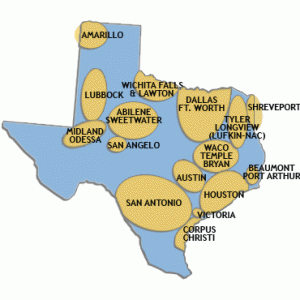
Suddenlink broadband customers in Lubbock and Midland, Texas will soon have a new option to boost their broadband speed to 36Mbps. Dubbed MAX36, the new tier leaps over the cable company’s former top broadband speed of 20Mbps. Upload speeds get a boost as well — to 2Mbps.
Suddenlink broadband customers in Lubbock and Midland, Texas will soon have a new option to boost their broadband speed to 36Mbps. Dubbed MAX36, the new tier leaps over the cable company’s former top broadband speed of 20Mbps. Upload speeds get a boost as well — to 2Mbps.
Multichannel News reports pricing for the new tier depends on how many other Suddenlink services you have. Standalone pricing is $75 per month. Bundle it with television or telephone service and the price drops to $65. Take all three services and MAX36 costs $60 a month.
If that is too rich for your blood, Suddenlink next week will be providing existing broadband customers in Lubbock and Midland free speed upgrades:
- 1Mbps service increases to 1.5Mbps
- 8Mbps upgrades to 10Mbps service
- 10Mbps service becomes 15Mbps
The new speeds are possible because of DOCSIS 3 upgrades underway at the nation’s ninth largest cable operator. Suddenlink has focused on DOCSIS 3 upgrades for many of its Texas systems, including Abilene, Bryan/College Station, Georgetown, Lubbock, Midland, San Angelo and Terrell. The operator also deployed the technology in Beckley, Charleston and Parkersburg, West Virginia, as well as Jonesboro, Arkansas, Humboldt County, California, and Nixa, Missouri. The company hopes to upgrade 90 percent of its cable systems within the next two years. Nationwide, Suddenlink reaches 1.3 million subscribers.
Last summer Suddenlink introduced a usage meter for subscribers in Clovis, New Mexico and included a chart of what constituted average usage for its customers.
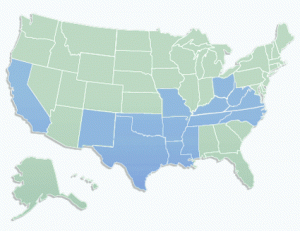
The company openly admits it limits customer use of its broadband service is several communities where bandwidth upgrades have yet to occur, but at least drops communities from the usage limit list after expansion is complete. As of February 4th, communities impacted by usage limits include:
- Arkansas: Charleston, Hazen, Mt. Ida, Nashville
- Kansas: Anthony, Fort Scott
- Louisiana: Ville Platte
- Missouri: Jefferson City, Maryville
- Oklahoma: Fort Sill, Healdton, Heavener, Hughes, Idabel
- Texas: Albany, Anson, Brenham, Burkburnett, Caldwell, Canadian, Center, Claredon, Crane, Dimmitt, Eastland, Electra, Hamlin, Henrietta, Junction, Kermit, Monahans, Nocona, Olney, Paducah, Rotan, San Saba, Seymour, Sonora, Trinity, Vernon, Wellington
Suddenlink also admits it engages in “network management” techniques which may spark controversy with the ongoing Net Neutrality debate, despite its declaration it “allows customers to access and use any legal Web content they prefer, thus honoring the principles of network neutrality.”
In addition to “mitigating network congestion, which can interfere with customers’ preferred online activities,” Suddenlink also discloses it “prioritizes certain latency-sensitive traffic such as voice traffic.”
Still, performing system upgrades to put a stop to usage limits and allowances is a move in the right direction, one that other providers seeking to monetize broadband traffic with Internet Overcharging schemes are loathe to take.
[flv width=”640″ height=”500″]http://www.phillipdampier.com/video/Suddenlink Ads.flv[/flv]
Watch some of Suddenlink’s more creative and amusing advertising. (2 minutes)


 Subscribe
Subscribe