The clock may be running out on Clearwire, America’s “4G-WiMax” wireless broadband provider controlled by Sprint, with close investment ties to Comcast and Time Warner Cable, who both resell Clear wireless broadband under their own brands.
At issue is money — the lack of it, and the wireless company’s cash on hand has grown so perilously low, Clearwire was forced to admit to its investors it may not survive beyond the first half of next year:
Based on our current projections, we do not expect our available cash and short-term investments as of September 30, 2010 to be sufficient to cover our estimated liquidity needs for the next 12 months. We also do not expect our operations to generate positive cash flows during the next 12 months. Without additional financing sources, we forecast that our cash and short-term investments would be depleted as early as the middle of 2011.
The Securities and Exchange Commission rules governing public companies represent a public relations nightmare for anyone trying to put a positive spin on bad news, and Sprint chief Dan Hesse desperately tried to make lemonade out of the financial lemon Clearwire increasingly represents for the wireless company.
“If you get to the point where you don’t have 12 months of cash in the till, even if you’ve got negotiations going on, or what have you, you have to, from an accounting perspective, say you have a going-concern issue,” Hesse said. “That doesn’t mean that Sprint and other partners won’t continue to fund Clearwire.”
 With Sprint’s 54 percent stake in Clearwire defining the entity as a subsidiary of Sprint, its demise could risk Sprint’s own financial well-being, something Sprint plans to address in 2011, potentially ending its majority stake in the company.
With Sprint’s 54 percent stake in Clearwire defining the entity as a subsidiary of Sprint, its demise could risk Sprint’s own financial well-being, something Sprint plans to address in 2011, potentially ending its majority stake in the company.
For Hesse and his cable partners, Clearwire’s financial problems are being spun as a result of the venture’s success. The company says it cannot afford the rapid expansion it has undertaken to expand its WiMax network into additional cities across the country, and faces serious financial challenges from the subsidies consumers demand when buying smartphones.
Hesse particularly complains about the latest whiz-bang smartphones consumers demand, many costing upwards of $600. Consumers in the United States don’t pay full retail price. In return for two year contracts carrying steep cancellation penalties, carriers cut the price of most high end phones to $200 or less.
“Subsidies are going through the roof in our industry,” Hesse said. Nearly 40 percent of Sprint customers use the company’s 4G network, and that number is rising.
Revenues are up 114 percent from a year earlier to US$147 million. But Clearwire’s losses for the last quarter alone amounted to $139 million, or $0.58 per share.
As a result, Clearwire slashed 15 percent of its staff, laying off nearly 600 employees and has indefinitely suspended its expansion plans to bring the network to additional cities. Clearwire will also shutter many of its planned retail outlets — some already built — and delay the introduction of its own branded smartphone.
But even that may not be enough.
Although Clearwire’s growth has been double the level anticipated, achieving a net gain of 1.23 million subscribers in the third quarter — reaching 2.84 million total subscribers, not all of those customers are sticking around once they begin using the service.
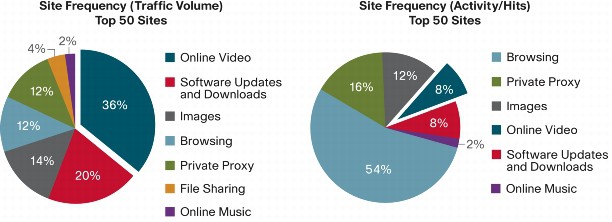
Complaints about the company’s poorly disclosed speed throttling continue to be a regular topic on Clear’s support forums. At least 1,000 complaints have been logged on Clear’s own support forums and elsewhere online about the speed traps. A Facebook group opposing the schemes has also been established.
Stop the Cap! filed a formal complaint with the New York Attorney General’s office accusing the company of false and misleading advertising and fraud for claiming customers would enjoy “blazing fast speeds” with no limits or speed throttling, despite the fact company officials later admitted they were throttling customers deemed to be “using the service excessively.” Dozens of additional complaints from Clearwire customers have been filed with state Attorneys General across the country, as well as with the Federal Trade Commission in Washington.
Just how much is too much has never been made clear by the company, but many users report the speed throttle reduces speeds to 250kbps, often for hours at a time.
Clearwire told Electronista:
Throtting is based on the current utilization for each cell tower, and many low-use towers do not throttle speeds at all. For high-use towers, throttling occurs during peak-use times.
A customer’s maximum speed is based on the number of gigabytes of data transferred in the past seven days and the download speeds for the past 15 minutes. Speeds are recalculated every 15 minutes, at which point a throttled customer will be bumped up to a higher speed. Rather than implementing one speed for throttling, the calculations will move customers between 48 different speed brackets.
The worst offenders using peer-to-peer software on Clearwire’s network may face repeated throttling.
Clearwire advertises a faster Internet experience for their 4G service, but many report they receive speeds far slower, even if they have engaged in very little usage.
Many consumers are also unknowingly finding themselves back on Clear’s network even though they signed up with a third party provider. Clear resells access to its network under a variety of different brands not limited to Sprint, Road Runner Mobile, Comcast Internet2Go, and Best Buy Mobile/Wireless.
[flv width=”640″ height=”380″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Clear Speed Woes 11-10-10.flv[/flv]
This Clearwire customer visits a Clear hotspot location and discovers even on a Wi-Fi network, Clear’s speeds don’t match their advertising claims. Then, he discovers just how sneaky Clearwire gets in disclosing important information about the company’s wireless speeds customers might want to know before signing up. (5 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe