed by the National Telecommunications Information Agency (NTIA) of the US Department of Commerce to determine whether there was overlap with existing carriers. NTIA determined that TRB would substantially improve access to high-speed Internet access in rural Maine. If material duplication had been discovered, TRB would not have been funded. TRB will offer a mid-mile, dark fiber service that is fundamentally different from what currently exists in rural Maine. In fact, carriers seeking to obtain dark fiber service along the TRB route have routinely been denied access by incumbent fiber providers.


 Subscribe
Subscribe